The UK Government’s Department for Communities and Local Government (DCLG) announced that there were only 127,780 new housing completions last year in Britain. British house building activity is down to levels of after the First World War, when reliable industrial records began, and still falling. In 1921 the British population was nearly back up to 43 million following the slaughter of the First World War. In 2011 the population of England, Wales, and Scotland is approaching 61 million people. By 2031 the British population is expected to be closer to 70 million. With such existing unmet and growing demand for new housing the DCLG, the Government department that runs the Planning System should be busy finding ways to allow developers to build.
Many feared that the National Planning Policy Framework (NPPF), prepared by the DCLG for an expected release in January 2012 would be a developer’s charter. We wish it was a developer’s charter! The NPPF continues planning policies, supported by all Parliamentary political parties, which continue to frustrate volume housebuilding. Developers have to prove that their proposals for house building are not merely about building useful homes at a profit, but are “sustainable development” when measured against disputable social and environmental criteria. No developer is free to build on their own land without first having to obtain planning approval from an array of third party interests all insisting on their interpretation of the moral idealism of sustainability.
This makes the NPPF an anti-development charter for all those who oppose house building and population growth. Anyone can claim that more house building and more households are unsustainable in their area, in the effort to stop a project which they don’t approve of.
The NPPF will do nothing to challenge the power of contemporary anti-development campaigners, who are well known. Anne Power, Lord Richard Rogers and other members of New Labour’s Urban Task Force (UTF) have correctly identified themselves as allied to the “Hands off Our Land” campaign run by The Daily Telegraph, the Conservative supporting newspaper. The UTF favors a continuing commitment to ‘… reclaiming brownfield sites and re-densifying cities.’ To build only on previously developed land is the green ideal of the UTF and the “Hands off Our Land” campaign.
We all know where these policies lead. Not to a golden age of regeneration for all, but to lucrative property investment for those with access to sufficient capital and the right connections to steer themselves through the planning system to obtain approvals. The volume of Greenfield land developed declined dramatically under New Labour. The present Conservative led Coalition Government continues the practice of obstructing development on Greenfield land.
Between 2000 and 2006 the total area of land built on for new housing fell by 23%, with a 42% fall in the annual amount of Greenfield land used. In 2010 76% of all housing was built on previously developed Brownfield land, a slight decrease from the 80% in 2009. Only 2% of housing was built on the Green Belts around major cities and towns. The Green Belt in England covers 13% of the land, or twice the area already developed for housing. Small wonder that the price of the shrinking supply of land with a prospect of being approved for sustainable development remains inflated.
House building was only increased from the low point of 2001 by increasing the density of development in the cities. Average densities rose from 25 dwellings per hectare (dph) in 2000, to 43 dph by 2010. In London the average density for new housing is much higher, at 115 dph in 2010.
Densification policies considered sustainable have meant that the majority of the working British public can no longer buy a new house with a garden, in ways that previous generations may have taken for granted. Instead the plan has been to squeeze more new households into less space. UTF supporters and the DCLG imagined they were regenerating cities and saving the planet for all of society. Like traditional Conservatives they mean to keep developers and the population off Britain’s ample supply of otherwise redundant farmland.
The Daily Telegraph’s campaign, best articulated by the conservative anti-growth philosopher Roger Scruton, is clearly the flip side of the UTF’s densification argument. He is happy as long as the population is kept away from the countryside he loves. ‘Thank God for obstacles to economic growth,’ says Scruton.
Scruton speaks for the comfortable who already enjoy plenty of space. The Daily Telegraph’s campaign is ultimately concerned that existing housing markets are protected, sustained through the division between Town and Country, and moralised as a concern for environment and heritage. New Labour supporters are more likely to read The Guardian, but its more middle-class readership finds nothing to object to in The Daily Telegraph’s campaign, in order to restrict the “sprawl” of suburbia and halt the imagined damage this will do to the environment and urban communities. The Guardian’s readership formed the bed-rock of New Labour’s support, and back Next Labour. The working class may have deserted Labour, but is depoliticized and passive. The Guardian and The Daily Telegraph – still supposed by many to be at opposite ends of the old-fashioned and defunct ideological spectrum of Left and Right – prove closer than either cares to think.
Labour Members of Parliament have traditionally feared the “flight to the suburbs” lest they lose voters and the associated tax revenue. The planning system has proved very effective in maintaining the political geography of Britain. Labour politicians negotiate their political dependency on urban containment with a Red-Green stance in urban areas, without threatening the Blue-Green interests of those who want to keep development out of the countryside. All depend on the denial of development rights that date from the 1947 Town and Country Planning Act, and which the NPPF reinforces.
Meanwhile working class families are squeezed into what little Twentieth Century suburbia is still affordable, competing unsuccessfully with the more affluent for ownership of this increasingly scarce and valued commodity. What new housing is built is at higher density, usually on the least attractive sites. That is land previously occupied by factories, old infrastructure, and utilities, or by council housing estates re-developed at higher densities. Yet even these unpopular sites enter the inflated British housing market, sustained through a chronic lack of house building.
The working class is caught in a political crusher made manifest through the planning system. The Red-Greens, who may imagine themselves on a new Left, gentrify towns and cities with “sustainable redevelopment”, and the Blue-Greens, who persist with being on the Right, protect their landscape for their exclusive enjoyment. Meanwhile the majority of home owners have come to depend on the inflated and unaffordable housing market. New Labour needed this house price inflation to allow the owner occupying majority to supplement inadequate wages by withdrawing equity from their homes. So does the Coalition. Deliberate or not, The Daily Telegraph’s commitment to building fewer new homes will stabilise what we have called the Housing Trilemma.
