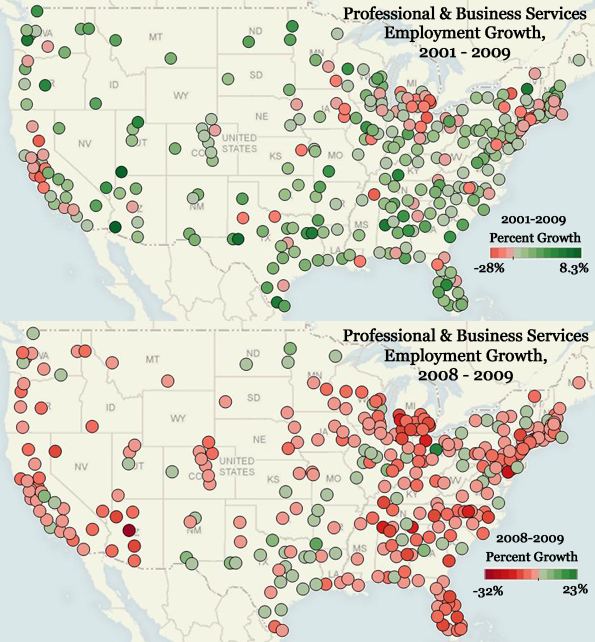
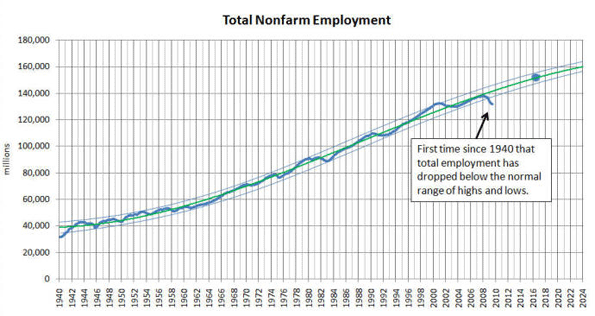
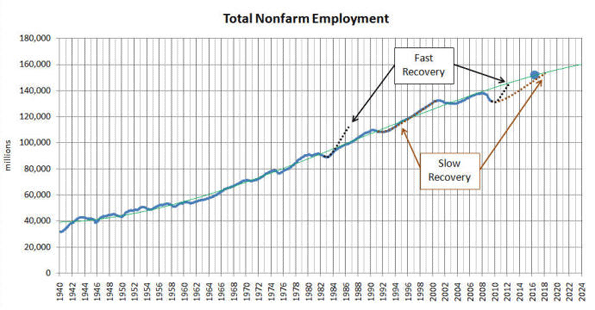
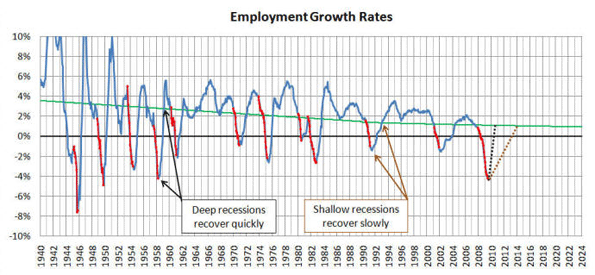
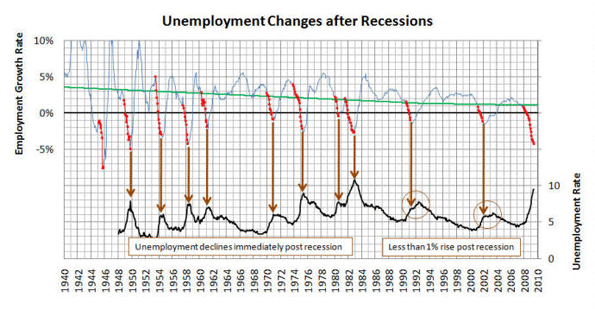
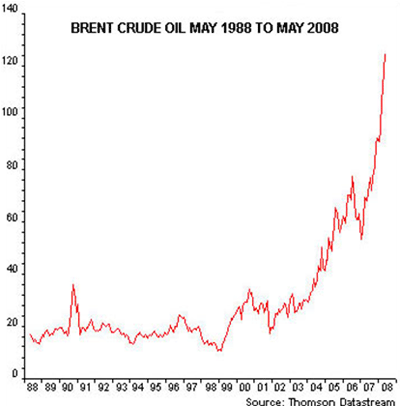
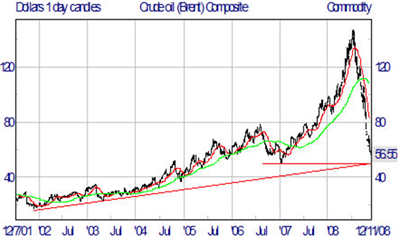
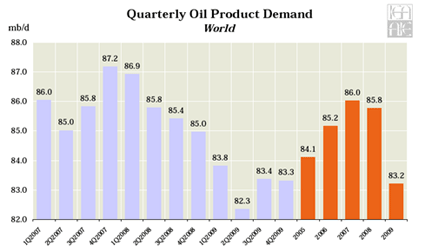
The person who caused the current world recession can be found not on Wall Street or the city of London, but instead could be you, and your next-door neighbor–the people who put so much of their savings and credit to buy a house.
