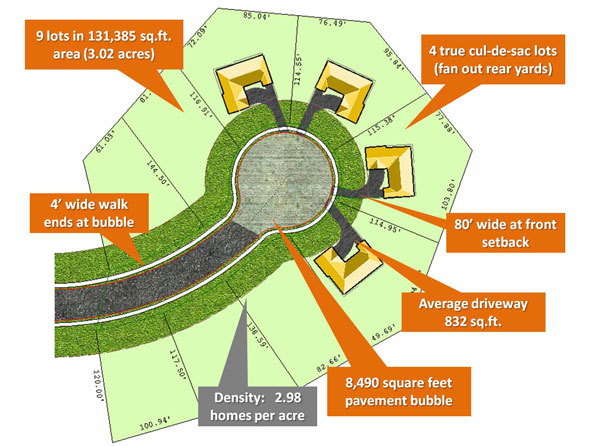
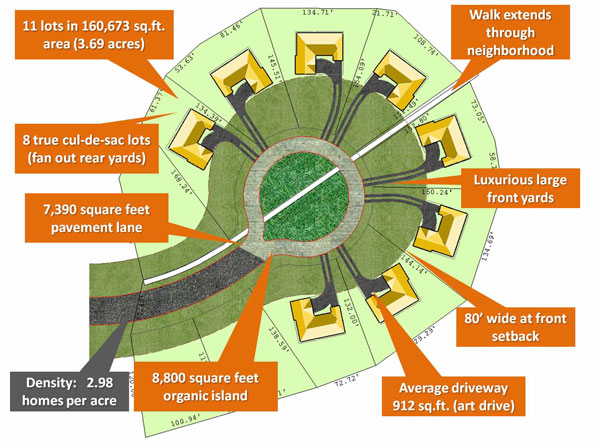
For more than one-third of a century Jerry Brown has proved one of the most interesting and original figures in American politics–and the 71-year-old former wunderkind might be back in office in 2010. If he indeed wins California’s gubernatorial election, the results could range from somewhat positive to positively disastrous.
Brown is a multi-faceted man, but in political terms he has a dual personality, split between two very different Catholic figures from the 15th century: Machiavelli and Tomas de Torquemada. For the sake of California, we better hope that he follows the pragmatism espoused by the Italian author more than the stern visage of the Grand Inquisitor.
Like a good Jesuit, Brown certainly can be flexible. Back in 1978, for example, he worked against Howard Jarvis’ Proposition 13, which capped real estate taxes. But once the measure was passed, Brown embraced it as his own. Indeed, he was so enthusiastic about the tax-cutting measure that Jarvis actually voted for Brown’s re-election late that same year. A month after the vote a Los Angeles Times poll revealed most Californians thought Brown actually supported 13.
Brown also has shown his flexibility by throwing even loyal allies under the bus. Elected largely due to the electoral coalition constructed by his father, Edmund G. “Pat” Brown, Brown made a point of tweaking and restraining the expanding bureaucracy largely created by his father. He also took on the University of California and the welfare bureaucracy as well as agriculture, residential real estate and manufacturing giants.
This Oedipal battle reflected Brown’s personal crankiness. He came into office, recalled top aide Tom Quinn, “questioning the values of the Democratic Party.”
Ascetic and even monk-like, he rejected his father’s “build, build, build” philosophy and embraced E. F. Schumacher’s “small is beautiful” ideology. Like the 15th-century Florentine Catholic monk Girolamo Savanarola, he came to rid Sacramento of suberbia and luxuria.
Brown was also ahead of his time. His early embrace of green politics–particularly energy conservation and renewable fuels–foreshadowed that of later Democrats, particularly Barack Obama. His strong outreach to Latinos and other minorities expanded his political base among California’s fastest-growing populations.
Yet Brown understood that economic prosperity–not civil rights or environmental zealotry–was key to political ascendancy. Eastern journalists dismissed him as “Governor Moonbeam,” but they ignored his Machiavellian skill in recognizing and reaching out to rising economic forces, notably the high-tech entrepreneurs in the Silicon Valley and across Southern California. The growth of this sector, along with rising trade with Asia and the military boom after the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, set the pace for the state’s strong rebound from its early 1970s doldrums.
But Brown’s inquisitorial side surfaced again as he prepared a second run–he had made a charmingly eccentric assault in 1976–for the White House. Perhaps the prospect of facing a man of infinite flexibility, Bill Clinton, pushed him over the top, but Brown re-invented himself as a high-octane and, at times, shrill populist.
After some years in the political wilderness, he reemerged in 1998 as Mayor of Oakland, a tough job even in good times. Although he remained predictably arrogant and aloof, the job of managing a working-class city seemed to have brought him to his senses. Like the ideal politician in The Prince, Brown governed with something approaching strategic precision, pushing economic development, embracing the police and supporting new infrastructure spending.
Brown’s newfound reputation as a canny realist helped him win the election as attorney general in 2006. Yet once back in statewide politics, the inquisitorial side found expression. Convinced about the impending threat of global warming, Brown used his new powers to push the Gorite agenda with the passion of a Torquemada.
