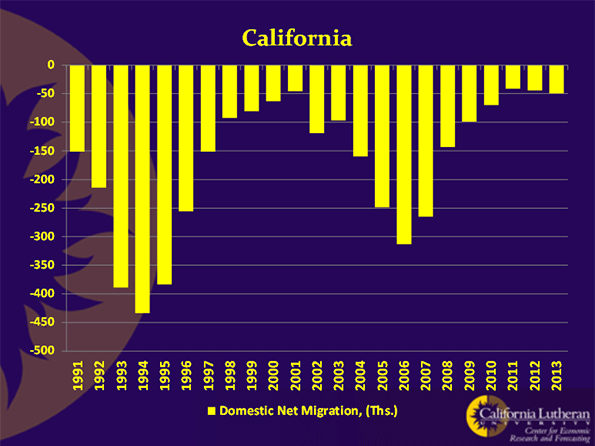
The British Talmudic scholar Abraham Cohen noted that, throughout history, children were thought of as “a precious loan from God to be guarded with loving and fateful care.” Yet, increasingly and, particularly, here in Southern California, we are rejecting this loan, and abandoning our role as parents.
This, of course, is a process seen around the high-income world, and even in some developing countries. But, here in America, some regions are moving in this post-familial direction faster than others, and, sadly, Southern California, for the most part, is leading the trend.
Historically, Southern California, as a lure first for domestic migrants and, later, for foreign immigrants, has been an incubator of families. As recently as 2000, the proportion of population ages 5-14 in Los Angeles and Orange counties stood at 16 percent, the sixth-highest level among the nation’s 52 largest metropolitan areas. Thirteen years later, that proportion had dropped to 12.8 percent, ranking 33rd. The area experienced a 20 percent drop in its share of youngsters, the largest decline among U.S. metro areas.
Of course, not everywhere in Southern California has experienced such a precipitous shift. The Inland Empire, which stands apart in census data, remains a relative bastion of familialism, with 15.3 percent of the population between ages 5-14. Yet even the Inland Empire is slipping somewhat, from having the highest percentage of children to a ranking of fourth, and experiencing a 17 percent decline in children’s share of the population, the fourth-largest percentage drop in the nation.
If we try to focus even more closely, the patterns of decline, and the few bright spots, become more clear. Using 2010 U.S. Census data for specific regions (more up-to-date numbers are not yet available at the local level), it’s clear where much of this loss is concentrated.
The most precipitous declines have been in the inner city, notably Central Los Angeles, which experienced a net loss of 87,000 youngsters from 2000-10. Although their rate of loss was not as severe as in the core, other, once family-rich parts of the region – the San Fernando and San Gabriel valleys, Santa Ana/Anaheim, Long Beach and Whittier-Southeast Los Angeles County – all posted double-digit percentage drops in children.
Only a few areas of Southern California experienced growth in the number of children. Much of the growth was in the vast, outer suburbs and exurbs – places such as the Victor Valley, San Bernardino, Perris-Temecula, Santa Clarita-Antelope Valley and Riverside-Moreno Valley, as well as decidedly more upscale Irvine-South Orange County.
In a sense, these numbers tell several stories. To be sure, high housing prices seem to have a direct impact on family formation, pushing people further out to the periphery or, in some cases, out of the region entirely. Overall, according to recent analysis of census data, high-cost areas tend to repel families; almost all the most expensive areas in the country, such as the Bay Area, New York and Boston, have all experienced strong drops in numbers of children.
This has resulted, as demographer Ali Modarres has demonstrated, in a gradual emptying out of families from the poor, but still expensive, inner core of Los Angeles. These areas tend to be heavily immigrant, and once were seen as the generators of a new generation of Angelenos. Now, however, as Modarres suggests, these areas are also “getting old,” with grandparents remaining but the new generation headed to other locales within or beyond the region. This process, he notes, has been accelerated by a decline in immigration to the region, particularly among Latinos, who long settled in these areas.
Housing prices are not the only determinant. Prices are even higher in the Bay Area, which has seen a falling number of children, but not as severe as in Los Angeles.