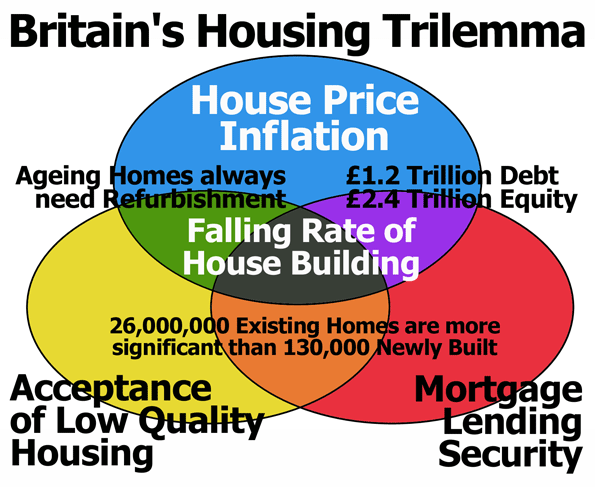
Our current predicament may be thought of as a Trilemma, in which house price inflation supports burdensome mortgage lending and private debt, while households in the owner occupied sector accept low quality housing conditions. High rents shadow private sector housing costs, and private rental housing quality is often of the lowest quality. Many in Britain, including the majority of the home owning middle class, are dependent on the Housing Trilemma remaining stable.
The planning system serves well in protecting the interests of existing home owners. Behind the NPPF’s moral idealism of sustainability, the immediate instrumental objective is to restrict new housing supply to avoid destabilising housing markets. Appearing as a moral mission to save the planet from developers, the NPPF and the denial of development rights sustains the Housing Trilemma. Debt is secured, but housing remains unaffordable, quality low, and house building activity is at an all time industrial low. This is not a conspiracy. It is a predicament.
When Britain’s elites talk about wanting to revive economic growth, they don’t mean a massive surge in new house building or an expansion of infrastructure. What they have in mind is a revival of financial services in The City, subject to uncertainties in the fragmenting Euro Zone, and the maintenance of high housing prices in the hope of more inflation to come. Meanwhile the countryside is kept pristine for the few who can afford access to it as a weekend retreat for the wealthy, including the pro-urban intelligentsia, in all their Red-Green-Blue moral plumage.
The Coalition could have challenged the Housing Trilemma. Instead they have reinforced it.
The result is predictable. Planning applications are falling in number and ambition. Only 25,000 new homes were approved in the second quarter of 2011 compared to 32,000 in the second quarter of 2010. This will be read by The Daily Telegraph campaign members as “proof” that there is no demand for development, inverting the causality. Money is being made out of an environmentally sanctioned scarcity rather than through increased productivity and innovation in a sector like house building and the wider construction industry. Britain’s already backward construction industry is further retarded, and it is becoming commonplace for social elites, and not only crazed nationalists, to blame immigration for housing shortages.
Britain’s economy needs growth, but is unlikely to get it from the house building sector. Britain too needs a dose of political reality while the pro-urban intelligentsia preen their green morality.
The Coalition cannot afford to confront the political problem of the Housing Trilemma if it is to sustain its fragile political base. Increasingly, only the elderly bother to vote and this equity rich group will be mostly satisfied with modest house price inflation as a hedge against general inflation, while savings in banks attract little return. Meanwhile an influential propertied elite still enjoys sustained house price inflation at the top of the market. They are anxious that environmental and heritage designations operate to enhance the exclusivity and enjoyment of their investments. The unelected charities, agencies and Non-Governmental Organisations that were aligned against the draft of the NPPF in July 2011 represent these elite interests. They may now back the redrafted 2012 NPPF with all its demands for sustainability. Their “Hands off Our Land” campaign has worked for them.
The NPPF means that house builders face a future in which building on Greenfield land is effectively considered an eco-crime. Only those who can develop Town Centre sites, perhaps as rental housing, or as luxury homes for the equity rich will thrive. Basically Britain is no longer building homes with gardens for sale to young working families on modest incomes.
If you are in a young working family, or hope to start one, the question is: What are you going to do about the housing predicament you and your friends face?
We have to face a stark reality. Sadly, there is no contemporary habit of young working families organising to demand housing collectively. Meanwhile the 2011 to 2012 production figures look set to be lower again, and the developmental uncertainties about to be articulated in a redraft of the NPPF in pursuit of sustainable development will further the decline in production.
Anticipating this feature of Britain’s ratcheting austerity does not make for a Happy New Year. Much depends on what the people of Britain, and particularly the young, do to demand that family houses are built at modest prices in places they want to live together. At present Britain fears a developer’s charter, even though the National Planning Policy Framework is nothing of the sort. Parliament might yet instead be in fear of people demanding cheap land on which to build a better place to live.
James Stevens is Strategic Planner at the Home Builders Federation, www.hbf.co.uk. Email him at james.stevens@hbf.co.uk. The views expressed are his own and not those of Home Builders Federation. Ian Abley is a site architect and runs the pro-development website audacity, www.audacity.org. Email him at abley@audacity.org. Together they organise the 250 New Towns Club, www.audacity.org/250-New-Towns-index.htm.