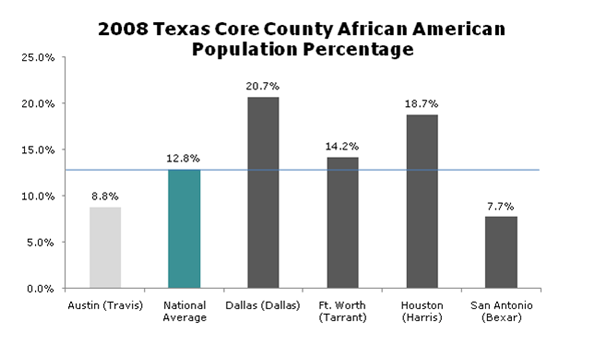
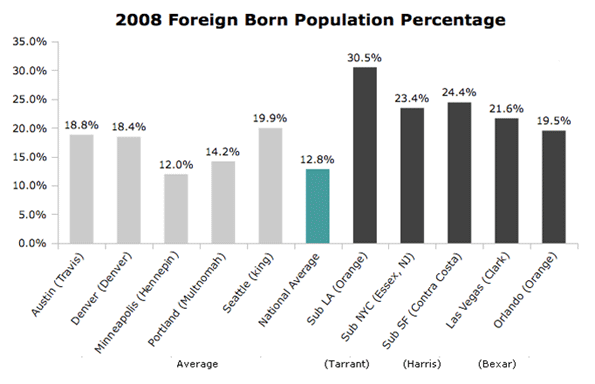
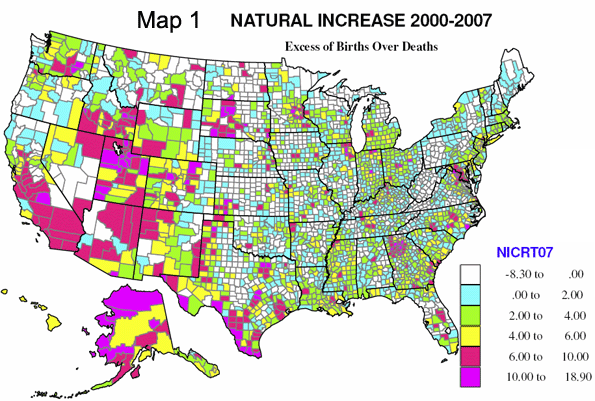
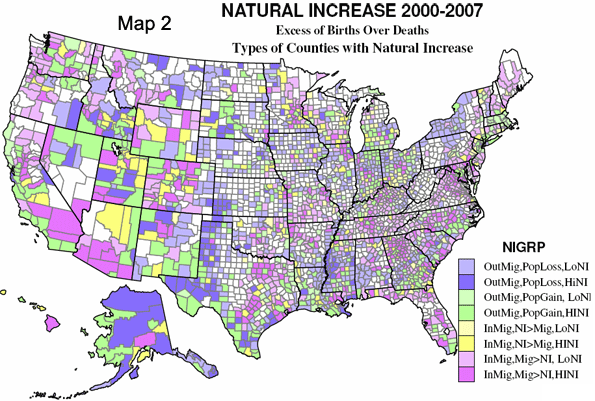
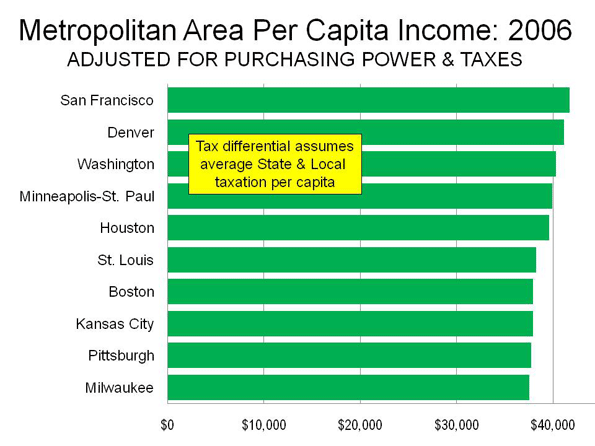
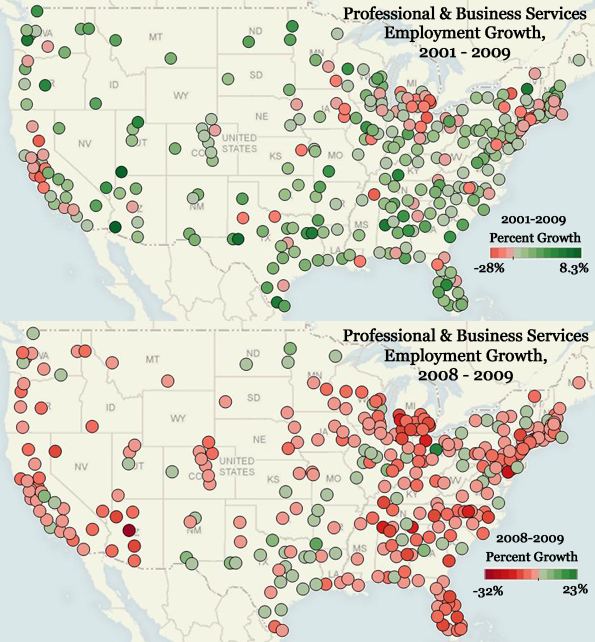
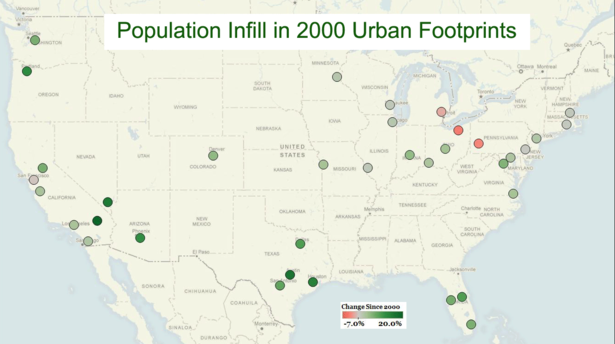
In today’s parlance a “smart” city often refers to a place with a “green” sustainable agenda. Yet this narrow definition of intelligence ignores many other factors–notably upward mobility and economic progress–that have characterized successful cities in the past.
The green-only litmus test dictates cities should emulate either places with less-than-dynamic economies, like Portland, Ore., or Honolulu, or one of the rather homogeneous and staid Scandinavian capitals. In contrast, I have determined my “smartest” cities not only by looking at infrastructure and livability, but also economic fundamentals.
These criteria unfortunately exclude mega-cities like New York, Mexico City, Tokyo or Sao Paulo, which suffer from congenital congestion, out-of-control real estate prices and expanding income disparities–symptoms of what urban historian Lewis Mumford described as “megalopolitan elephantiasis.”
Instead, today’s “smart” cities tend to be smaller, compact and more efficient: places like Amsterdam; Seattle; Singapore; Curitiba, Brazil; and Monterrey, Mexico. This is not an entirely new notion: Between the 14th and 18th centuries, modest-sized cities like Venice, Italy; Antwerp, Belgium; and Amsterdam nurtured modern capitalism and created canals and vibrant urban quarters that remain wonders even today.
In the Pacific-centric modern era, smart commercial cities are increasingly found outside Europe. Indeed, the most likely 21st-century successor to 15th-century Venice is Singapore, a commercially minded island nation that, like its forebear, is run by an often enlightened authoritarian regime.
When it first achieved independence in 1965, Singapore’s condition was comparable to other developing cities like Bombay, Cairo, Lagos or Calcutta. The island city’s neighbors included unstable countries like Vietnam, Malaysia and Thailand. Its GDP per capita ranked well below those of Argentina, Trinidad, Greece or Mexico.
The country’s first prime minister and current eminence grise, Lee Kuan Yew, was determined to change reality. Today, Singapore, with a population of less than 5 million, boasts an income level close to the wealthiest Western countries and a per-capita GDP ahead of most of Europe and all of Latin America. Once largely semi-literate, its population is now among the best-educated in Asia.
To be sure, this enviable achievement was accomplished in an authoritarian fashion, but much of what Singapore has done must be considered “smart” by any reasonable accounting. Strategic investments taking advantage of its location between the Indian and Pacific Oceans have paid off handsomely: Today Singapore Airport is Asia’s fifth largest, and the city’s port ranks as the largest container entrepôt and is the second biggest, after Shanghai, in terms of cargo volume in the world.
