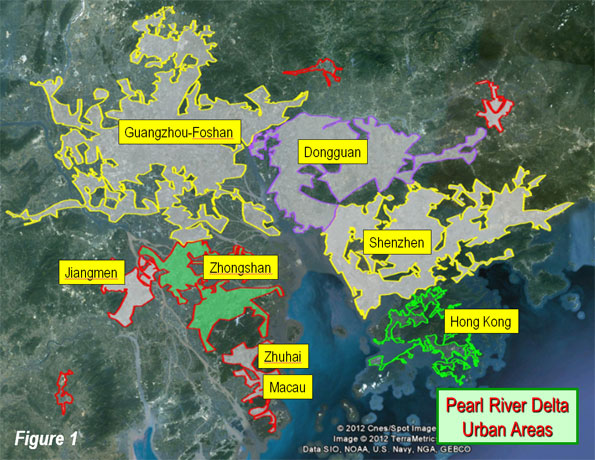
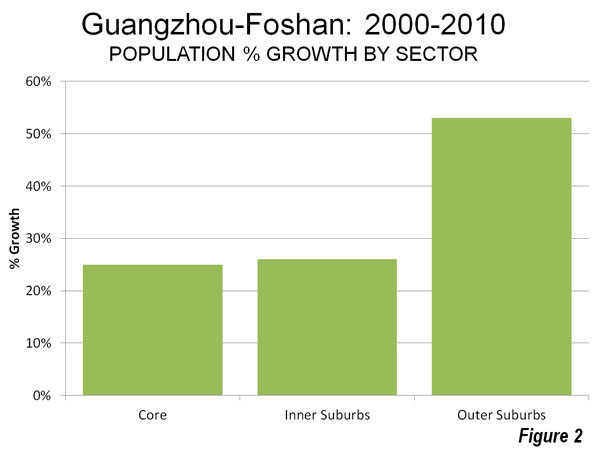
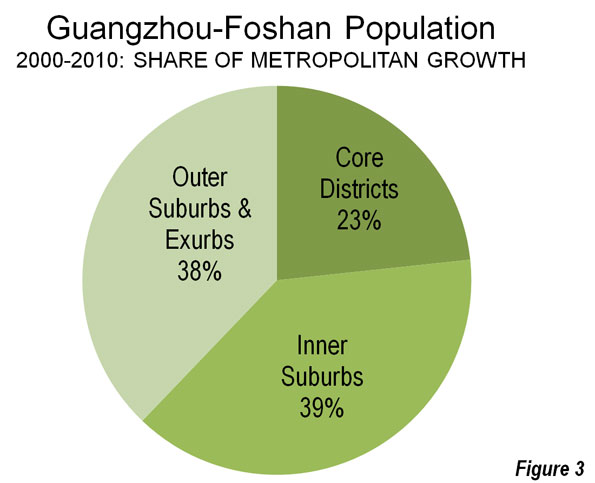
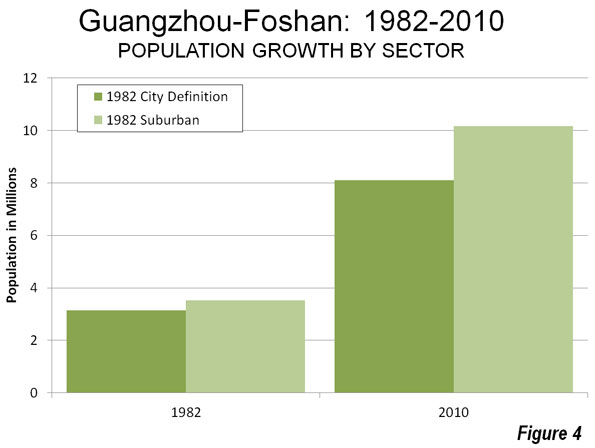
For the last two decades, America’s pundit class has been looking for models to correct our numerous national deficiencies. Some of the more deluded have settled on Europe, which, given its persistent low economic growth over the past 20 years and minuscule birth rates, amounts to something like looking for love in all the wrong places.
More rational and understandable have been those who have looked for role models instead in East Asia. After all, East Asia has been the world’s ascendant power for the better part of past 30 years. It is home to both China and Japan, the world’s second and third largest economies, as well as the dynamic “tiger” economies of Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong and Singapore.
Thomas Friedman, long enamored by authoritarian leviathan China, recently praised the tiger countries as exemplars of forward thinking. He traces their strong emphasis on “highly effective teachers, involved parents and committed students” as keys to turning their resource-poor countries into first world successes.
Yet for all their laudably good school test scores, these tigers could turn somewhat toothless in the future. Already Japan, which fashioned the first great Asian model, is beset by a series of massive challenges including a lack of technological competitiveness and disastrously declining demographics. They also face competition from places like China and India, behemoths which may not equal the Tigers’ spectacular per-capita education numbers, but which can marshal overwhelming numbers of ambitious, educated and skilled people.
Many in the tiger nations recognize this competitive plight far more than their western cheerleaders. Some even wonder if they may even have been too rational and credential-obsessed for their own good. Like Japan after the Second World War, they invested heavily in educating their young people to excel on tests and work long hours . But this also fostered high levels of stress and hyper-competition that discourages both family formation and child bearing .
