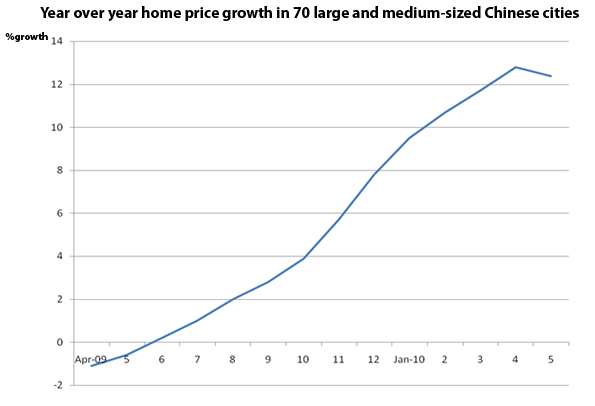
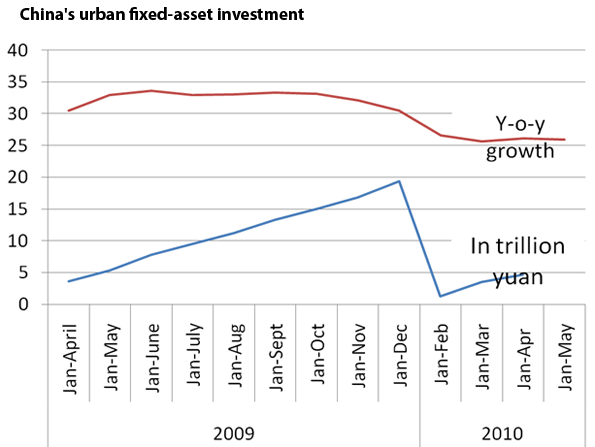
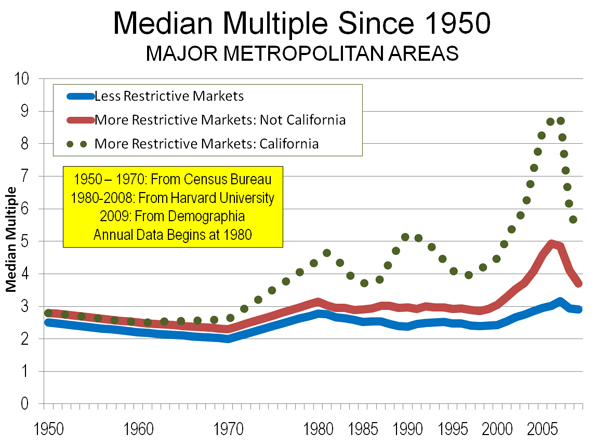
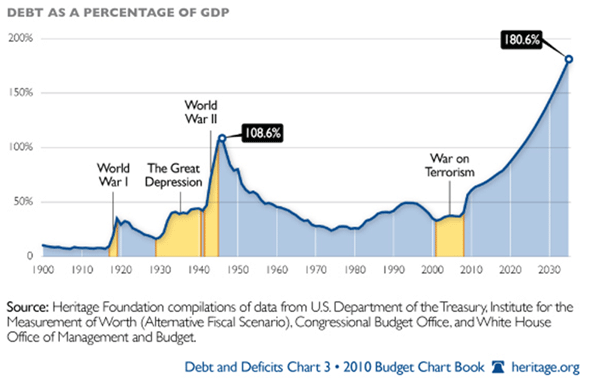
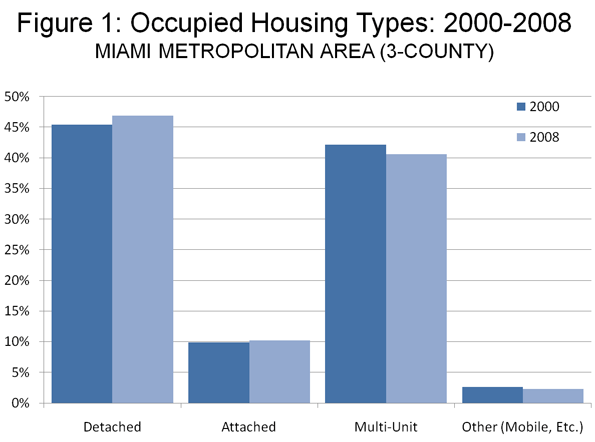
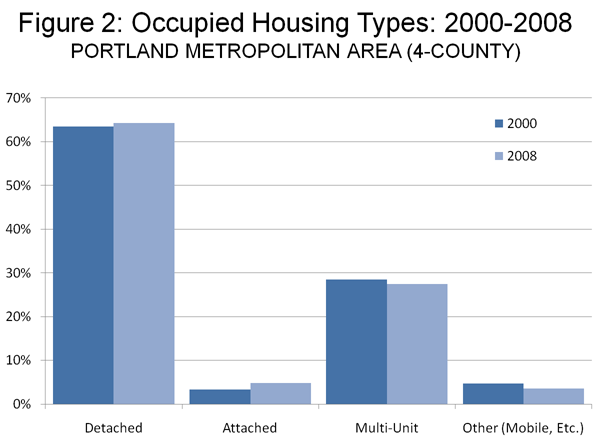
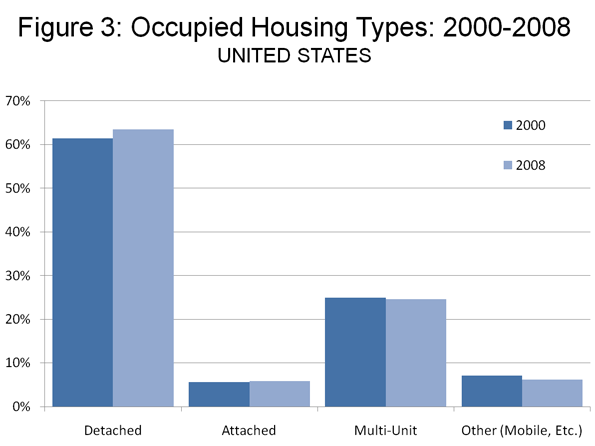
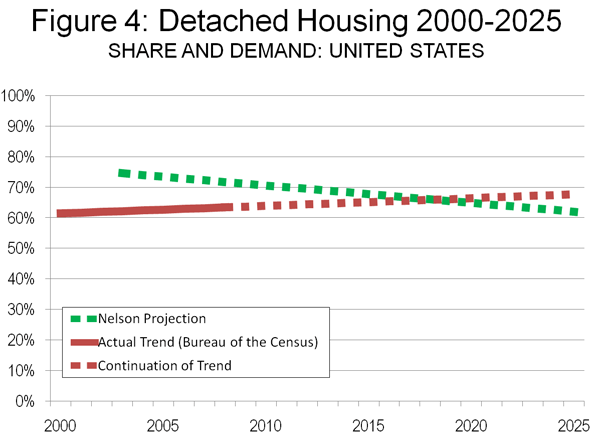
A year ago we were hearing all about green shoots. Analysts claimed to find them everywhere.