All this has made Singapore a huge lure for foreign companies, with over 6000 multinationals, including 3600 regional headquarters, now located there. For foreign managers, engineers and scientists, largely English-speaking Singapore offers a pleasant and predictable environment, particularly compared with other Asian centers.
At least one recent survey by the World Bank’s International Finance Corporation rates Singapore No. 1 in the world for ease of doing business. Although its growth has been slowed by the recession, the city’s close ties to the resurging economies of Southeast Asia, China and India lead many forecasters to predict a strong recovery over the next year.
Hong Kong, yet another outpost of British imperialism, has also performed well. Last year the World Bank ranked the area No. 3 for ease of doing business, compared with No. 89 for the rest of China. As long as Chinese Communists allow wider freedoms in Hong Kong than in the mainland, the area should continue to take advantage of its basic assets, including the world’s third-largest container port, an excellent airport and a highly skilled entrepreneurial population.
The continuing appeal of Hong Kong was vindicated by the recent decision of Hong Kong Shanghai Bank Chief executive George Geoghegan to relocate there from London. As the center of the world economy continues to shift to Asia while Europe and America struggle, he is likely to find more company.
Not all the world’s “smart” cities are trading giants like Hong Kong and Singapore. They also include well-run metropolises, such as the city of Curitiba. The south Brazilian city is regarded as an innovator in everything from bus-based rapid transit, used by some 70% of residents, and its balanced, diverse economic development strategy.
With a population of 3.5 million, Curitiba demonstrates how to achieve the evolving Brazilian dream without the mass violence, transportation dysfunction and ubiquitous grinding poverty that plague many other Latin American metro areas. The city’s program of building “lighthouses”–essentially electronic libraries–for poorer residents has become a model for developing cities world wide. These are among the reasons Reader’s Digest recently named Curitiba the best place to live in Brazil.
Another similarly “smart” city in the developing world is Monterrey, Mexico, which has emerged from relative obscurity and turned itself into a major industrial and engineering center over the past few decades. The city of 3.5 million sits adjacent to the dynamic U.S.-Mexico border region and has 57 industrial parks specializing in everything from chemicals and cement to telecommunications and industrial machinery.
Over the last decade, the area has consistently grown at a faster rate than the rest of Mexico–or, for that matter, the United States. Monterrey and its surrounding state, Nuevo Leon, now boast per-capita GDP roughly twice that of the rest of Mexico.
Although hard-hit by the current recession, Monterrey seems poised for an eventual recovery. Dominated by powerful industrial families, the area has long been business-friendly. It has also become a major education center, with over 82 institutions of higher learning and 125,000 students, led by the Instituto Technologico de Monterey, considered by some Mexico’s equivalent of MIT or Cal Tech.
Of course, “smart” cities also exist in the advanced industrial world. Amsterdam, a longstanding financial and trading capital, is home to seven of the world’s top 500 companies, including Philips and ING. Relatively low corporate taxes and income taxes on foreign workers attract individuals and companies, one reason why, in 2008, the Netherlands was largest recipient of American investment in Europe. Amsterdam’s advantages include a well-educated, multilingual population and a lack of political corruption.
Amsterdam’s relatively small size–740,000 in the city and 1.2 million for the entire metropolitan area–belies its strategic location in the heart of Europe and proximity to the continent’s dominant port, Rotterdam. The city’s Schiphol airport, Europe’s third-busiest, is only 20 minutes from the center of Amsterdam, a mere jaunt compared with commutes to the major London or Paris airports. Schipol has also spawned a series of economically vibrant “edge cities” that appear like more transit-friendly versions of Houston or Orange County, Calif.