Although Brown was not quite torturing heretics, he certainly applied the legal equivalent of thumbscrews to anyone–developers, cities, counties–who did not follow his prescriptions about “carbon neutrality.” Even proposals for sensible, relatively dense “in fill” development were turned aside in favor of utopian, economically unsustainable ideas about forced density and transit friendliness.
Today, with California’s economy is in tatters–its unemployment well over 12%–and Brown’s crusade seems likely to make it worse. Onerous regulation threatens everything from the construction of new single-family homes to new employment tied to anything that releases demon carbon–including manufacturing, oil drilling and large-scale agriculture.
All this has made Brown widely feared in much of California’s fractured, traumatized business community. Even worse, he has emerged as the standard-bearer of the public employee unions, the very force whose political power and pensions are bringing the state to the verge of economic ruin. The fact that Brown’s campaign is funded largely by these unions makes it, at least on the surface, unlikely to challenge the hegemony of our putative “civil servants.” They are said to be ready to spend up to $40 million on “independent” campaigns to help beat back any chance of a GOP victory.
This is worrisome given Brown’s role in fostering the expansion of public-sector unions during his term, a group whose ascendancy has become arguably the single biggest factor in the state’s precipitous decline during his last gubernatorial reign. As author Steven Greenhut has pointed out, unfunded pension liabilities in excess of $50 billion are one key element driving the state toward ever more depressed bond ratings and possible bankruptcy.
Under normal circumstances, Brown’s ties to the public sector, his fickle nature and his dubious accomplishments would spell political doom. But amazingly, Brown’s long, if mixed, record might actually prove an advantage against his most likely opponent, former
The problem for Whitman or any GOP candidate lies with the miserable legacy of another nominally Republican outsider, Arnold Schwarzenegger. The Terminator’s record of ineptitude and empty blather stands as a mega-advertisement against inexperience. Compared to the former body builder’s amateurish blundering, Brown’s wealth of knowledge of government looks appealing.
Whitman, or her main challenger Insurance Commissioner Steve Poizner, also must struggle with a Republican Party out of sync with an increasingly multi-racial and socially liberal state. As long-time political analyst Allan Hoffenblum notes, for the first time there is not one congressional, state senate or assembly district with a GOP majority.
So in the end, California’s fate may end up resting on which Jerry Brown emerges after the election. If he continues on his inquisitorial assault on carbon-creators, you can pretty much expect California’s middle class to continue diminishing while the state’s aspirational appeal ebbs ever further. The state could end up resembling Kevin Starr’s description of his native San Francisco– “a cross between Carmel and Calcutta.”
But given his history, Brown could still surprise us. Stuck with responsibility for a decaying economy and fiscally burdened by the voracious public unions, Brown could do a “Nixon in China,” imposing controls on pensions and salaries. He could recognize that “green jobs” can not save California from the abyss and that a new “era of limits” must apply to the public sector as well as the rest of us. With the passionate climate-change constituency shrinking, he might even decide to accept a modicum of carbon heresy as a necessary evil.
Brown should heed Machiavelli’s advice for rulers to be “merciful and not cruel” and “proceed in a temperate manner with prudence and humanity.” If in his old age Brown adopts the Italian writer’s credo of tactical flexibility, reason and tolerance, the Golden State may yet revive itself, and with it restore the legacy of its most storied political family.
This article originally appeared at Forbes.com.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050
, released in Febuary, 2010.
Photo: Troy Holden
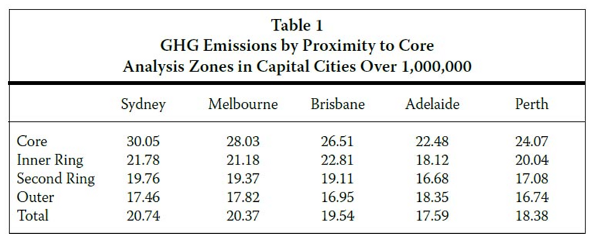
 The New Urbanism was always rather more than an architectural style, but also a vision of the good life. It hoped to address the social divide, and the solipsistic withdrawal from city life. Curiously, it seems if anything to have played a part in accelerating the social divide, in particular the gentrification of inner city enclaves. Far from making the city more diverse, the new urbanism seems to be making it more uniform. In London the trend towards in-fill by building on brownfield land has had the unintended effect of the loss of green spaces in the City. In the north of the city, Londoners gathered to protest at the recreation of urban overcrowding, when Islington’s municipal authorities planned to force yet another apartment block on top of garages in Pilgrim’s Way.
The New Urbanism was always rather more than an architectural style, but also a vision of the good life. It hoped to address the social divide, and the solipsistic withdrawal from city life. Curiously, it seems if anything to have played a part in accelerating the social divide, in particular the gentrification of inner city enclaves. Far from making the city more diverse, the new urbanism seems to be making it more uniform. In London the trend towards in-fill by building on brownfield land has had the unintended effect of the loss of green spaces in the City. In the north of the city, Londoners gathered to protest at the recreation of urban overcrowding, when Islington’s municipal authorities planned to force yet another apartment block on top of garages in Pilgrim’s Way.