For most of recent history, the world has worried about the curse of overpopulation. But in many countries, the problem may soon be too few people, and of those, too many old ones. In 1995 only one country, Italy, had more people over 65 than under 15; today there are 30 and by 2020 that number will hit 35. Demographers estimate that global population growth will end this century.
Rapid aging is already reshaping the politics and economies of many of the most important high-income countries. The demands of older voters are shifting the political paradigm in many places, including the United States, at least temporarily to the right. More importantly, aging populations, with fewer young workers and families, threaten weaker economic growth, as both labor and consumption begin to decline.
We took a look at the 56 countries with populations over 20 million people, nine of which are already in demographic decline. The impact of population decline will worsen over time, particularly as the present generation now in their 50s and 60s retires, begins drawing pensions and other government support.
Europe: Homeland of Demographic Decline
Heading up our list of slowly dissipating large countries is the Ukraine, a country chewed at its edges by its aggressive Russian neighbor. According to U.N. projections, Ukraine’s population will fall 22% by 2050. Eastern and Southern Europe are home to several important downsizing countries including Poland (off 14% by 2050), the Russian Federation (-10.4%), Italy (-5.5%) and Spain (-2.8%). The population of the EU is expected to peak by 2050 and then gradually decline, suggesting a dim future for that body even if it holds together.
The most important EU country, Germany, has endured demographic decline for over a generation. Germany’s population is forecast to drop 7.7% by 2050, though this projection has not been adjusted to account for the recent immigration surge. The main problem is the very low fertility rate of the EU’s superpower, which according to United Nations data was 1.4 between 2010 and 2015. It takes a fertility rate of 2.1% to replace your own population so we can expect Germany to shrink as well as get very old.
Nor can Europe expect much help from its smaller countries. Although too small to reach our 20 million person threshold, many of Europe’s tinier “frontier” countries have abysmal fertility rates. Among the 10 smaller countries with the greatest population declines, all are in Europe, and outside Western Europe, with Bulgaria’s population expected to shrink 27% by 2050 and Romania’s 22%. Each of these have below replacement rate fertility. Things are not that much better in Western Europe, where fertility rates are also below replacement rates, but not quite so low. Long-term, the only option for Europe may be to allow more immigration, particularly from Africa and the Middle East, although this may be impossible due to growing political resistance to immigration.
Demographic Decline: The Asian Edition
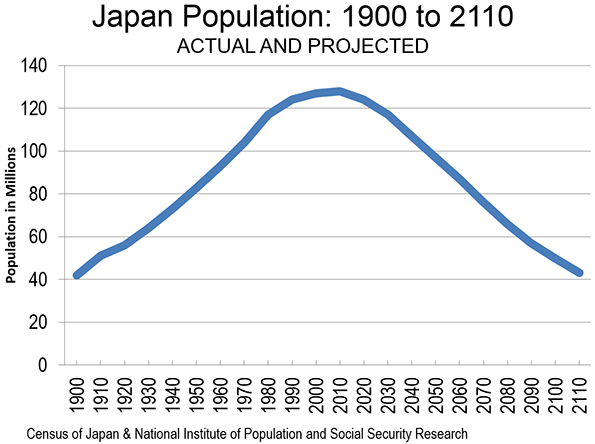
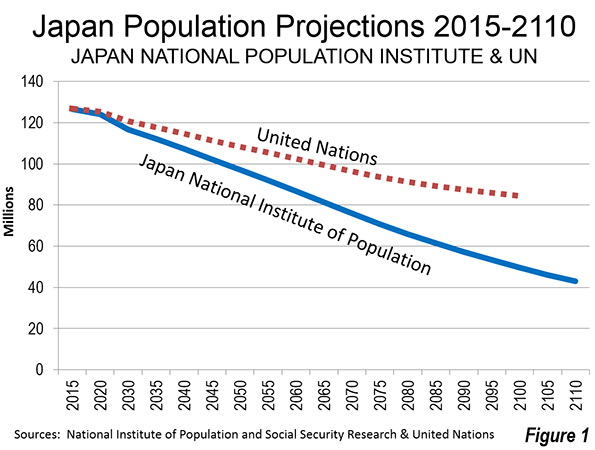
If this were just a European disease, it would not prove such a challenge to the economic future. Europe is gradually diminishing in global importance. The big story in demographic trends is in Asia, which has driven global economic growth for the past generation. The decline of Japan’s population is perhaps best known; the great island nation, still the world’s third largest economy, is expected to see its population fall 15% by 2050, the second steepest decline after Ukraine, and get much older. By 2030, according to the United Nations, Japan will have more people over 80 than under 15.
But the biggest hit on the world economy from the new demographics will come from China, the planet’s second largest economy, and the most dynamic.
Until a generation ago, overpopulation threatened China’s future, as it still does some developing countries. Today the estimates of the country’s fertility rate run from 1.2 to 1.6, both well below the 2.1 replacement rate. By 2050 China’s population will shrink 2.5%, a loss of 28 million people. By then China’s population will have a demographic look similar to ultra-old Japan’s today — but without the affluence of its Asian neighbor.
