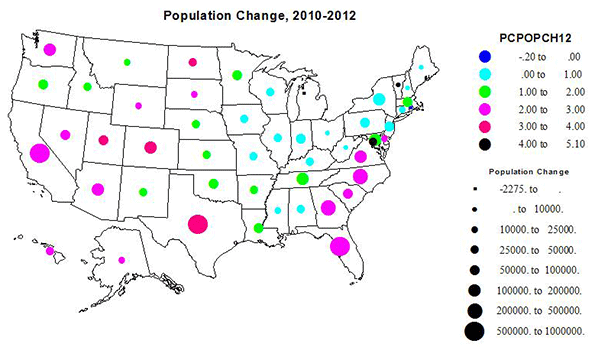
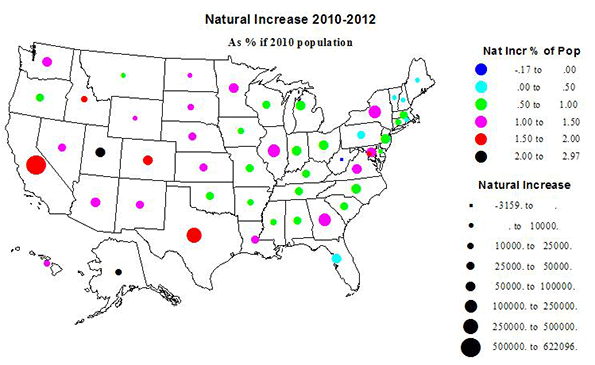
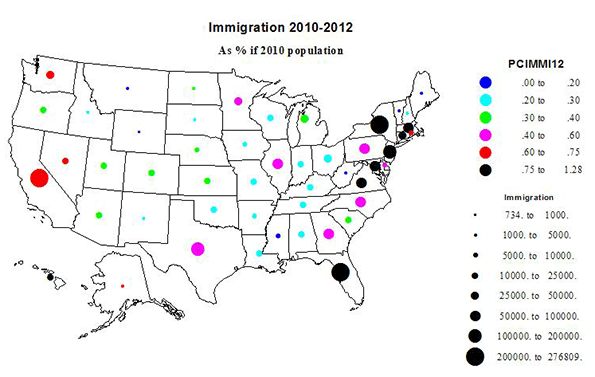
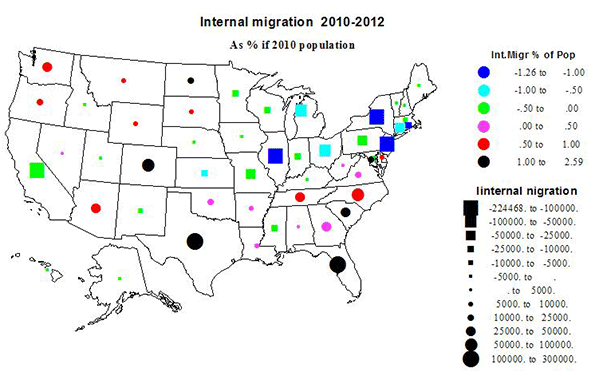
With the stock market hitting new highs, and unemployment easing, albeit slightly, President Obama can now seize his moment. After spending four years blaming George W. Bush for his lousy hand, the president now sits at the table with three strong aces among his cards.
The key question is: Will he play them?
One reason he might not is that most of his good hand stems primarily not from his stewardship but America’s economic and demographic kismet. In fact, this resurgence is primarily not taking the "green," urban and high-tech form, as preferred by most coastal Democrats, but stems largely from the productive forces being unleashed in the nation’s largely red heartland.
But Barack Obama is president, and if the country resurges on his watch, he will get much of the credit. This country, for all its problems, is naturally blessed, with both human and physical resources. It is beginning to both pull away from laggard Europe and Japan and seems far more well-positioned to compete with China than most observers believe. The choice for the president is whether to ride this resurgence, or throw it away as incompatible with his political agenda.
This dichotomy starts with energy, the thing most propelling the real, as opposed to the paper, economy. The current energy boom is taking place in a manner precisely what Obama and, certainly, many of his strongest backers, least likely would have preferred. In his first term, Obama charted a path on energy typical of the university faculty lounge. His departing energy secretary, Steven Chu, embraced the idea that Americans used fossil fuels irresponsibly, comparing them to teenagers. He liked forcing higher costs for energy while using our tax dollars to subsidize often-dodgy renewable schemes.
Yet, history, as is often the case, played out quite differently than the expected script. Rather than being required to accept enforced scarcity, Americans, largely due to new drilling techniques and advanced technology for identifying previously undiscovered fields, now are on the cusp of a massive energy boom. This has changed the country’s trade and economic prospects immeasurably. Since 2009, the industry, according to the consultancy EMSI, has added some 430,000 jobs, in contrast to the much subsidized "green" energy industry, which has suffered a spate of embarrassing failures.
