The Pearl River Delta of China is home to the largest extent of continuous urbanization in the world. The Pearl River Delta has 55 million people in the jurisdictions of Hong Kong, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou, Foshan, Zhongshan, Jiangmen, Zhuhai and Macau. Moreover, the urban population is confined to barely 10 percent of the land area. These urban areas are the largest export engine of China and reflect the successful legacy of Deng Xiaoping’s reforms which had their start with the special economic zone in Shenzhen and spread to the rest of the Delta and then much of the nation.
Adjacent Metropolitan Areas: However, the Pearl River Delta today is not a metropolitan area, as is often asserted. Instead it is rather a collection of adjacent metropolitan areas or labor markets (Figure 1). Metropolitan areas are not created by a large number of people living close to one another. Metropolitan areas are labor markets, crudely delineating the geography of the jobs-housing balance. There is little commuting between the Pearl River jurisdictions. Moreover, as labor markets, metropolitan areas cannot be international unless there is virtual free movement of labor (Note). In the case of Hong Kong and Macau, commuting between the neighboring jurisdictions of Shenzhen and Zhuhai requires crossing the equivalent of an international border.
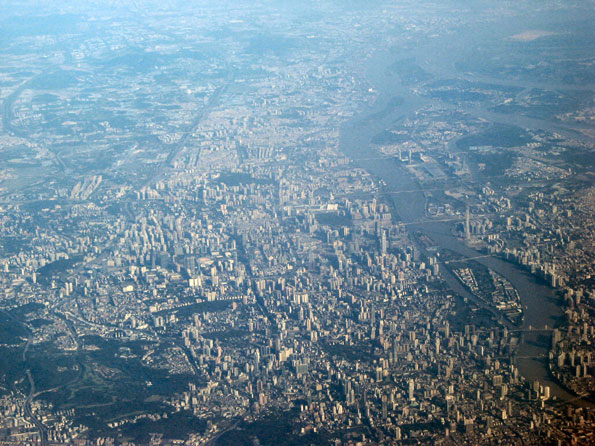
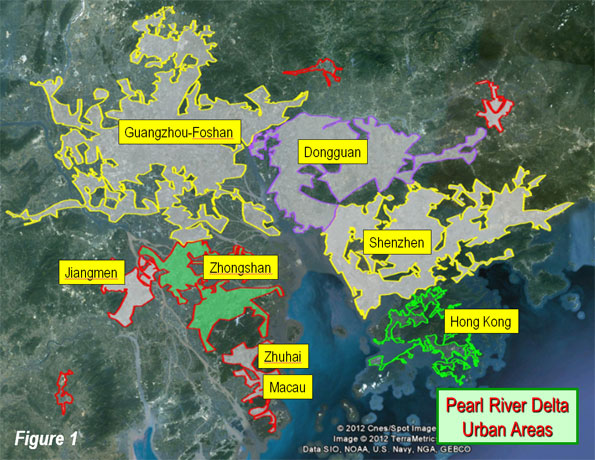



Integrating Guangzhou and Foshan: Transportation integration has already come to two of the jurisdictions, Guangzhou and Foshan. The adjacent prefectures (confusingly interpreted into English as "cities") are now linked by a subway and unlike the other Pearl River Delta jurisdictions, the continuous urbanization does not narrow at the border (Figure 1). There are even proposals to merge the adjacent prefectures.
Guangzhou and Foshan are separated by a tributary of the Pearl River, with a number of bridges that provide similar crossing capacity as exists in cross-river metropolitan areas like Portland (Willamette River), Cincinnati (Ohio River) and St. Louis (Mississippi River).
Guangzhou itself is the capital of Guangdong, the largest province of China, with approximately 105 million people. Guangdong is the third largest state or province (sub-national jurisdiction) in the world, trailing the states of Uttar Pradesh (contains the eastern suburbs of Delhi) and Maharashtra (capital Mumbai) in India.
Guangzhou is larger than Foshan. It is better known to many Westerners as Canton, and for many years served as China’s “window” on the west. Even in China, the alternative name is still used, for example in the annual Canton Fair, one of the largest trade fairs in the world.
Canton was also a principal flashpoint of 19th century hostilities between the British and Chinese. The First Opium War (1839-42) began at Canton and led to the cession of Hong Kong to Great Britain and the establishment of British treaty ports at Fuzhou, Xiamen, Ningbo, Shanghai and Canton (Guangzhou). After the Second Opium War (1856-60), other treat ports were established and France, the United States, Russia, Germany, Japan and others gained similar rights to the British from a weakened Chinese government.
In 2010, the metropolitan area county and district level jurisdictions of Guangzhou-Foshan had 18.3 million people. This is an increase of 4.4 million from 2000 and 11.6 million from 1982. This is surely a rapid rate of growth, but Shanghai and Beijing grew even faster over the last decade, each adding more than 6 million people.
