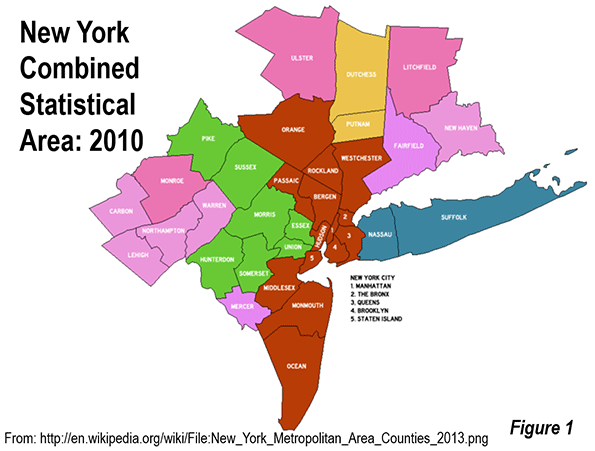
The New York commuter shed (combined statistical area) is the largest in the United States, with 23.6 million residents spread across 13,900 square miles in New York, New Jersey, Connecticut and Pennsylvania. It includes 35 counties, in eight metropolitan areas, including New York (NY-NJ-PA), Allentown-Bethlehem (PA-NJ), Bridgeport-Stamford (CT), East Stroudsburg (PA), Kingston (NY), New Haven (CT), Torrington (CT) and Trenton (NJ). The criteria for designation of combined statistical areas is here and Figure 1 is a map of the New York CSA.
This article examines employment and commuting in the New York area by broad geographic sector. The core sector, of course, is Manhattan (New York County). The second sector is the balance of the city of New York, the outer boroughs of the Bronx, Brooklyn, Queens and Staten Island. The inner counties are Westchester and Nassau in New York as well as Bergen, Essex, Hudson, Middlesex, Passaic and Union in New Jersey. The balance of the CSA is in the outer counties.
Distribution of Employment
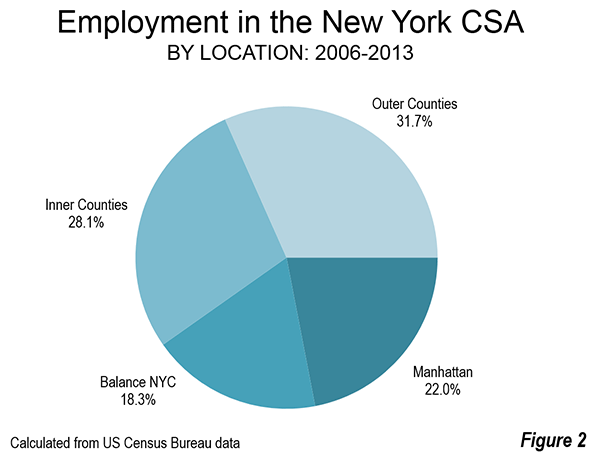
The New York CSA is home to the world’s second largest central business district (CBD). Only Tokyo’s Yamanote Loop has more employment. Overall, Manhattan (New York County) has 2.4 million jobs, with approximately 2.0 million jobs in the CBD, which covers virtually all of the area to the south of 59th Street. Yet, despite this impressive statistic, unmatched anywhere in the country, Manhattan contains only 22 percent of the employment in the New York area. The largest portion of employment is in the outer counties, with 32 percent (Figure 2). Combined, the inner and outer county suburbs represent 60 percent of the jobs in the New York commuting shed.
Where People Live and Work
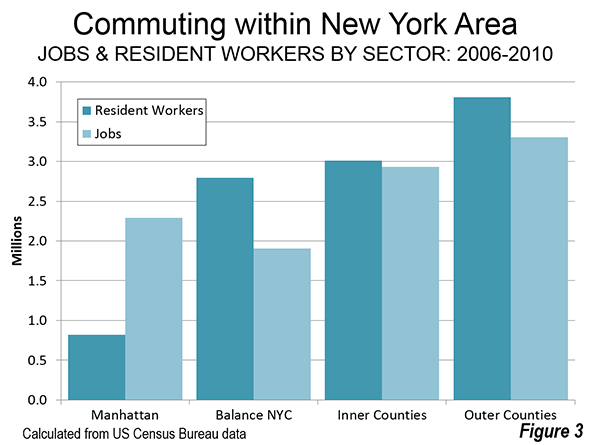
The distribution of employee residences contrasts sharply with that of employment. Manhattan displays the most extreme imbalance between jobs and where people live. (Figure 3). There are nearly three times as many jobs as resident employees in Manhattan (2.8 jobs per resident employee). The most evenly balanced sector is the outer counties, which are at near parity, with 0.97 jobs for every resident employee. The outer counties are relatively balanced, with 0.87 jobs per resident employee. The balance of New York City has 2.7 million resident workers and only 1.9 million jobs. There are only 0.68 jobs per resident employee. When the entire city is considered, including Manhattan, there is a much closer balance, with 1.16 jobs per resident worker.