Increasingly, conventional wisdom places the fundamental blame for the worldwide downturn on people’s desire–particularly in places like the U.K., the U.S. and Spain–to own their own home. Acceptance of the long-term serfdom of renting, the logic increasingly goes, could help restore order and the rightful balance of nature.
Once considered sacrosanct by conservatives and social democrats alike, homeownership is increasingly seen as a form of economic derangement. The critics of the small owner include economists like Paul Krugman and Ed Glaeser, who identify the over-hot pursuit of homes as one critical cause for the recession. Others suggest it would be perhaps nobler to put money into something more consequential, like stocks.
Homeowners also get spanked by leading new urbanists, like Brookings scholar and urban real estate developer Chris Leinberger. He lays blame for the downturn not on unscrupulous financiers but squarely on aspiring suburban home buyers. “Sprawl,” he intones, “is the root cause of the financial crisis.”
If only we built more high-density, transit-oriented housing–which, incidentally, is not exactly thriving–the crisis could be happily resolved, he believes. This approach is echoed by big-city theoreticians like Richard Florida, who believes that both homeownership and the single-family house “has outlived its usefulness.” In his “creative age,” we won’t have much room for either single-family homes or owners. Instead, we will be leasing our ever-more-tiny cribs–just like yuppies with their BMWs–as we wander from job to job.
To be sure, many people who bought homes in the last few years should not have qualified. Weak lending standards, promoted by both unscrupulous industry figures like Countrywide’s Angelo Mozillo as well as Congress–including the many “friends” receiving cut-rate loans from the disgraced mortgage firm–clearly made things worse.
Yet the recent real estate debacles should not obscure the tremendous positives associated with homeownership. Widespread and diffuse ownership of property has been a critical element in successful republics, from early Rome and the Dutch Republic to the foundation of the United States. Jefferson held that “small land holders are the most precious part of a state.” In the ensuing generation, progressives embraced widespread ownership of property as central to democratic aims. Lincoln’s Homestead Act stands out as a prime example.
Even by the 1940s, this model was only partially realized. Barely 40% of the population owned their homes. Homeownership remained confined largely to small-town denizens and the urban upper classes. No one in my mother’s family–growing up in the tenements of Brownsville, Brooklyn–even considered homeownership an achievable goal. It was hard enough simply to pay the rent and put food on the table.
Yet by the 1960s, rising prosperity and government-subsidized loans helped most of my numerous aunts and uncles own their residence.
Presidents from Roosevelt to Clinton all identified homeownership as a critical social goal. Government loan programs exploded as housing starts doubled in the post-war era. By 2005, the homeownership rate was approaching 70%.
This trend also took place in other advanced countries, from the U.K. and Australia to Canada and Spain. It reflected what the Italian urbanist Edgardo Contini once referred to as “the universal aspiration.” In some cases, such as Japan, societies that had been divided between landlords and peasants for millennia now boasted a huge, and growing, cadre of small owners.
In virtually every country, this was largely a suburban phenomenon. People bought houses where land was cheaper, stores and schools newer. Here, too, people could transcend the often confining social limits of the old neighborhood. It was also, as the novelist Ralph G. Martin, noted “a paradise for children.”