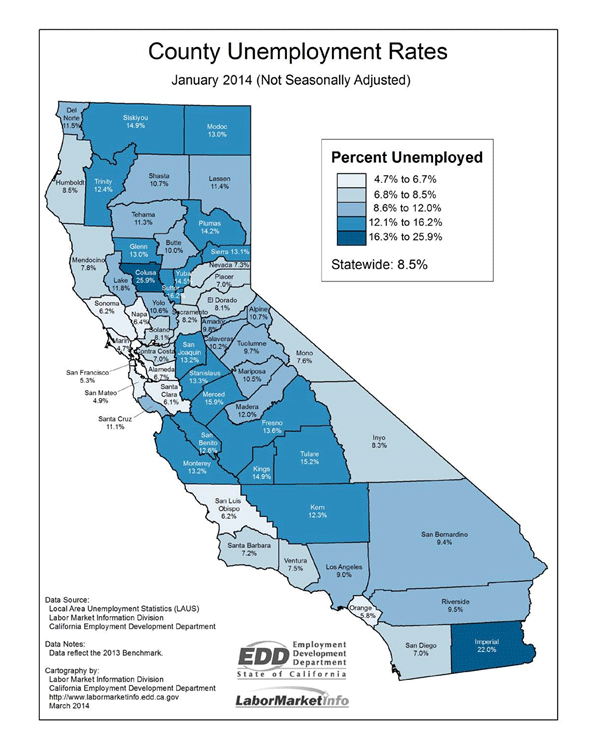
One likely explanation is the Southland’s relatively weak economy, which continues to create jobs sluggishly, and an unemployment rate, particularly in Los Angeles County, well above the state and national averages. High prices repel families, but this is particularly true in a region generating relatively little economic opportunity.
There are other factors, particularly for middle-class families, who tend to have more choice where to locate. One seems to be education. For example, Irvine-South Orange County does well in this regard, but its housing costs are beyond the budgets of most other than upper-middle-income households, which tend to be Asian or non-Hispanic white. Irvine has a national reputation for excellent schools, a major lure to families who wish to avoid the expense of private education.
For some in Southern California, particularly those pushing high-density and rental housing, these shifts may be considered a boon. After all, households with children, even more than most people, tend to prefer single-family homes and tend to embrace the notion of ownership. Single people are more likely to choose – by preference or because of cost – rental properties. The vision of Southern California as primarily dominated by high-density rentals correlates with requirements of state law and plans of the Southern California Association of Governments.
At the same time, the economic languor of this region may make many of these bold designs untenable. People without decent – or any – employment do not make ideal tenants any more than they constitute potential homeowners. Given the high costs of high-density construction, this suggests that many units will be rentable only by aging former homeowners or by several families sharing a unit.
Sadly, the decline in homeownership and the single-family housing market may contribute long term to the region’s continued relative economic eclipse. Single-family home construction is among the most reliable contributors to local economic growth and job creation. In contrast, each multifamily unit constructed contributes 60 percent less to the GDP.
More important still, the loss of families presages a future that we can already see in many European and east Asian countries. There is the development of an aging, inner core, made up largely of retirees, both poor and affluent, sprinkled among areas dominated by young, mostly childless, people. Over time, this leads to a less-dynamic region, as the workforce and consumer base shrinks, and politics shift emphasis from economic growth to redistribution. Meanwhile, many of the poor and working-class families are forced out toward the furthest periphery, often far from employment and relatives.
Can this process be reversed? Certainly a stronger economy, with more middle-wage jobs, might encourage people to have families, and give them the incentive, as well as the wherewithal, to buy a house. It would provide parents, and potential parents, with the notion that they can create a new generation with reasonable economic prospects.
The other key factor is a radical reordering of our education systems. It is clear from the data that areas with good schools, such as Irvine, continue to attract families, even at very high housing price points. If middle-class families feel they can access a decent public education in the older, settled areas, such as the San Fernando Valley, L.A.’s Westside or North Orange County, they might be more willing to put down roots in these places, which would help create the greater stability generally associated with families, especially homeowners.
Sadly, political leadership in most of Southern California and Sacramento seems blissfully unaware of these trends, or the potential danger to the area’s economic, as well as its demographic, vitality. Perhaps a region dominated by aging populations, and fewer families, by nature tends to look backward and neglect the kind of infrastructure investment, including in education, that families and business require.
A resurgent hipster economy may not require much economic growth, or changes in the political system, but the region’s families need a thorough reversal in course if this region hopes to retain its appeal as an incubator of future generations.
This piece originally appeared at The Orange County Register.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and Distinguished Presidential Fellow in Urban Futures at Chapman University, and a member of the editorial board of the Orange County Register. His newest book, The New Class Conflict is now available at Amazon and Telos Press. He is author of The City: A Global History and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. His most recent study, The Rise of Postfamilialism, has been widely discussed and distributed internationally. He lives in Los Angeles, CA.
Baby photo by Bigstock.