“Rust Belt Chic is the opposite of Creative Class Chic. The latter [is] the globalization of hip and cool. Wondering how Pittsburgh can be more like Austin is an absurd enterprise and, ultimately, counterproductive. I want to visit the Cleveland of Harvey Pekar, not the Miami of LeBron James. I can find King James World just about anywhere. Give me more Rust Belt Chic.” Jim Russell, blogger at Burgh Diaspora
National interest in a Rust Belt “revival” has blossomed. There are the spreads in Details, Atlantic Cities, and Salon, as well as an NPR Morning Edition feature. And so many Rust Belters are beginning to strut a little, albeit cautiously–kind of like a guy with newly-minted renown who’s constantly poking around for the “kick me” sign, if only because he has a history of being kicked.
There’s a term for this interest: “Rust Belt Chic”. But the term isn’t new, nor is the coastal attention on so-called “flyover” country. Which means “Rust Belt Chic” is a term with history–loaded even–as it arose out of irony, yet it has evolved in connotation if only because the heyday of Creative Class Chic is giving way to an authenticity movement that is flowing into the likes of the industrial heartland.
About that historical context. Here’s Joyce Brabner, wife of Cleveland writer Harvey Pekar, being interviewed in 1992, and introducing the world to the term:
I’ll tell you the relationship between New York and Cleveland. We are the people that all those anorexic vampires with their little black miniskirts and their black leather jackets come to with their video cameras to document Rust Belt chic. MTV people knocking on our door, asking to get pictures of Harvey emptying the garbage, asking if they can shoot footage of us going bowling. But we don’t go bowling, we go to the library, but they don’t want to shoot that. So, that’s it. We’re just basically these little pulsating jugular veins waiting for you guys to leech off some of our nice, homey, backwards Cleveland stuff.
Now to understand Brabner’s resentment we step back again to 1989. Pekar–who is perhaps Cleveland’s essence condensed into a breathing human–had been going on Letterman. Apparently the execs found Pekar interesting, and so they’d book him periodically, with Pekar–a file clerk at the VA–given the opportunity to promote his comic book American Splendor. Well, after long, the relationship soured. Pekar felt exploited by NYC’s life of the party, with his trust of being an invited guest giving way to the realization he was just the jester. So, in what would be his last appearance, he called Letterman a “shill for GE” on live TV. Letterman fumed. Cracked jokes about Harvey’s “Mickey Mouse magazine” to a roaring crowd before apologizing to Cleveland for…well…being us.
Think of this incident between two individuals–or more exactly, between two realities: the famed and fameless, the make-up’d and cosmetically starved, the prosperous and struggled–as a microcosm for regional relations, with the Rust Belt left to linger in a lack of illusions for decades.
But when you have a constant pound of reality bearing down on a people, the culture tends to mold around what’s real. Said Coco Chanel:
“Hard times arouse an instinctive desire for authenticity”.
And if you can say one thing about the Rust Belt–it’s that it’s authentic. Not just about resiliency in the face of hardship, but in style and drink, and the way words are said and handshakes made. In the way our cities look, and the feeling the looks of our cities give off. It’s akin to an absence of fear in knowing you aren’t getting ahead of yourself. Consider the Rust Belt the ground in the idea of the American Dream.

Photo credit: Sean Posey
Of course this is all pretty uncool. I mean, pierogi and spaetzle sustain you but don’t exactly get you off. Meanwhile, over the past two decades American cities began their creative class crusade to be the next cool spot, complete with standard cool spot amenities: clubs, galleries, bike paths, etc. Specifically, Richard Florida, an expert on urbanism, built an empire advising cities that if they want creative types they must in fact get ahead of themselves, as the young are mobile and modish and are always looking for the next crest of cool.
These “Young and the Restless”–so they’re dubbed–are thus seeking and hunting, but also: apparently anxious. And this bit of pop psychology was recently illustrated beautifully in the piece “The Fall of the Creative Class” by Frank Bures:
I know now that this was Florida’s true genius: He took our anxiety about place and turned it into a product. He found a way to capitalize on our nagging sense that there is always somewhere out there more creative, more fun, more diverse, more gay, and just plain better than the one where we happen to be.