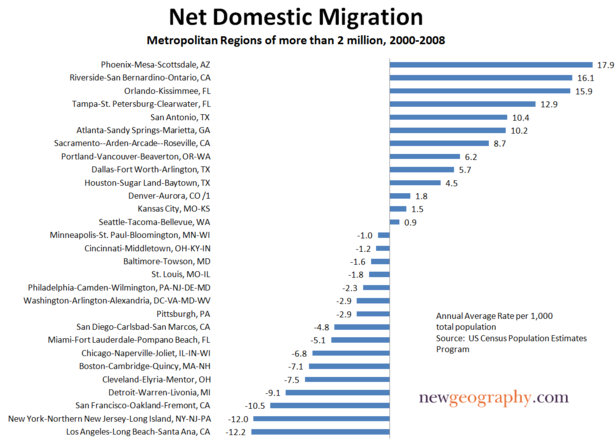
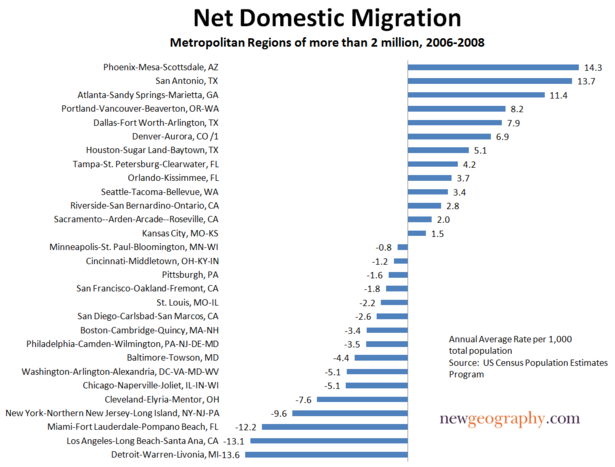
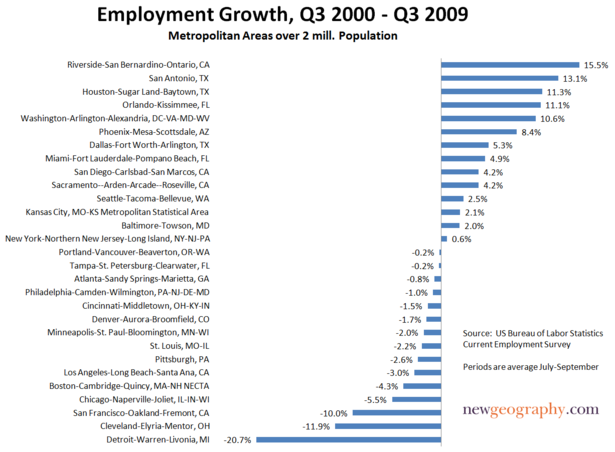
North America also has its share of smart cities. Although self-obsessed greens might see their policies as the key to the area’s success, Seattle’s growth really stems more from economic reality. In this sense, Seattle’s boom has a lot to do with luck–it’s the closest major U.S. port to the Asian Pacific, which has allowed it to foster growing trade with Asia.
Furthermore, Seattle’s proximity to Washington state’s vast hydropower generation resources–ironically the legacy of the pre-green era–assures access to affordable, stable electricity. The area also serves as a conduit for many of the exportable agricultural and industrial products produced both in the Pacific Northwest and in the vast, resource-rich northern Great Plains, linked to the region by highways and freight rails.
As North America’s economy shifts from import and consumption toward export and production, Seattle’s rise will be a model for other business-savvy cities in the West and South. Houston’s close tie to the Caribbean, as well as its dominant global energy industry, thriving industrial base, huge Texas Medical Center complex and first-rate airport, all work to its long-term advantage. Arguably the healthiest economically of America’s big cities, Houston is also investing in–not just talking about–its green future; last year it was the nation’s largest municipal purchaser of wind energy.
Another smart town poised to take advantage of an industrial expansion is Charleston, S.C., which has expanded its port and manufacturing base while preserving its lovely historic core. Once an industrial backwater, Charleston now seems set to emerge as a major aerospace center with a new Boeing 787 assembly plant, which will bring upward of 12,000 well-paying jobs to the region.
Further inland, Huntsville, Ala., has long had a “smart” core to its economy–a legacy of its critical role in the NASA ballistic missile program. Today the area’s traditional emphasis on aerospace has been joined by bold moves into such fields as biotechnology. Kiplinger recently ranked the area’s economy No. 1 in the nation.
With the likely rise in commodity prices over the next decade, Canada also seems likely to produce several successful cities. Perhaps the best positioned is Calgary, Alberta. Over the past two decades, the city’s share of corporate headquarters has doubled to 15%, the largest percentage of main offices per capita in Canada.