Today, we never see the term. In fact, there seems to be a growing malaise. By the end of June the first quarter’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) estimate was revised downward a full half a percent, to 2.7 percent. Pundits are depressed. Our President and Secretary of the Treasury are telling the world that the United States cannot lead the world to sustained economic growth. Our Vice President announced that “there’s no possibility to restore eight million jobs lost in the Great Recession.” Our stock markets are down and volatile. Risk premiums have soared.
What happened?
Reality happened. The green shoots were always ephemeral, the result of massive government spending increases or temporary government programs. We had housing stimulus programs. We had Cash for Clunkers. We had foreclosure programs. We had bailouts.
The increased spending and the various programs had an impact. Because of the way GDP is calculated, an increase in government spending results in an increase in GDP, but that is today’s GDP, not tomorrow’s. Tomorrow’s economic growth is a result of investment today, investment in physical capital, technology, and human capital.
To the extent that government spending detracts from those investments, the growth we saw was cannibalized from the future. For example, the housing stimulus programs served only to change the timing of real estate purchases. Sales fell when the programs ended.
Even worse, some programs resulted in temporary GDP growth, but were actually detrimental to long-term economic growth. The Cash for Clunkers program destroyed capital, since perfectly good cars were crushed. The foreclosure prevention programs delayed the needed decline in home ownership rates.
The bailouts prevented assets from being transferred to more productive uses. Bailouts are inefficient, and they prolong periods of economic weakness. Uncertainty and risk premiums remain elevated, holding investment to a minimum, limiting short-term and long-term economic growth. They also leave a hangover of debt, which limits future growth.
None of the programs addressed the underlying problems of the current economic circumstances, or paved the way for sustained economic growth. The immediate problem was that businesses, consumers, and governments were over-leveraged after September 2008’s asset-value collapse. The longer-term problem was insufficient investment, a result of years of credit-fueled consumption.
What was needed was investment. What was provided was more credit-fueled consumption. You might be able to borrow your way to prosperity, but to do that you better be investing the borrowed funds. We didn’t do that. Instead we used the government as a bank to increase consumption. Credit-based consumption is not the way to long-term prosperity, regardless of who does the borrowing.
And, while it appears that most of the decline in asset values has ended, over-leverage is still with us. Indeed, the increase in government leverage makes it more difficult to employ effective government intervention, government investment in productivity-enhancing capital and technology, and investment tax credits.
Add to these factors the millions of American households, employed and unemployed, that remain over-leveraged. Millions of consumers have been unemployed for months, and many of those still working are uncertain about their future employment. Those who have the income to do so are attempting to pay down debt, and to reduce consumption in the process. The consumer is not likely to soon be a source of rapid economic growth.
So, we have most or all of the problems of a year ago, but now, because of increased government debt, we have fewer options. Even worse, we now have new problems that were not present in September 2008.
Today, sovereign default risks are significant and increasing. While potential sovereign debt problems in Europe have received a great deal of attention, the problems are not limited to the continent. Japan continues to have very high debt and deficits. Several U.S. states could also default. A failure of an American state is likely to have impacts very similar to the failure of a small European country.
I don’t believe that the failure of a country is the most likely outcome, however. Instead, expect to see more international bailouts, just as you can expect to see the federal government bailout several American states.
Our options are limited, but we do have one option that would provide immediate and sustained economic growth without increasing leverage. That option would be a massive increase in immigration.
The initial benefits of a new wave of immigration would be seen remarkably quickly. Housing demand would increase, leading to renewed vigor in our real estate markets and the construction industry. Our inner cities would be renewed, as they always have been by immigration waves. New business formations would soar. The tax base would increase, helping to fund debt repayment and baby-boomer retirements.
Many would oppose such an immigration increase. They worry about increasing job competition, unemployment, crime, and even more demand on welfare programs.
These fears are misplaced. Criminals are easily sorted out by effective screening processes. People don’t migrate for welfare benefits, but if this is a concern, it is easy to deny immigrant access to social programs for some number of years after immigration. Similarly, people don’t migrate to be unemployed, and unemployment benefits can be denied to immigrants.
People migrate to more effectively use their human and physical capital, their technology, and their labor. Effectively, immigration would provide new capital, technology, and labor. This is exactly what we need, and it is free. Immigration has served America well in the past. It can serve us well today.
Red and Green, photo by Rupert Maspero
Bill Watkins is a professor at California Lutheran University and runs the Center for Economic Research and Forecasting, which can be found at clucerf.org.