Energy employment
One problem for the president: The big winners to date have come from outside the coastal strips whose residents constitute his base. Over the past decade, Texas alone has added 180,000 mostly highly paid energy-related jobs. Oklahoma added 40,000, and the Intermountain West well over 30,000. In what could be a persuasive case, Pennsylvania, a blue state with a hunger for jobs, has joined the party; the original center of the U.S. energy industry is now enjoying a resurgence.
In contrast, energy-rich California, despite the nation’s third-highest unemployment rate, has chosen to stand largely on the sidelines, creating a mere 20,000 such energy-related jobs. The same can be said about New York, which so far has chosen to follow the lead of celebrity "fracktivists" and is refusing to exploit its rich natural gas resources. Yet even in California, some normally progressive voices, such as former longtime Los Angeles Times columnist Tim Rutten, suggest that, in order "to jump-start" its economy, the state ought to climb on the energy bandwagon.
To be a successful president, Obama can embrace this growth while maintaining his green bona fides. As the environmentalists at the Breakthrough Institute have noted, America’s recent remarkable progress in reducing greenhouse gases primarily is not the result of the sort of green technologies financed by the president’s venture-capitalist friends and embraced by his media allies. Instead, it has been overwhelmingly the result of the gradual replacement of coal usage with natural gas.
Embracing gas – not only to generate electricity but also for transportation – serves both Obama’s interest and the country’s long-term interest. But his task is made more perilous by his efforts to appease his urban, green constituency, once strongly supportive of natural gas, but now decisively against it. Two contrarian environmentalists, an increasingly endangered species, have labeled the celebrity-driven protesters of hydraulic fracturing drilling techniques as "fracktivists for global warming."
Some observers, such as former Al Gore aide Morley Winograd, suggest that Obama’s appointment of Ernie Moniz as energy secretary will bolster the notion that the president has shifted towards "pragmatic idealism" on energy. Obama may still be reluctant to allow much drilling in publicly held land but he could countenance a negotiated reasonable solution to the contentious issue of fracking.
High-flying farming
Energy is only one, albeit the most dramatically apparent, ace in the presidential hand. Another is agriculture, which is on a historic tear. This has been led, particularly in the Great Plains and the Midwest, by a boom in agriculture exports: The U.S. exported a record $135 billion in 2011, with a net favorable trade balance of $47 billion, the highest in nominal dollars since the 1980s.
What accounts for this boom? One driver is growing markets in the developing world – notably, China, which consumes almost 60 percent of the world’s soybean exports and 40 percent of its cotton. The Great Plains Corridor, in particular, produces both these crops in abundance, which is one reason for its increased share of U.S. exports.
Most farmers and farm communities – outside of some who might ship to lovocore (eat local) restaurants – tilt conservative, but the exports of this sector drive growth in services and even technology. Farming today is increasingly tied to science, and that includes efforts to reduce the use of fertilizers and water. Cities from Omaha, Neb., to Kansas City to New Orleans all benefit from agricultural trade.
Cars come back
The last of Obama’s aces comes from manufacturing, whose resurgence has been among the most surprising developments of the past five years. Some of this is tied to the energy boom, which is boosting industry along the Gulf Coast, with its burgeoning petrochemical complex. By itself, the expansion of energy – particularly cheap and plentiful natural gas – will create, according to a recent PricewaterhouseCoopers study, more than 1 million industrial jobs nationwide.
But more politically important for the president is the resurgence of the U.S. auto industry. Whatever one thinks of how the GM and Chrysler bailouts were conducted, the return to profitability in Detroit represents a big win for Obama and may be one of the reasons for his surprisingly strong electoral showing in the industrial Great Lakes. In comparison with Europe and, increasingly, even China, American manufacturers are showing great resiliency and growing competitive strength.
Yet, even here Obama needs to be careful. What a recent Boston Consulting Group report described as the incipient "reallocation of global manufacturing" will primarily benefit lower-cost, nonunion red states such as South Carolina, Alabama and Tennessee. This is where most new investment from German, Japanese and Korean firms is going. Yet, if this growth continues, Obama is helping his core constituencies, notably African-Americans, who now can see the prospect of higher-wage employment with benefits.
Ultimately, as the former Gore aide Winograd suggests, how Obama plays these cards may well determine the success of his tenure.
He could choose to throw out his trump cards in a gesture to placate his gentry funding base, urban progressives and his most devoted media claque. Or he could, like most great politicians, choose, instead, to play the great hand providence has provided him, irrespective of his core supporters, thereby all but assuring his stature as one of the more successful presidents in recent history.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University, and a member of the editorial board of the Orange County Register. He is author of The City: A Global History and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. His most recent study, The Rise of Postfamilialism, has been widely discussed and distributed internationally. He lives in Los Angeles, CA.
This piece originally appeared in the Orange County Register.
Barack Obama photo by Bigstock.