Other Asian countries have similar problems. Thailand ranks as the fifth most demographically challenged, with a projected population loss of 8%. The population of Sri Lanka, just across Adam’s Bridge from still fast-growing India, is projected to increase only 0.6%.
Also going into a demographic stall is South Korea, another country which a generation ago worried about its expanding population. With its fertility rate well below replacement (1.3), the country will essentially stagnate over the next 35 years, and will becoming one of the most elderly nations on earth.
Full List: The Countries Shrinking The Fastest
Smaller Singapore is an anomaly. The city-state has a rock-bottom fertility rate of 1.2, but projects a population increase of 20% by 2050 due to its liberal and vigorously debated immigration policies.
Economic Consequences
Most world leaders are fixated on the unpredictable new administration in Washington in the short term, but they might do better to look at the more certain long-term impacts of diminishing populations on the world’s most important economies. Economists, including John Maynard Keynes, have connected low birth rates to economic declines. On the “devil” of overpopulation, Keynes wrote, “I only wish to warn you that the chaining up of the one devil may, if we are careless, only serve to loose another still fiercer and more intractable.”
It is already fairly clear that lower birthrates and increased percentages of aged people have begun to slow economic growth in much of the high-income world, and can be expected to do the same in long ascendant countries such as China and South Korea. Economists estimate that China’s elderly population will increase 60% by 2020, even as the working-age population decreases by nearly 35%. This demographic decline, stems from the one-child policy as well as the higher costs and smaller homes that accompany urbanization, notes the American Enterprise Institute’s Nicholas Eberstadt. China’s annual projected GDP growth rate will likely decline from an official 7.2% in 2013 to a maximum of 6% by 2020.
There are several reasons these demographic shifts portend economic decline. First, a lack of young labor tends to drive up wages, sparking the movement of jobs to other places. This first happened in northern Europe and Japan will increasingly occur now in Korea, Taiwan, and even China. It also lowers the rate of innovation, notes economist Gary Becker, since change tends to come from younger workers and entrepreneurs. Japan’s long economic slowdown reflects, in part, the fact that its labor force has been declining since the 1990s and will be fully a third smaller by 2035.
The second problem has to do with the percentage of retirees compared to active working people. In the past growing societies had many more people in the workforce than retirees. But now in societies such as Japan and Germany that ratio has declined. In 1990, there were 4.7 working age Germans per over 65 person. By 2050, this number is projected to decline to 1.7. In Japan the ratios are worse, dropping more than one-half, from 5.8 in 1990 to 2.3 today and 1.4 in 2050. China, Korea and other East Asian countries, many without well-developed retirement systems, face similar challenges.
Finally, there is the issue of consumer markets. Aging populations tend to buy less than younger ones, particularly families. One reason countries like Japan and Germany can’t reignite economic growth is their slowing consumption of goods. This challenge will become all the more greater as China, the emerging economic superpower, also slows its consumption. The future of demand, critical to developing countries, could be deeply constrained.
What about the USA?
To a remarkable extent, the United States has avoided these pressing demographic issues. The U.N. has the U.S. tied with Canada for the fastest projected population growth rate of any developed country: a 21% expansion by 2050. Yet this forecast could prove inaccurate.
One threat stems from millennials who, even with an improved economy, have not started families and had children at anything close to historical rates. Today the U.S. fertility rate has dropped to 1.9 from 2.0 before the Great Recession; population growth is now lower than at any time since the Depression. This places us below replacement level for the next generation. Projections for the next decade show a stagnant, and then falling number of high school graduates, something that should concern both employers and colleges. The United States’ high projected population growth rate, like that of Singapore, is entirely dependent upon maintaining high rates of immigration.
But even before the election of Donald Trump, who is hell-bent on cracking down on at least undocumented immigration, total immigration to the United States has been slowing. At the same time the fertility rates of some immigrant groups, notably Latinos, have been dropping rapidly and approaching those of other Americans. This is despite the fact that as many as 40% of women would like to have more children; they simply lack the adequate housing, economic wherewithal and spousal support to make it happen.
In the coming decades, the countries that can maintain an at least somewhat reasonable population growth rate, and enough younger people, will likely do best. To a large extent, it’s too late for that in much of Europe and East Asia. For countries like the United States, Canada and Australia, with among the most liberal immigration policies and large landmasses, the prospects may be far better. However, we also need native-born youngsters to launch, get married and start creating the next generation of Americans.
This piece originally appeared at Forbes.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com. He is the Roger Hobbs Distinguished Fellow in Urban Studies at Chapman University and executive director of the Houston-based Center for Opportunity Urbanism. His newest book, The Human City: Urbanism for the rest of us, was published in April by Agate. He is also author of The New Class Conflict, The City: A Global History, and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. He lives in Orange County, CA.
Photo: Ahmet Demirel [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons