Statistics Canada’s newly released National Household Survey indicates changes in the distribution of median household incomes among the provinces and territories. The new data is for 2010, and indicates that an increase of 13.9 percent per household at the national level from the 2005 data collected in the 2006 census.
The big story, however, is the progress in parts of Canada that have grown used to laggard economic performance. In 2005, few would have expected the progress made in the provinces of Saskatchewan and Newfoundland & Labrador. In both cases, the resource boom had much to do with the turnaround.
Gains in Saskatchewan and the Prairies
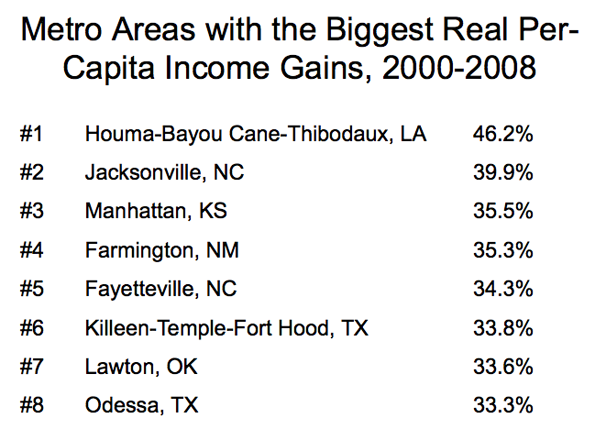
Saskatchewan’s median household income grew 32.1 percent, out-distancing perennial champion Alberta and emerging Newfoundland & Labrador by nearly a third (Figure). Alberta’s income was up 22.9 percent, while Newfoundland & Labrador experienced a nearly as great 22.7 percent increase. Saskatchewan had trailed British Columbia by more than 10 percent five years before, but had edged ahead by 2010. Saskatchewan’s income level now leads all of the provinces except Alberta and Ontario.
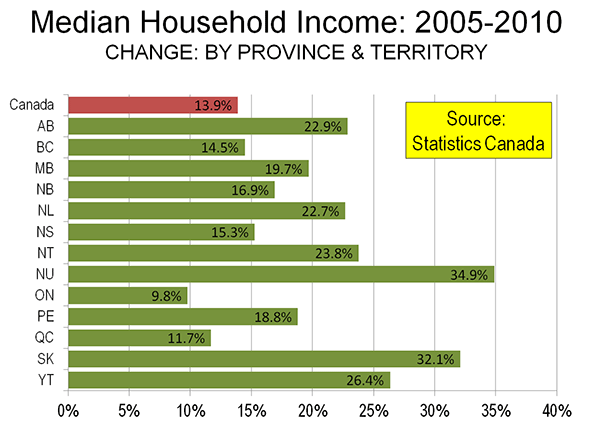
All three of the Prairie Provinces did well. In addition to Saskatchewan and Alberta, household income in Manitoba grew at a 20 percent, stronger than all provinces outside the prairies except for Newfoundland & Labrador.
A New Day in Newfoundland and Labrador
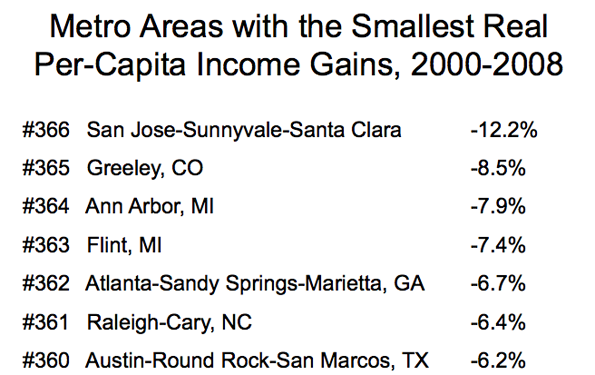
While Saskatchewan has experienced prosperity from time to time in its history, the same is not so true in Newfoundland and Labrador. In fact, in 1933, the government of Newfoundland (as it was then known) voted itself out of existence as a Dominion of the British Empire because of its serious financial difficulties. Effectively, the Dominion was relegated to the status of a British crown colony (like former Hong Kong). Newfoundland joined Canada as the 10th province in 1949. With that, representative government was restored, but Newfoundland always lagged behind (generally along with the Maritime provinces of New Brunswick, Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island). In 2005, Newfoundland and Labrador ranked 10th out of the 10 provinces in median household income. By 2010, the ranking had improved to 7th.
The Prosperous Territories
The greatest income growth (35 percent) was in the territory of Nunavut, which was created by carving out the eastern portion of the Northwest Territories in 1999. Nunavut covers a land area about 1.3 times that of Alaska, but has only 30,000 residents (about the same as live in a square kilometer of Manhattan or Paris). The Yukon experienced a 26 percent increase, while the Northwest Territories had a 24 percent increase. The Yukon and the Northwest Territories had stronger income growth than all of the provinces, except Saskatchewan.
The Old Dynamos Trail
Meanwhile, the economic dynamo of the nation, Ontario experienced household income growth of less than 10 percent, nearly a third less than the national average, and less than one-third of Saskatchewan. Ontario is home to more than one-third of the national population. British Columbia, which has historically experienced strong economic growth, could muster only slightly above average household income growth (14.4 percent compared to the national 13.9 percent).