In December 2010, Meredith Whitney, the financial analyst, appeared on 60 Minutes, where she predicted that the United States would see between 50 and 100 defaults of municipal bonds. Since she was one of the earliest analysts to predict the financial meltdown, publishing a research report in October 2007 that said that because of mortgage losses Citigroup might have to cut its dividend, it was not surprising that her statement attracted a great deal of attention, but also significant pushback from industry representatives, who insisted that municipal bonds were safe. This book, "Fate of the States: The New Geography of American Prosperity" is her effort to elaborate on that call.
Whitney begins her analysis with a review of the housing bubble and banking crisis, which by now is well trod ground, but she does so in a highly informed and balanced way. Where some commentators want to place most of the blame on government, others on Wall Street, and yet others on the Federal Reserve Bank for keeping interest rates too low for too long, she argues that everyone behaved badly. The self-destructive behavior that she witnessed on the part of many banks and financial institutions during this period remains an enduring and puzzling part of the story.
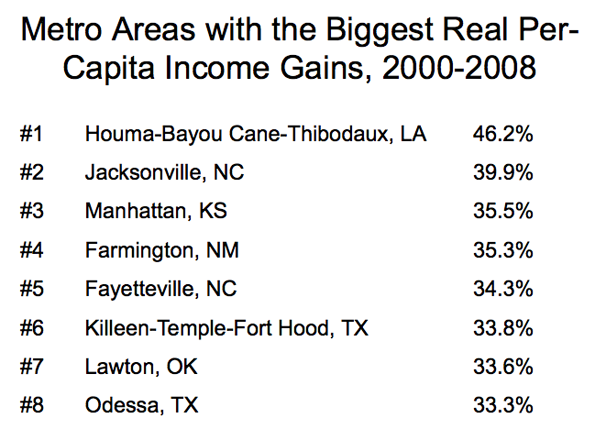
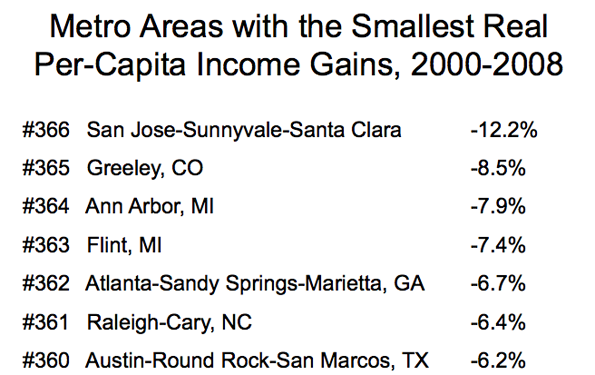
Readers of New Geography will be familiar with two of the themes that she articulates. One is the rise of a zone of prosperity from the Gulf Coast through the heartland and up to North Dakota that has been built on pro-active energy policy and strong global demand for agricultural commodities. A second theme she articulates is the striking disparity in the cost of living between states like California and New Jersey compared with far more affordable states like Texas. Low cost states, she says, will continue to attract new investment and jobs.
In arguably the core section of the book, she explains how the housing bubble interacted with banking and government to create what she calls “The Negative Feedback Loop from Hell.” By way of background, it should be noted that the underlying economics of banking are unusual. As economist Joseph Stiglitz demonstrated in the 1980s, the price of money does not necessarily clear markets. Instead, banks often employ credit rationing in order to control risk. As she argues, this is exactly what happened in the states where the housing bubble inflated the most. These are the states where the subsequent economic decline was the greatest.
As Whitney shows, it was also these states, where government officials handed out the most generous pay packages, including large back loaded pensions. On top of that, these states often piled on the most government debt, which nearly doubled between 2000 and 2010. The result has been significant retrenchment on core government services, from police and fire protection to public education. In her view, this is the negative feedback loop from hell, and the reason that she believes that fiscal stress will continue for a long period of time.
As the fight for limited resources works itself out, she believes that besides government there will be three parties at the negotiating table. Two are straightforward enough: the bondholders, who expect to be paid back the money they lent, and the public sector employees, who expect to receive the pensions they were promised. But she also sees a third party. Writing shortly before the bankruptcy in Detroit, she presciently recognized that citizens will also have a claim on resources, arguing that they need and deserve the services that government is supposed to provide.
Although the sub title of the book mentions geography, Whitney largely dismisses what a contemporary textbook on economics and geography calls the “who, why, and where of the location of economic activity.” This is not surprising. There are probably few people who are aware that this branch of economics even exists. (Among professional economists, more attention has been paid in recent years with the advent of New Economic Geography as championed by Paul Krugman, although, ironically, empirical research indicates that key elements of of Krugman’s theoretical work are almost certainly wrong.)
While Whitney rightly focuses on the economic growth that distinguishes many of the states in the central corridor of the country, she cites data that shows that most economic activity continues to occur elsewhere. She observes, “These so-called flyover states contributed 25 percent of U.S. GDP in 2011, up from 23 percent in 1999.” That is nearly a 10 percent increase, but obviously from a lower base. A current and highly visible example of the importance of geography is the huge growth in the number of warehouses along the New Jersey Turnpike, as engineering projects deepen New York harbor and expand the Panama Canal. Access to water will always be important.
Additionally, I would argue that the issues that Whitney addresses cannot be fully understood without taking into account the challenges that continue to face older industrial cities. All economies must constantly re-invent themselves. In the case of cities with a large industrial legacy, however, intrinsic market failures caused by asymmetric and imperfect information have made redevelopment significantly more difficult. Theoretical and empirical work in recent years has also shown that joint and several liability under U.S. environmental law undermines efficient price discovery for properties that once had an industrial use.
These issues aside, Whitney has written a book that is both provocative and necessary. Clearly, certain states have instituted policies that are far more effective at attracting business and new residents. At the same time, other states appear unable to reform. Perhaps her central insight is that problems associated with debt can take on a life of their own. Therefore, her message is clear. States that properly manage their debt and pension obligations will enjoy a prosperous future. States that do not will encounter severe problems. Investors and public sector employees take note.
Eamon Moynihan is the Managing Director for Public Policy at EcoMax Holdings, a specialty finance company that focuses on the redevelopment of previously used properties.