After long–and with billions invested not in infrastructure, but in the ephemerality of our urbanity–chunks of America had the solidity of air. Places without roots. People without place. We became a country getting ahead of itself until we popped like a blowfish into pieces. Suddenly, we were all Rust Belters, and living on grounded reality.
Then somewhere along the way Rust Belt Chic turned from irony into actuality, and the Rust Belt from a pejorative into a badge of honor. Next thing you know banjo bingo and DJ Polka are happening, and suburban young are haunting the neighborhoods their parents grew up in then left. Next thing you know there are insights about cultural peculiarities, particularly those things once shunned as evidence of the Rust Belt’s uncouthness, but that were–after all–the things that rooted a history into a people into a place.
Take the Pittsburgh Potty. For recent generations it was about the shame of having a toilet with no walls becoming the pride of having a toilet with no walls. From Pittsburgh Magazine:
We purchased a house with a stray potty, and we’ve given that potty a warm home. But we simply pretended as if the stray potty didn’t exist, and we certainly didn’t make eye contact with the potty when we walked past it to do laundry.
The Pittsburgh Potty is basically a toilet in the middle of many Pittsburgh basements. No walls and no stalls. It existed so steel workers can get clean and use the bathroom without dragging soot through ma’s linoleum.
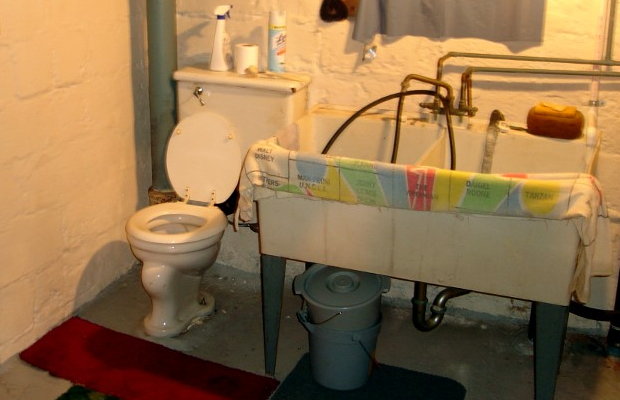

Photo credit: Brookline Connection
Authentic: yes. Cool? A toilet?
Only in the partly backward Rust Belt of Harvey Pekar and friends. From the twitter feed of @douglasderda who asked “What is a Pittsburgh Potty?” Some responses follow:
“I told my wife I wanted to put ours back in, but she refused. I threatened to use the stationary tubs.”
“In my house, that would be known as my husband’s bathroom.”
“It’s a huge selling feature for PGH natives. I’m not kidding. We weren’t so lucky in our SS home.”
“We’re high class people. Our Pittsburgh Potty has a bidet. Well, it’s a hose mounted on the bottom, but still ….”
Eventually, this satisfaction found in re-rooting back into our own Rust Belt history has become the fuel of wisdom for even Coastal elites. Here’s David Brooks recently talking about the lessons of Bruce Springsteen’s global intrigue being nested in the locality that defines Rust Belt Chic:
If your identity is formed by hard boundaries, if you come from a specific place…you are going to have more depth and definition than you are if you grew up in the far-flung networks of pluralism and eclecticism, surfing from one spot to the next, sampling one style then the next, your identity formed by soft boundaries, or none at all.
Brooks continues:
The whole experience makes me want to pull aside politicians and business leaders and maybe everyone else and offer some pious advice: Don’t try to be everyman…Go deeper into your own tradition. Call more upon the geography of your own past. Be distinct and credible. People will come.
And some are coming, albeit slowly, unevenly. But more importantly, as a region we are once again becoming–but nothing other than ourselves.
Authenticity, reality: this was and always will be the base from which we wrestle our dreams back down to solid ground.
American splendor, indeed.
This is an excerpt from the forthcoming book Rust Belt Chic: A Cleveland Anthology. It first appeared at RustBeltChic.com.