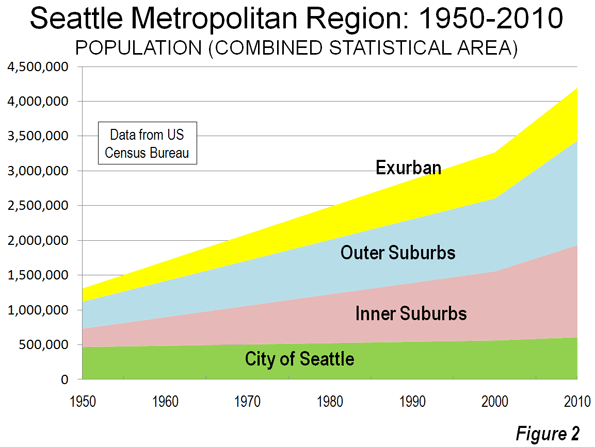
Distribution of Population Growth: In contrast to Shanghai and Beijing, where virtually all of the growth has been outside the core, the Guangzhou-Foshan core is growing robustly. From 2000 to 2010, the core districts increased from a population of 4,040,000 to 5,050,000. With a land area of 107 square miles (279 square kilometers), the core is similar in size to the city (municipality) of Sacramento, which has less than one-tenth the population. The core density is 46,800 per square mile (18,100 per square kilometer), up from 37,500 per square mile (14,500 per square kilometer) in 2000. This is about one-third less dense than Manhattan or the ville de Paris (the central city).
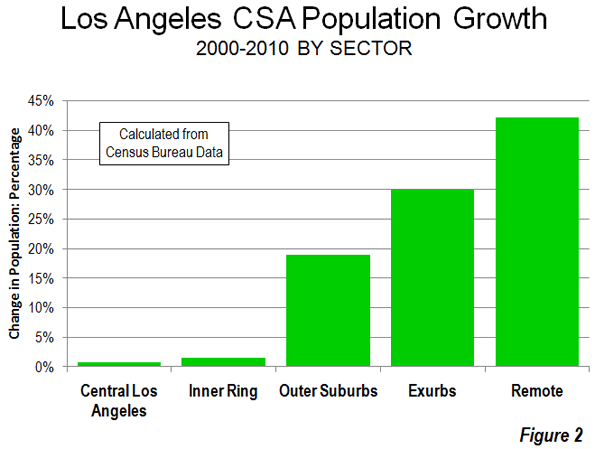
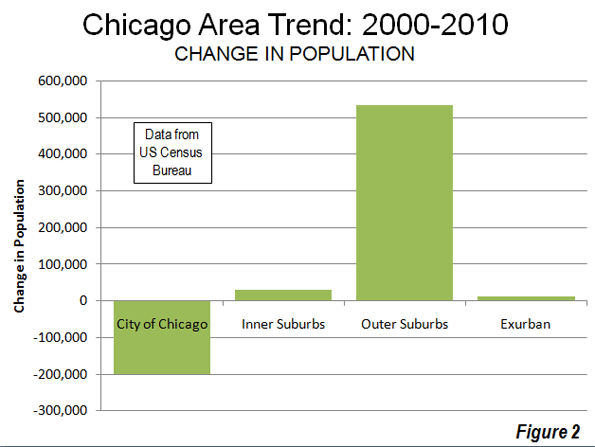
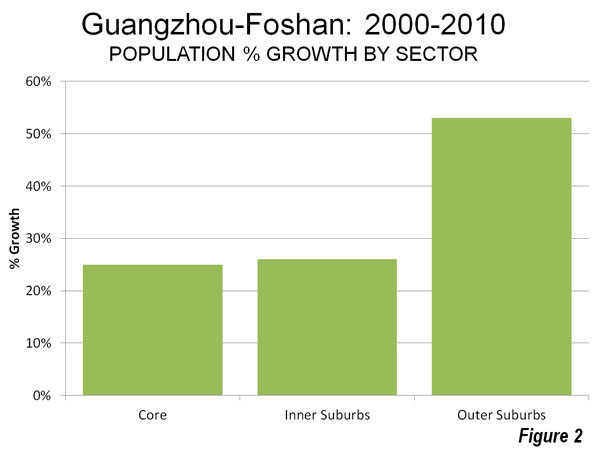
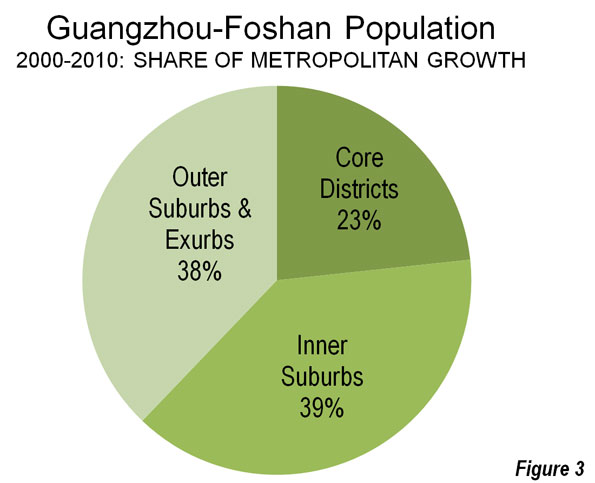
However, as is typical for metropolitan areas around the world, Guangzhou-Foshan’s growth has been most concentrated in suburban areas. The core accounted for 23% of the population growth over the past decade, while the suburbs accounted for 77%.
