A couple weeks ago I wrote some thoughts after a recent visit to Las Vegas. Most of what I wrote about concerned the Strip and downtown areas of the city, without question the two most recognizable and most frequently visited parts of the region. But in a rapidly growing region of nearly 2.2 million people (the Las Vegas Valley held only 273,000 residents in 1970, meaning it has increased its population by 8 times since then), clearly there’s much more to the region than its most iconic and visible parts. Here I’ll offer some thoughts on the broader region, its built environment, its economy, and thoughts on its future.
First, for those tl;dr readers who won’t click through to read Part I, here’s a quick summary of it:
• The Strip and Las Vegas are two entirely different entities.
Again, as someone who’s “part urbanist, part sociologist, and part economist,” I offer some observations and thoughts on the rest of the city and region.
The balance of the city and region consists of unremarkable suburbia. This is probably evident to anyone who puts any amount of thought into it, but it does bear repeating. Step away from the Strip and downtown, and Las Vegas’s built environment is amazingly consistent: according to the U.S. Census Bureau American Community Survey in 2015, the metro area is about 60% single family detached homes, with about 4,000-6,000 people per square mile throughout. There’s no sudden or even slight gradation in density as one commonly finds in many eastern cities; the city quickly establishes its suburban character and spits it out relentlessly. And, I’ve been struck on this visit and previous ones at how similar Vegas looks to suburbia in other places. Yes, there are newer, upscale areas that stand out (Summerlin comes to mind), but if you replace Vegas’s palm trees with oaks and elms, it looks a lot like suburbia anywhere else in America, except with Spanish tile roofs. Similarly…
Nothing in the region is old; the region will have to learn the art and skills of redevelopment. Fifteen years ago when I did some consulting work in Las Vegas, I thought it was weird when city officials referred to West Las Vegas, just northwest of downtown, as “historic”. Most of the homes and businesses there were built in the ’50s and through the ’70s, and in my mind they were the kind of structures that were just beginning to establish some character. But when the median year of structure built in the region is 1995 (the same for Chicago’s metro is 1967), you simply won’t find the pre-WWII type of development that is called historic in other places. There will come a time when the structures of the Las Vegas Valley will be viewed as obsolete and inconsistent with modern living (whatever that is), and the region will have to undergo one of the more difficult transitions for municipalities — shifting from easy greenfield development to complex redevelopment.
Low wage and low skill jobs proliferate in the region. Like the unremarkable nature of the suburban pattern, here’s another conventional observation that bears repeating. As one would expect, the accommodations/food services employment sector dominates in Las Vegas — nearly one-third of all Las Vegas workers work in hospitality. Those have traditionally been low-paying jobs, and that’s true of the region today. Overall, 44% of Vegas workers earn less than $40,000 a year. Contrast that with Austin, a similarly-sized and similarly-fast-growth metro, where only 9% of workers are employed in accommodations/food services, and just 34% of workers earn less than $40,000 a year (and consider that Austin is a college town that has many recent grads, possibly pushing incomes downward). My concern for Vegas in this regard is that there is growing research that suggests that the kind of work automation that decimated much of the Rust Belt’s manufacturing jobs may now enter a phase that targets food services, administration and office support, sales and even retail jobs — precisely the kinds of jobs that many new Las Vegas residents moved there to occupy. Las Vegas workers could be quite vulnerable to the kinds of challenges that reshaped the Rust Belt.
The Las Vegas Valley is nearing its physical limits. According to Wikipedia, the Las Vegas Valley is a 600 sq. mi. basin surrounded on all sides by mountains. I don’t know the precise delineations between flat and inclined topography, but a look at Google Earth tells me the region is near its limit:
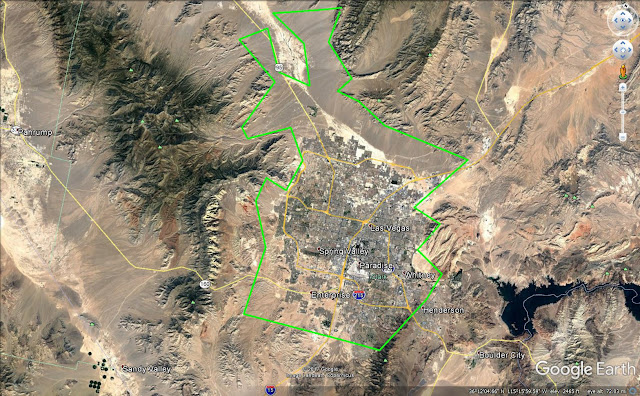
I could be wrong, but it looks as if Vegas has available land to the north and southwest, and the Valley might be approaching 90% developed. It could be that the region hits the wall (literally) within the next 10 years. What will that mean for a region that is as low-density suburban as this one? Will the Valley’s communities have the ability to shift their focus inward? Time will tell.
What happens to the region if tourism… changes? Wikipedia’s Atlantic City page has a good explanation for the decline of tourism there after World War II. It connects its decline with the car; prior to the war, people generally traveled to Atlantic City by train and stayed for a week or two. Cars made people more mobile and they made shorter visits. Suburbanization and its creature comforts, like backyards and air conditioning, also took visitors away from AC. The final nail in the coffin was affordable jet service, opening up vacation spots like Miami, Havana, and the Bahamas (and Vegas) in the 50’s and onward. I don’t know what challenge is out there for Vegas now, but what will be crucial to the region’s survival is how it responds.
What impact will climate change have on a desert resort city? When flying into Las Vegas I couldn’t help but notice the low level of Lake Mead, just southeast of the city. It was clear from the air; bleached rock that had once been under water now exposed. Las Vegas is blessed to have one of the largest reservoirs in the nation at its back door, but could continued drought and increased demand for water undermine everything? The Strip’s casinos tout themselves as leaders in water conservation, but whether their efforts will be enough as conditions worsen is an open question.
Las Vegas is truly a unique place. It’s a place that seems to serve a certain time and space, and is concerned about now more than its future. But I’m sure if the region squints its eyes and looks, it will see the future is getting closer. It will need to figure out how it will be sustainable as that future approaches.
This piece originally appeared on The Corner Side Yard.
Pete Saunders is a Detroit native who has worked as a public and private sector urban planner in the Chicago area for more than twenty years. He is also the author of “The Corner Side Yard,” an urban planning blog that focuses on the redevelopment and revitalization of Rust Belt cities.
Photo by Stan Shebs [GFDL, CC BY-SA 3.0 or CC BY-SA 2.5], via Wikimedia Commons