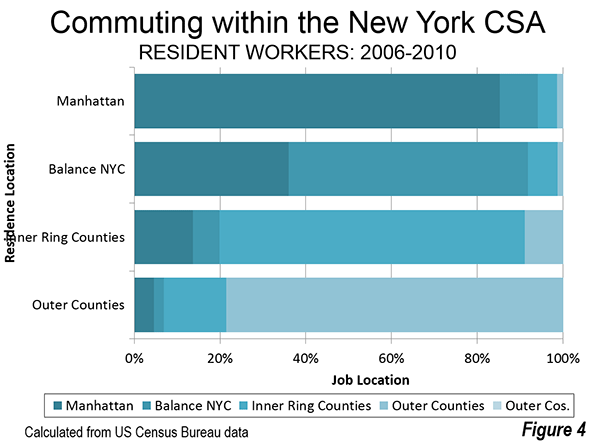
Most employees work in their sector of residence. About 85 percent of Manhattan residents work in Manhattan. Nearly 79 percent of outer county residents work in the outer counties, while 71 percent of inner county residents work in the inner counties. Perhaps surprisingly, nearly two-thirds as many inner county residents work in the outer counties as work in Manhattan. Only 55 percent of resident workers in the four outer boroughs of New York City work in the outer boroughs (Figure 4)
Commuting to Manhattan
One of the most enduring urban myths is built around the idea of the monocentric city. This is the conception that most people work downtown (the CBD). This has been an inaccurate characterization for decades, even in New York. In New York, as noted above, the CBD accounts for little more than 20 percent of employment. By comparison, however, this is a substantial number compared to other large North American commuter sheds. The Chicago CSA, for example (the Loop) has about 11 percent of its employment downtown (the Loop), Toronto has less than 15 percent and Los Angeles is under two percent.
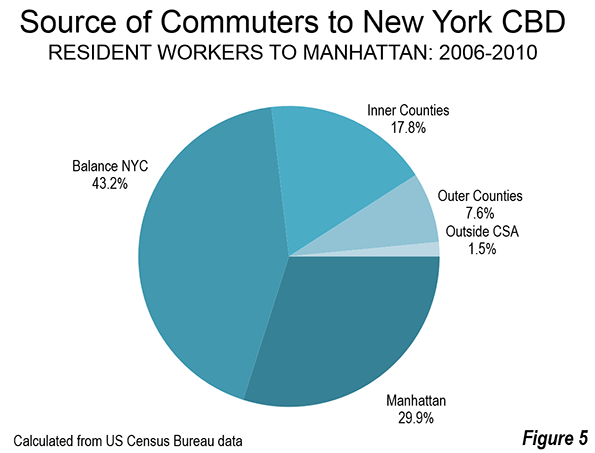
The overwhelming majority of jobs in Manhattan are filled by local residents or nearby commuters. According to American Community Survey "flow" data for 2006-2010, 73 percent of Manhattan commuters live in Manhattan or in the balance of New York City. Another 18 percent of commuters travel from the inner counties. This leaves less than eight percent of commuters traveling from the outer counties. Less than two percent of commuters travel to Manhattan from outside the CSA (Figure 5).
How Commuters Travel
New York relies on transit far more than any other US commuter shed. Overall approximately 27 percent of work trip travel is on transit. However, the extent of transit use varies widely by sector. Transit accounts for 75 percent of work trip travel to Manhattan employment. Transit also has a significant market share to jobs in the outer boroughs (38 percent). Jobs in the city of New York account for 88 percent of the transit commuting in the CSA. Outside the city, transit carries a much smaller share. In the inner counties, transit captures nine percent of commuters, while accounting for a much smaller 2.6 percent in the outer counties. In the outer counties, transit’s market share is slightly more than one-half the national average (Table).