The inner suburbs grew from a population of 6,670,000 to 8,400,000. The density rose from 5,000 to 6,300 per square mile (1,900 to 2,500 per square kilometer), similar to that of the San Francisco urban area. The inner suburbs accounted for 39% of the growth and grew 26%.
The outer suburbs grew from a population of 3,150,000 to 8,200,000 over the past decade. The population density rose from 2,000 to 3,100 per square mile (800 to 1,200 per square kilometer), slightly more dense than the Philadelphia urban area and slightly less dense than the Portland urban area. The outer suburbs accounted for 38% of the growth and grew at the greatest rate, 53% (Figures 2 & 3, Table).
| Guangzhou-Foshan Metropolitan Area & Urban Area | ||||
| 2000 & 2010 Census | ||||
| Metropolitan Area | Core | Inner Suburbs | Outer Suburbs | Total |
| 2000 | 4,040,000 | 6,670,000 | 3,150,000 | 13,860,000 |
| 2010 | 5,050,000 | 8,400,000 | 4,820,000 | 18,270,000 |
| Change | 1,010,000 | 1,730,000 | 1,670,000 | 4,410,000 |
| % | 25% | 26% | 53% | 32% |
| Share of Growth | 23% | 39% | 38% | 100% |
| Area (KM2) | 279 | 3,429 | 4,003 | 7,711 |
| Area (Square Miles) | 108 | 1,324 | 1,546 | 2,977 |
| Density (KM2) | 18,100 | 2,400 | 1,200 | 2,400 |
| Density (Square Miles) | 46,800 | 6,300 | 3,100 | 6,100 |
| Urban Area | Core | Suburbs | Total | |
| 2010 | 5,050,000 | 11,225,000 | 16,275,000 | |
| Area (KM2) | 279 | 2,894 | 3,173 | |
| Area (Square Miles) | 108 | 1,117 | 1,225 | |
| Density (KM2) | 18,100 | 3,900 | 5,100 | |
| Density (Square Miles) | 46,800 | 10,000 | 13,300 | |
| Notes | ||||
| Boundary changes render district area data incomplete. | ||||
| Core: Yuexiu, Liwan, Haizhu, Tianhe | ||||
| Inner Suburbs: Baiyun, Huangpu, Panyu, Nansha, Nanhai, Changcheng | ||||
| Outer Suburbs: Huadu, Luogang, Gaoming, Shunde, Shanshi | ||||
| Nansha is in the inner suburbs because 2000 data is combined with Panyu (should be in the outer suburbs) | ||||
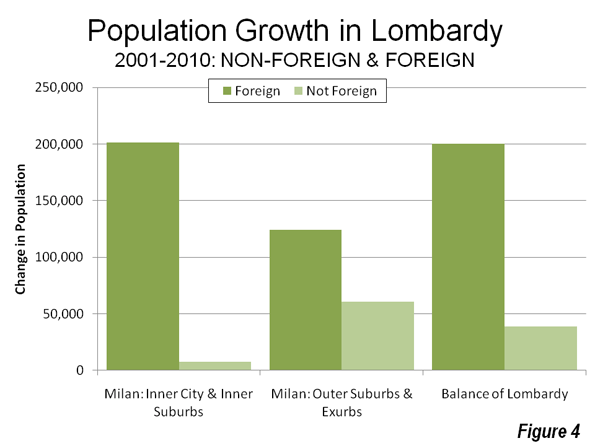
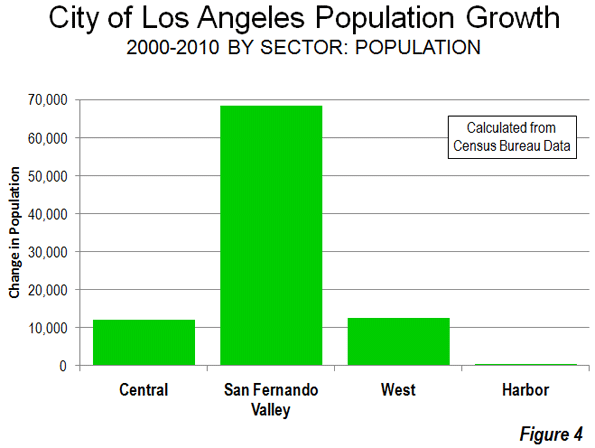
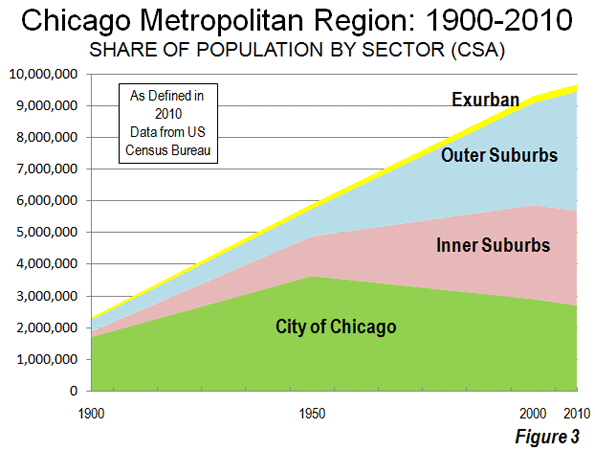
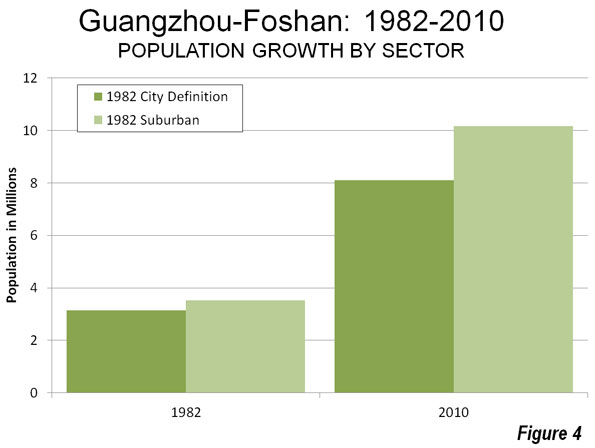
Earlier data shows this suburban pattern has been a long term trend. Between 1982 and 2010, the suburbs accounted for 57% of the growth outside the city of Guangzhou as then defined (Figure 4). District boundary changes limit a more precise analysis based upon a core that did not include large areas without development.