Although last year’s plunge in oil prices hit hard, rising demand for commodities in Asia should help revive the Albertan economy by next year.
In their press releases, all these cities make a point of bragging about being green and environmentally conscious. Yet they have demonstrated their “intelligence” in other ways–by exploiting their locations and resources to make savvy business and development decisions. At the end of the day, it will not be their clean air but their commercial prowess–as has been the case in history–that will sustain their success in the decades ahead.
List of the World’s Smartest Cities
- Singapore The 21st-century successor to 15th-century Venice, this once-impoverished island nation now boasts an income level comparable to the wealthiest Western countries, with a per-capita GDP ahead of most of Europe and Latin America. Singapore Airport is Asia’s fifth-largest, and the city’s port ranks as the largest container entrepot in the world. Over 6,000 multinational corporations, including 3,600 regional headquarters, are located there, and it was recently ranked No. 1 for ease of doing business.
- Hong Kong As the center of the world economy continues to shift from West to East, Hong Kong is certainly reaping the benefits. Hong Kong Shanghai Bank’s chief executive recently relocated there from London. Its per-capita GDP is ranked 15th in the world. The Heritage Foundation and The Wall Street Journal have ranked Hong Kong the freest economy in the world.
- Curitiba, Brazil This well-run metropolis in southern Brazil is famous for its rapid bus-based transit, used by 70% of its residents, and its balanced, diverse economic development strategy. The city’s program of building “lighthouses”–essentially electronic libraries–for poorer residents has become a model for developing cities worldwide. Environmental site Grist recently ranked Curitiba the third “greenest” city in the world.
- Monterrey, Mexico Over the past few decades Monterrey has emerged from relative obscurity into a major industrial and engineering center. The city of 3.5 million has 57 industrial parks, specializing in everything from chemicals and cement to telecommunications and industrial machinery. Monterrey and its surrounding state, Nuevo Leon, boast a per-capita GDP roughly twice that of the rest of Mexico.
- Amsterdam This longstanding financial and trading capital is home to seven of the world’s top 500 companies, including Philips and ING. Relatively low corporate taxes and income taxes on foreign workers attract companies and individuals. Amsterdam’s advantages include a well-educated, multilingual population and a lack of political corruption, as well as its location–in the heart of Europe, close to a major international airport and a short train trip to Rotterdam, the continent’s dominant port.
- Seattle, Wash. Seattle’s location close to the Pacific Ocean has nurtured trade with Asia, and its proximity to Washington state’s vast hydro-power generation station assures access to affordable, stable clean electricity. The area also serves as the conduit for many of the exportable agricultural and industrial products produced both in the Pacific Northwest and in the vast, resource-rich northern Great Plains, closely linked to the region by highways and freight trains.
- Houston, Texas Houston’s close tie to the Caribbean, as well as its dominant global energy industry, thriving industrial base, huge Texas Medical Center complex and first-rate airport all work to its long-term advantage. Arguably the big city in the U.S. with the healthiest economy, Houston is also investing in a “green” future; last year it was the nation’s largest municipal purchaser of wind energy.
- Charleston, S.C. Charleston has expanded its port and manufacturing base while preserving its lovely historic core. Once an industrial backwater, Charleston now seems poised to emerge as a major aerospace center, with the location of a new Boeing 787 assembly plant there, which will bring upward of 12,000 well-paying jobs to the region.
- Huntsville, Ala. This southern city has long had a “smart” core to its economy, a legacy of its critical role in the NASA ballistic missile program. Today the area’s traditional emphasis on aerospace has been joined by bold moves into such fields as biotechnology. Kiplinger recently ranked the area’s economy No. 1 in the nation.
- Calgary, Alberta With the likely rise in commodity prices over the next decade, Canada seems likely to produce several successful cities. Over the past two decades, Calgary’s share of corporate headquarters has doubled to 15%, the largest percentage of main offices per capita in Canada. Although the plunge in oil prices hit hard, rising demand for commodities in Asia should help revive the Albertan economy by next year.
This article originally appeared at Forbes.com.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University. He is author of The City: A Global History . His next book, The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050
. His next book, The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050 , will be published by Penguin Press early next year.
, will be published by Penguin Press early next year.