The Atlantic’s Alex Madrigal announces "The Beginning of the End for Suburban America," a wish and hope long dressed-up as reality by a well-placed few who believe that the "be – all and end – all" is living anywhere but the suburbs. This is not to suggest that there is anything wrong with living in the core urban core if that is what one wants to do. I certainly have enjoyed living part-time in the inner core of the ville de Paris for some years. At the same time, however, the behavior of people has revealed an overwhelming preference for more space. From New York to Paris and Tokyo, some people choose to live in dense urban cores and a lot more choose to live in suburbs (and exurbs).
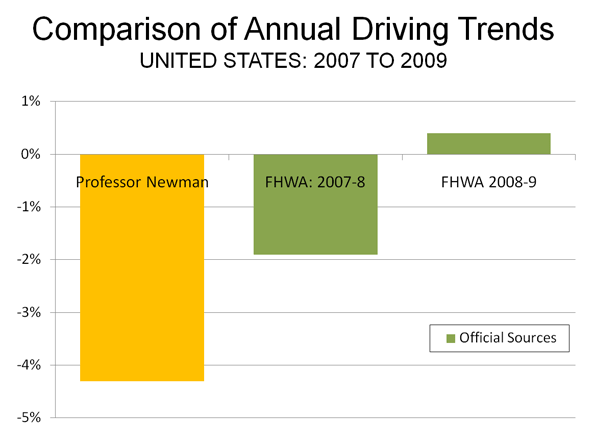
What data does Madrigal cite to show "the beginning of the end for suburban America"? Driving is down from a peak in 2007, also the year that employment peaked. These are not disconnected events. With the total unemployed now about equal to the number of employed workers in the New York and Chicago metropolitan areas, work trips that are not made nearly equal the decline in driving. The higher gas prices appear to have induced people (in the suburbs and in the dense cores) to make modest reductions in discretionary trips or to more efficiently organize their shopping trips.
Madrigal also points out that in 2010 new houses were smaller than their peak (also 2007). The median house size was still larger than any year before 2005 and 100 square feet larger than 2000. Madrigal cites declining rates of demand increase for electricity.
The connection between these trends and the suburbs is unclear. Madrigal does not separate the trends by residential geography, the more dense cores of metropolitan areas, the suburbs and exurbs of metropolitan areas and the balance of the nation. Granted, the data is not immediately available for such analysis.
Fortunately, there is more precise data that differentiates between dense core and suburban trends. It is the United States Census, conducted every 10 years and most recently in 2010. Between 2000 and 2010, the core municipalities of the 51 metropolitan areas with more than 1 million population captured 9% of the population growth, while the suburbs and exurbs captured 91%. The suburbs actually did better in the 2000s than in the 1990s, when they accounted for only 85 percent of the growth.
True, the relative decline of the denser cores did not resemble the disastrous decade of the 1970s. Further, the gains made by very small areas of the core over the past 10 years have been an important advance. But to suggest that the 2000s represent "the beginning of the end for suburban America" is profoundly at odds with reality.
So, the decade of the 2000s was another false start for the heralds of the suburban "end-times." The wishing and hoping has to be delayed yet again.