Singapore (where I serve as Senior Visiting Fellow at the Civil Service College) is arguably the best planned and most cleverly conceived of all the Tigers. Singaporeans live well — their per-capita incomes surpass those of Americans — but this edge is largely blunted by extremely high costs. As in all the Tiger countries, consumer goods like cars are extraordinarily expensive (a modest Korean model can run upwards of $75,000 or more in Singapore) and housing costs far higher than experienced by most Americans. In Hong Kong, notes researcher Wendell Cox, an average apartment, usually quite small, costs roughly twice as much as one in New York or San Francisco, two most elite metro U.S. markets, relative to income.
These conditions, observes Vatsala Pant, a former Nielsen executive and long-time Singapore resident, create what amounts to an accounting-like mentality about their lives. “Singaporeans seem to be born with a calculator in their heads,” she notes. “Every decision seems to weighed in a cost and benefit analysis, including such things as family. If it’s not perfect, they don’t want it.”
This turn from family represents a sharp break in these countries. All the “tiger” economies flourished based on a Confucian culture that places kinship at the top of the value pyramid. Parents are still widely revered, but Li Lin Chang, an associate director of the Lee Kuan Yew School of Public Policy, suggests that Singapore’s “Confucian roots may not be as evident and some may argue that it may have disappeared.”
Certainly increasing number of Singaporeans and others from Tiger countries are opting out of marriage. In 2000, 14% of women between age 30-39 chose to remain childless, according to demographer Gavin Jones of the National University of Singapore. By 2009, this figure has gone up to 20%. Jones estimates in some east Asian societies up to a third of all women will remain childless.
Japan, the original model for all these countries, is now leading the way off the demographic cliff. In Japan, notes researcher Mika Toyota, 20% of 50-year-old males have never married, up from 12 percent just a decade ago. By 2030, she estimates nearly 30% of 50-year-old males will have never wedded. And unlike the U.S. and Europe, very few people have children out of wedlock in East Asia, so no marriage means no children.
This plunge in marriage and family formation is not entirely voluntary. Few of the 40 or more Singaporean younger adults I have interviewed in recent months celebrated singleness like some of their Western counterparts. Most still wanted children and linked their reluctance to wed or to have babies on the high cost of living, intense competition in their workplace and even increasingly crowded mass transit.
“Most of my friends are not married,” one 35-year-old female civil servant told me. “They don’t want to be single but they are too busy with their work commitment. My friends are consumed by work. Money, status, prestige, climbing the ladder. You expect things to change when you get older but it doesn’t. The calculation just doesn’t work out”
For many of these people, not having offspring makes sense in terms of concentrating on career goals and reducing financial pressure. But it could prove a social disaster in the long run. All Tiger nations now suffer fertility rates roughly half the 2.1 children per household needed to replace the current population. By 2030 these countries could have fewer people under 15 than over 60.
Not surprisingly, many Tiger country policymakers place a priority on producing more cubs. Most offer highly generous packages of support offered to those willing to take the nativity plunge. Some who have children cope with entrenched male reluctance to share in child-raising by relying on low-cost maids, often from the Philippines and other poorer countries. A recent move by the Singapore government to require giving maids the day off elicited howls of protests from female professionals, who, as authors Teo You Yenn and Vivienne Wee put it, regard “care of one’s own offspring as tedious, beneath oneself and rightfully the responsibility of a hired woman.”
Some professionals who desire children consider taking their finely honed skills elsewhere. A recent survey by the MRI China Group showed that a majority of professionals surveyed in Taiwan and some forty percent in Singapore, as well as roughly one-third of those in Hong Kong, were actively looking to relocate to another city. Most covet a move to less high-pressure, lower-density Australia or New Zealand. Others, particularly from Taiwan, are attracted to greater opportunities in China.
There may not be too much the bureaucracies can do immediately to address these problems. Clearly adding more degrees per capita or bringing in more foreign expertise, as is common in Singapore and Hong Kong, has not addressed looming baby shortage. Instead, as one one young University researcher put it, “we need a new mindset.”
Most particularly, these countries need to change the incentives that, albeit unintentionally, create unsustainable levels of singleness, childlessness and the prospect of massive, rapid aging of their societies. They may have to consider more flexible work-styles, the promotion of home based business and better use of their limited space. Individual entrepreneurship, more rooted in each country and able to meld with family life, could be stressed as a counterbalance to employment in often fickle multinational corporations who can always move to greener, or at least cheaper, locales.
More difficult still will be shaping attitudes that restore the primacy of family that propelled these societies in the first place. This is an existential challenge that would have seemed unimaginable 40 years ago when these countries fretted about overpopulation and widespread poverty. But success in the future can not be purchased by simply continuing what has worked so well for a generation. To avoid a toothless future, the Tigers need to unlearn some of the secrets of their past success.
This piece originally appeared in Forbes.com.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University, and contributing editor to the City Journal in New York. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050, released in February, 2010.
Singapore skyline photo by Bigstockphoto.com.