Through all this, the chattering class never lost its contempt for homeowners and their suburban refuges. Old gentry long disliked the idea of dispersed ownership of property–even if many got rich selling their own estates to developers. Aesthetes disliked the seemingly banal housing tracts “rising hideously,” as Robert Caro put it, from the urban periphery. This critique was applied not only to Queens and Long Island but also to places like Milton Keynes or Basildon outside London, and greater Tokyo’s Chiba prefecture.
Along with the fashion police, the new owners also took criticism from their urban betters, many of them also owners of country homes, for deserting the city. Some on the left feared the homeowners as a bastion of conservative politics. Architects, planners and developers identified them as opponents of their grand plans to refashion suburbia into a denser, more rental-oriented environment.
Yet, despite the disdain, the dream of homeownership survived. Many boomers, who in their 1960s radical phase denounced suburban tracts as sterile and racist, meekly ended up buying homes there. So, increasingly, did middle-class minorities, whose rates of homeownership rose faster after 1994 than that of whites.
To be sure, the financial crisis has led to a sharp drop in levels of homeownership, as occurred in the last big recession of the early 1990s. In the future, some suggest that aging boomers will force the home market to collapse even more due both to the current mortgage meltdown and changing demographics.
Yet there are limits to how far homeownership will drop. Urban boosters, apartment-builders and greens–all advocates of expanding the renter class–tend to ignore several key facts. For one thing, the vast majority of boomers are holding onto their mostly suburban homes far longer than ever suspected. Many will remain there until forced into assisted living, nursing homes or the cemetery.
Then we have the X generation, who, if anything, has favored large homes and exurbs in large numbers. In addition, behind them lie the large cohorts of millenials, who according to surveys conducted by generational chroniclers Morley Winograd and Mike Hais, prioritize the ownership idea even more than their boomer parents do.
No doubt, the weak economy will slow this generation’s push into the home market. However, by the next decade, as this generation enters the late 20s and early 30s, they will find their economic footing and be ready to enter the market for houses in a big way.
The real question then will become which companies and regions will meet the expanding demand. Over the past decade, we saw the demand for housing push middle-class families toward destinations as varied as Las Vegas and Phoenix, Austin, Houston, Dallas and Atlanta. Others have started heading to more affordable markets in the nation’s heartland, to the metropolitan areas like Kansas City, Des Moines and Sioux Falls.
Rather than a source of economic weakness, this renewed quest for homeownership could underpin a sustainable recovery. As prices fall to reasonable levels, more people will qualify for reasonable loans. First, the empty houses and somewhat later, the condominiums now on the market will find buyers, in most places in a matter of a few years.
This shift will create huge opportunities for a diverse set of geographies. For urban areas like New York or Los Angeles, there will be a unique–perhaps once in a generation–chance to induce middle-class people to settle down in big-city homes or condominiums. If they become homeowners, they will be more likely to stay than move elsewhere to the suburbs or other regions when the time comes to buy a home.
Other, more affordable, less regulated and often more economically dynamic places like Texas and the Great Plains may realize even greater gains. Over time, we will likely see a recovery in some now-suffering parts of the Sunbelt. The renewal of home demand could also help revitalize many of our hardest-hit sectors, including construction and manufacturing.
Sadly, some policymakers in Washington seem less than enthusiastic about this prospect. Many close to President Obama seem to dislike single-family homes and suburbs. Some embrace the policy which the British called “cramming,” essentially forcing people into ever smaller, denser units. Energy Secretary Steven Chu recently praised the notion of small apartments with numerous people. “You know, body heat keeps a lot of the apartment warm,” he suggested. You can’t do this in a big apartment with a few people.”
My suspicion is that most Americans are not quite ready to become their own heaters, any more than modern farm families like having farm animals live with them–although they, too, generate warmth. Instead, we should explore less unpleasant ways to cut energy use though such things as incentives for decentralizing work, promoting home-based labor, more tree planning and effective insulation.
An administration that places itself at odds with the “universal aspiration” that has driven growth in the advanced world for over a half-century could delay a full recovery unnecessarily. Advocacy of what amounts to declining living standards and a return to feudalism might also prove a less than successful political strategy.
This article originally appeared at Forbes.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University. He is author of The City: A Global History . His next book, The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050, will be published by Penguin early next year.
. His next book, The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050, will be published by Penguin early next year.