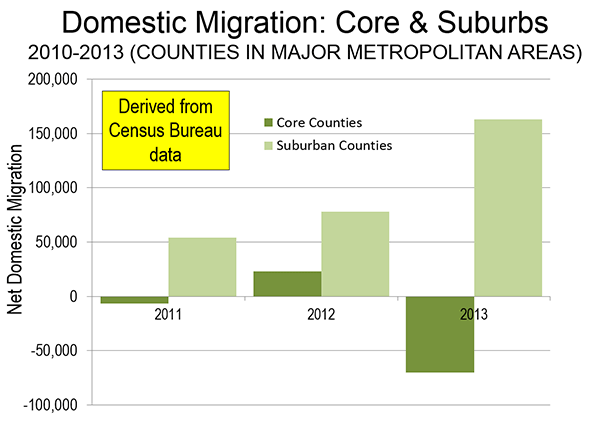
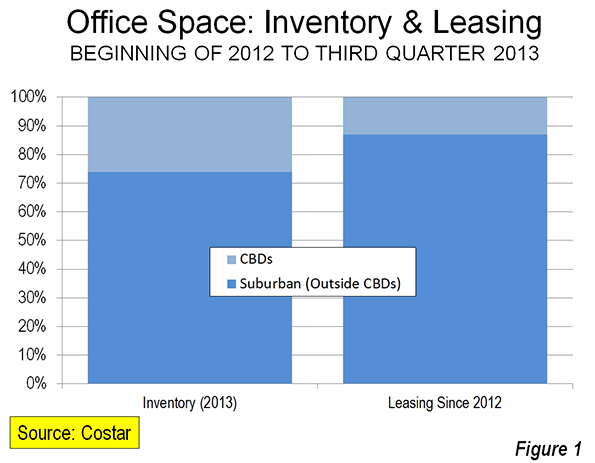
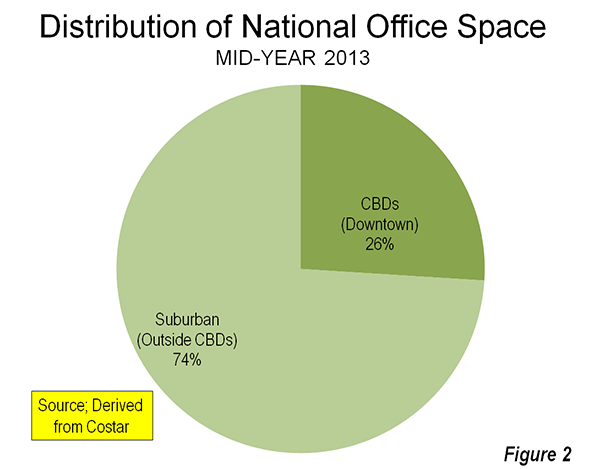
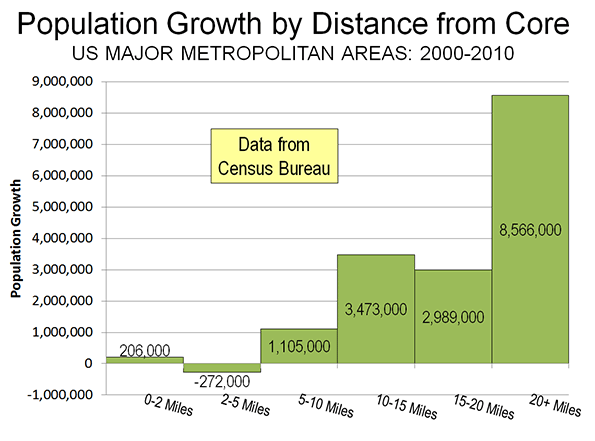
What’s often forgotten in politics and governance is municipalities are the creation of state legislatures. A good deal of the population growth in major cities in the second half of the nineteenth century was due to annexation. One of the best examples is New York‘s amazing growth due to annexing Brooklyn. Few people are talking about it but it’s time to consider smaller political units. As Detroit struggles with failure of bankruptcy, the geographical size of the Motor city is becoming a major issue.
Detroit’s long decline eventually put it a federal bankruptcy court. The reasons are numerous but the reality is here. How Detroit exists from bankruptcy court is now an issue. Putting Detroit on a sound economic footing is essential to preventing another bankruptcy. The Detroit Free Press reports:
The investment banker representing the City of Detroit had talks with billionaire real estate investor Sam Zell and investment firm the Blackstone Group about selling them the city’s vacant property — but the investors weren’t interested, the Free Press has learned.
The revelation comes as the value of Detroit’s abandoned and blighted property — which the city considers assets in its Chapter 9 bankruptcy — is in dispute.
Creditors argue that city-owned property is a source of significant value that is being ignored in the city’s bankruptcy restructuring blueprint, called a “plan of adjustment.” The creditors argue the approximately 22 square miles of vacant or blighted property the city owns could be sold — with the proceeds distributed to creditors and even reinvested in the city.
But Ken Buckfire, president of the city’s investment banking adviser Miller Buckfire, testified that city-owned land “to some extent has negative value,” according to a deposition transcript obtained by the Free Press.
One way to interpret the comment about “negative value” is where the land is located. If Michigan’s state legislature re-drew Detroit‘s geographical boundaries, investors would be more interested in the land. A new municipality, without Detroit’s corrupt and expensive politics would be a major reform. Detroit as it exists today isn’t viable for job growth and a stable population. Detroit’s local politicians and special interest groups would obviously fight any changes in geographical boundaries in Michigan’s state legislature because a declining Detroit was a way to plunder taxpayers. But Michigan taxpayers need to start asking themselves: is Detroit’s 143 square miles a viable long term enterprise?