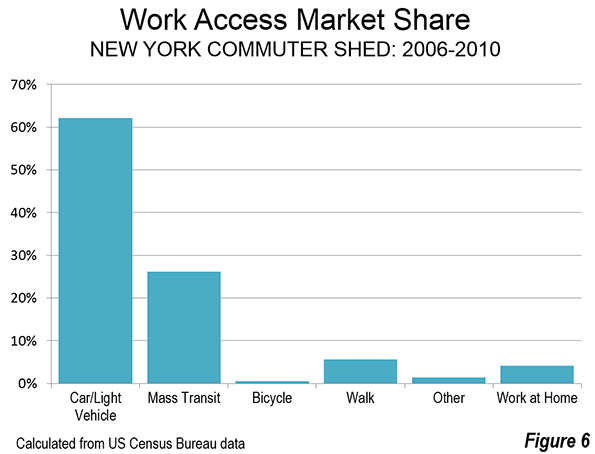
Cars have the largest work trip market share in every commuter shed in the nation, including the New York area, where they provide 61 percent of trips. Again, however, there is a very wide variation between the sectors. Cars provide less than 15 percent of commute trips to jobs in Manhattan. They provide a larger 44 percent share in the outer boroughs. In the inner counties and outer counties, cars are strongly dominant, providing for 80 percent and 88 percent of the commutes respectively.
The walking commuter share is lower than might be expected in famously pedestrian oriented Manhattan. Manhattan has by far the densest urbanization in the United States. With more than 70,000 residents per square mile (28,000 per square kilometer), Manhattan is nearly four times as dense as San Francisco, which has the highest density of any large municipality in the US outside New York. With such a high density, and a job density of more than 100,000 per square mile (nearly 40,000 per square kilometer), it may be surprising that workers in the outer boroughs rely on walking to work to a greater extent. Walking has a 7.4 percent commuting share in Manhattan, and a 9.6 percent share in the outer boroughs, despite their much lower population and employment densities.
| Table | |||||||
| New York CSA Means of Transportation: Work Location: 2013 | |||||||
| Area | Drive Alone | Car Pool | Transit | Bicycle | Walk | Other | Work at Home |
| Manhattan | 10.0% | 2.7% | 74.7% | 1.0% | 7.4% | 1.8% | 2.4% |
| Balance: NYC | 37.0% | 7.3% | 38.7% | 1.1% | 9.6% | 1.4% | 4.8% |
| Inner Counties | 71.6% | 8.6% | 9.4% | 0.3% | 4.2% | 1.7% | 4.2% |
| Outer Counties | 79.6% | 8.6% | 2.6% | 0.3% | 2.8% | 1.1% | 5.0% |
| New York CSA | 54.3% | 7.1% | 26.9% | 0.6% | 5.4% | 1.5% | 4.2% |
| Exhibit: United States | 76.4% | 9.4% | 5.2% | 0.6% | 2.8% | 1.3% | 4.4% |
| Calculated from American Community Survey | |||||||
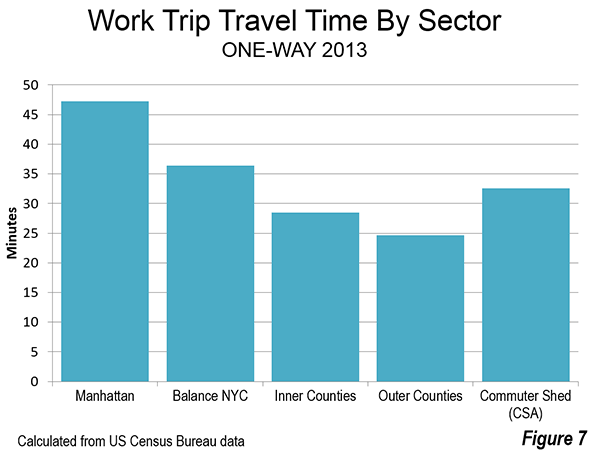
The faster work commute trips of cars is illustrated in the sectoral analysis. Automobile commuting is most dominant in the outer county suburbs, which have the largest number of resident workers and jobs. The average one-way work trip travel time is 24.7 minutes in the outer counties, little more than one half the 49.7 minute one way trip to jobs in Manhattan. The inner counties have the second shortest travel time, at 28.5 minutes. Jobs in the outer boroughs of New York City have an average work trip travel time of 36.4 minutes (Figure 7).
A Dispersed Commuter Shed
Despite its reputation for monocentricity, and its primacy in terms of the sheer numbers of core area employees, the New York combined statistical area remains surprisingly dispersed when it comes to jobs, contrary to popular accounts, although less so than others.
—–
Wendell Cox is Chair, Housing Affordability and Municipal Policy for the Frontier Centre for Public Policy (Canada), is a Senior Fellow of the Center for Opportunity Urbanism (US), a member of the Board of Advisors of the Center for Demographics and Policy at Chapman University (California) and principal of Demographia, an international public policy and demographics firm.
He is co-author of the "Demographia International Housing Affordability Survey" and author of "Demographia World Urban Areas" and "War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life." He was appointed to three terms on the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission, where he served with the leading city and county leadership as the only non-elected member. He served as a visiting professor at the Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, a national university in Paris.
Photograph: Inner County New York CSA: City of Elizabeth, seat of Union County, New Jersey (by author)