The Guangzhou-Foshan Urban Area: The soon to be released 8th Annual Demographia World Urban Areas will show the Guangzhou urban area (area of continuous development within the metropolitan area) to have a population of approximately 16.275 million, with a land area of approximately 1,225 square miles (3,173 square kilometers). Barring later data from the multiple national censuses that will soon be reporting data, Guangzhou-Foshan is likely to be ranked the 14th largest urban area in the world. The population density is approximately 13,300 per square mile (5,100 per square kilometer), roughly comparable to the London or Barcelona urban areas. The suburbs of the urban area have a density of approximately 10,000 per square mile (3,900 per square kilometer). Most of the new residential development is multi-unit, such as high rise condominium buildings and work related housing, including dormitories. However, there is some detached housing, which is very expensive.
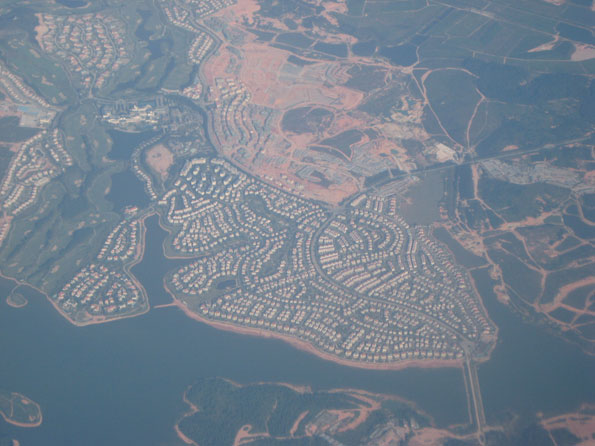

A Larger Metropolitan Area: In the longer run a much larger metropolitan (and urban) area could result, if Chinese residents begin traveling to work over much longer distances between these jurisdictions and should the border restrictions at Hong Kong and Macau be eliminated. To achieve this end, there will need to be important local transportation improvements between the jurisdictions, such as more urban railways (which are planned) and wider automobile ownership, to use the already comprehensive (toll) freeway system.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris and the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life”
——
Note: International metropolitan areas can now exist in the European Union, where there is free movement of labor across national borders. For example, the Lille metropolitan area is located in both France and Belgium. France and Switzerland (not a member of the European Union) provide another example, where treaty provisions permit international movement of labor with little difficulty in the resulting international metropolitan areas of Geneva (Switzerland-France) and Basel (Switzerland-France).
Photo (top): Pagoda: Temple of the Six Banyan Trees, Guangzhou (all photos by author)