A high speed rail battle is brewing in Great Britain, not unlike the controversies that have lit up the political switchboard in the United States over the past six months.
The Department for Transport has announced a plan to build a "Y" shaped high speed rail route that would connect Leeds and Manchester, to Birmingham, with a shared line on to London and London’s Heathrow Airport.
The government places the construction cost at £32 billion and makes familiar claims that the economic benefits would be 2.6 times the cost.
These apparently impressive benefits relative to costs are not convincing to George Monbiot, the well-known environmental columnist for The Guardian. He points out that much of the purported benefit is a mere conversion of time savings into currency, which hardly produces "investment grade" projections.
Monbiot further observes that these monetized time savings benefits largely will not be returned to the taxpayers who pay for the system. This raises a fundamental question. If the time savings benefits are so great to the users, why shouldn’t they pay for the whole system instead of the projected (and perhaps unreliable) 60 percent? Why should taxpayers be required to pay 40 percent (or probably more)?
As in the United States, the critics get little respect. The Financial Times refers to the Taxpayers Alliance, which opposes the high speed rail program as an "anti-public spending group." In fact, like taxpayers organizations around the world, the Taxpayers Alliance does not oppose public spending but rather opposes wasteful public spending. The Transport Secretary himself, Philip Hammond employs a form of populist character assassination, calling opponents of the high speed rail line "truck importers and climate change deniers," echoing similar sentiments from this side of the Atlantic where promoters would have you believe that anyone who questions high speed rail is best described as an enemy of the people. Demonization should not be used as a substitute for debate.
In the above referenced article, the Financial Times notes that 69 business people signed a letter favoring the project. FT refers specifically to executives of three companies, including Seimens, without mentioning that the firm is among the world’s biggest builders and promoters of high speed trains.
Meanwhile, as in the United States, the government and much of the British media have accepted cost, ridership and revenue projections as produced by the consultants as if they were holy writ. Given the experience of Britain on this very corridor, this makes "child-like faith" look like ultimate truth.
Much of the proposed high speed rail line would be built parallel to the West Coast Main Line (which runs from London, through Birmingham and Manchester to Glasgow). Nothing short of a dog’s breakfast has been made of West Coast Main Line projects. In the 1980s, the tilting Advanced Passenger Train was developed to increase speeds to 155 miles per hour along the West Coast Main Line. The project was scrapped and all of the expenditure lost. Then there was the West Coast Main Line upgrade in the late 1990s and 2000s, to increase speeds to 140 miles per hour, which was to have cost £2 billion. The trains never exceeded 125 miles per hour, but the costs exceeded projections approached £10 billion instead, a world record cost blowout of Big Dig proportions (Figure).
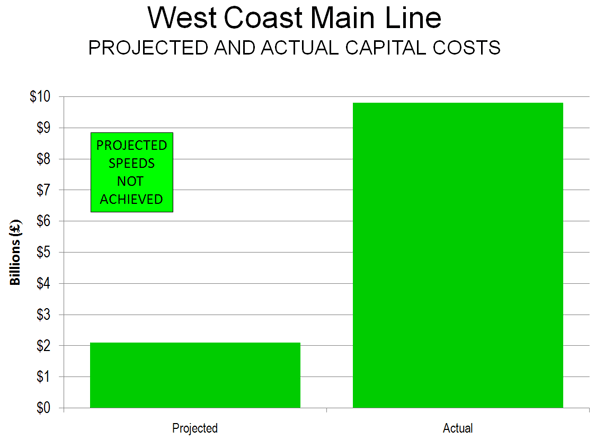
This should not be a surprise. The international record of high-speed rail projections is nothing short of horrific.Not only have costs proven far higher, but ridership and revenue have been less than projected. All of this means that taxpayers end up paying more.
Again, Britain is a prime example. The Eurostar London to Brussels and Paris continues to attract at least 50 percent less ridership originally projected. High speed rail systems in Taiwan and Korea have had similar ridership shortfalls.
As in Britain, costs have been higher as well. In Korea, the high speed rail line costs rose three times projections. Costs in California have increased 50 percent in two years and doubled over a decade even before the first shovel has been turned (inflation adjusted). The cost escalation has already equaled the high end of the range predicted by Joe Vranich and me in our Reason Foundation Due Diligence Report on the California system in 2008.
If the proposed high speed rail project were simply to miss its cost and revenue targets by the international average (which is far better than the British experience), the benefits to users would fall below £1.00 for each £1.00 of cost. Both the strategic case and the business case for high speed rail would be blown apart. The spectre of cost overruns was a major factor in Governor Scott’s cancellation of the Florida high speed rail project.
Not surprisingly, there is rising concern about high speed rail in Britain.A group of 21 officials, including former Chancellor of the Exchequer (minister of the treasury, finance and economics) Nigel Lawson, signed a letter to the Daily Telegraph calling the project "an extremely expensive white elephant isn’t what the economy needs. If the government wants to encourage growth there are better ways to get Britain growing and make us more competitive than getting each family to pay over £1,000 for a vanity project we cannot afford." The signatories also included Mark J. Littlewood, Director-General of the Institute of Economic Affairs, one of Great Britain’s leading free-market think tanks.
Further, as in the United States there is also strong opposition from neighborhood groups concerned about the impact of trains operating at more than 200 miles per hour or faster through their neighborhoods. Eventually, up to 18 trains per hour are projected in each direction. This means that a 1,300 foot long train will pass houses and other adjacent development every one minute and forty seconds.
There are the usual claims that the high speed rail line will reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, as in California, the reality dissipates quickly, like steam into the air. Areport prepared for the Department for Transport by Booz Allen Hamilton concluded that the busiest section of the line, from London to Manchester would result in a net increase in greenhouse gas emissions when construction emissions are included (over a 60 year time analysis). Perhaps the intention is to begin reducing greenhouse gas emissions sometime after 2075?
Monbiot further dismantles the environmental case, looking into the government reports to find that 92% of the passengers would switch to high-speed rail from alternatives that produce lower levels of greenhouse gas emissions (including conventional train, new travel and air).
In Britain, as opposed to the United States, the proposed high speed rail system would relieve congestion on a passenger rail line. In contrast, US high speed rail lines would be built in corridors where there are few, if any rail passengers, much less passenger rail congestion.
Even so, there are disagreements in Britain over whether high speed rail is the least costly way to address the problem, or indeed, whether there is a "problem" of sufficient magnitude to justify the public expenditure.
The huge ridership increases projected may well be "over the top" given Britain’s less than population replacement fertility rate. As in the United States, some question the wisdom of high speed rail subsidies at a time that the government is (or in the case of the United States, should be) committed to an unprecedented austerity program that is falling heavily on middle income people who will not be the principal beneficiaries of high speed rail.
In the final analysis, the questions will come down to who rides, how far and how fast. Will riders, in this third iteration, ride as fast as promised? More likely it’s Britain’s beleaguered taxpayers who will be taken for a ride, with costs low-balled and ridership exaggerated as before.
Revised on 3/22/2011. The original version had inappropritately refered to George Monbiot in the sentence about Transport Secretary Hammond. This was due to an editing error.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris and the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life”
Photo by Jon Curnow
