No sooner had Florida Gov. Rick Scott rejected federal funding for the Tampa to Orlando high-speed rail line, than proponents both in Washington and Tallahassee set about to find ways to circumvent his decision. While an approach has not been finalized, a frequently suggested alternative is to grant the federal money to a local government, such as a city or county or even to a transit agency.
Eliminating State Taxpayer Risks, Creating Local? In an announcing his decision, Governor Scott cited the substantial risks to Florida taxpayers from cost overruns, the ongoing obligation under the federal grant to subsidize operations and the fact that under certain circumstances Florida might even have to repay the $2.4 billion in federal grants. Any local government accepting the federal money would expose itself to the financial risks from which Florida taxpayers have been exempted by Governor Scott’s action.
None of these risks is an idle threat.
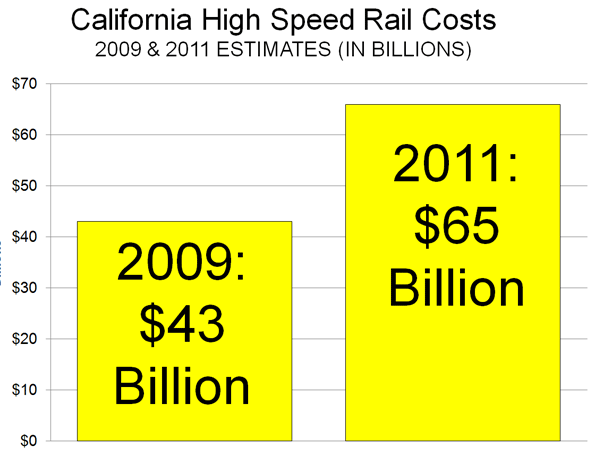
(1) Capital Cost Overruns: Based upon the international experience, the eventual construction cost overruns for the Tampa to Orlando high-speed rail line could easily run to $3 billion, more than doubling the price of the project (Note on Extent of Taxpayer Liability, below). In light of the recently reported 50 percent increase in California high-speed rail construction costs, even the $3 billion estimate could turn out to be conservative. The problem is that any local federal grant recipient (city, county or transit district) would be responsible for these cost overruns.
(2) Ongoing Operating Subsidies: The ridership projections for the Tampa to Orlando high-speed rail line are exceedingly optimistic. This could well lead to a situation in which substantial subsidies are necessary to operate the trains, despite claims of proponents to the contrary. These subsidies would be the responsibility of any city, county or transit district that becomes a grant recipient.
(3) Federal Pay-Back: If, for any reason, the eventual high-speed rail service levels are not sufficiently high because of lower than projected ridership or if service is canceled, any city, county or transit district could be required to return the $2.4 billion in federal grants. Florida is already paying millions annually for a similar "transgression." In 2009, service reductions on the Tri-Rail Commuter Rail System in the Miami area led the Obama Administration’s Department of Transportation to demand repayment of one quarter billion dollars in grants. Tri-Rail was saved from this obligation only by a multimillion dollar Tallahassee bailout. Proponents have claimed that this rail obligation could be negotiated away for high-speed rail. Why was the Tri-Rail obligation not negotiated away in 2009?
By rejecting the federal funding, Gov. Scott has inoculated Florida taxpayers against these risks.
However, there would be no inoculation for any local jurisdiction whose commissioners or city council accepted the expensive "gift" of federal funding for the high speed rail line. Their taxpayers would have to pay. The very financial viability of any such jurisdiction could be at risk.
The Risk Could Revert to State Taxpayers: Eventually, the risk could be again be visited upon state taxpayers as a local government facing virtual bankruptcy would doubtless seek a bailout in Tallahassee, repeating the Tri-Rail experience, though much more expensively. Moreover, canceling a half built project, which might be tempting as costs escalate above projections, would simply not be viable. The political pressure to complete the project, at whatever cost, could prove to be overwhelming.
Delusions About Private Responsibility for Cost Overruns: Some proponents claim that these huge obligations can be somehow transferred to the private builder/operator that is selected for the project. Nothing like this has ever happened in public-private partnerships around the world, and for good reason. Companies do not stash away billions of dollars for cost overruns.
Further, the winning bidder will be a consortium of other companies, established with limited liability by larger companies. The consortium would abandon a project it could not afford sooner rather than later. Any bankruptcy of the builder/operator would be limited to the consortium and would not extend to the parent companies, leaving the local taxpayers to pay.
There is no escaping the fact that the taxpayers of any city or county accepting the federal money would be providing financial guarantees to an international infrastructure industry that has left a "train" of huge and unanticipated financial obligations around the world in its wake (Note on Cost Escalation, below).
Believing in Santa Claus? Public officials, and most recently Orlando Mayor Teresa Jacobs, have indicated support for high-speed rail if private and federal funds pay for it, and state and local taxpayers aren’t exposed to liability. This is a wise position, but untenable. Expect Santa Claus to arrive in the midst of a Florida summer before that, with a sleigh full of billions.
—-
Note on Extent of Taxpayer Liability: This $3 billion is in addition to the already committed $280 million of taxpayer funding. Proponents of the high-speed rail line have assumed that the $280 million would be the limit of taxpayer obligations. As this article shows, the $280 million could be a "drop in the bucket" compared to the likely eventual taxpayer liability.
Note on Cost Escalation: An international team of researchers led by Oxford University Professor Bent Flyvbjerg has found in Megaprojects and Risks: An Anatomy of Ambitionthat similar projects routinely cost far more than taxpayers and other funders are told. They also attract fewer riders and generate less revenue (which can require operating subsidies). The Flyvbjerg team implies that these "lowball" (our term) projections are not accidental but all are the result of "strategic misrepresentation," (their term) which project promoters employ to increase the potential that projects will be approved. The researchers also refer to "strategic misrepresentation" as "lying," which is an exceedingly strong term for academic research and is reflective of the strength of the conclusions.