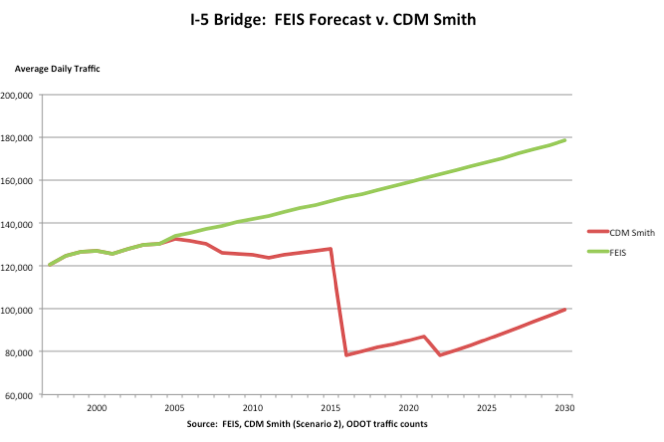
Among urban planners, there is probably not a more revered urban area in the world than Portland (Oregon). The Portland metropolitan area and its core urban area , principally located in Oregon, stretches across the Columbia River into the state of Washington (Figure 1). Nearly four decades ago, the state of Oregon adopted strong urban planning requirements, including the requirement of an urban growth boundary. Two principal purposes of the resulting policies (referred to as “smart growth,” “urban containment, “compact cities,” etc.) were densification and transferring travel demand from cars to transit.
Portland’s progress toward these objectives has been modest, at best. Most growth has continued to be in the suburbs. There has been only modest densification, and employment has continued to disperse from the core. At the metropolitan area level, travel by car remains virtually as dominant as before and traffic congestion has intensified materially. Finally, house prices have been driven up relative to incomes (Note 1).
Portland: A Dispersing Metropolitan Area
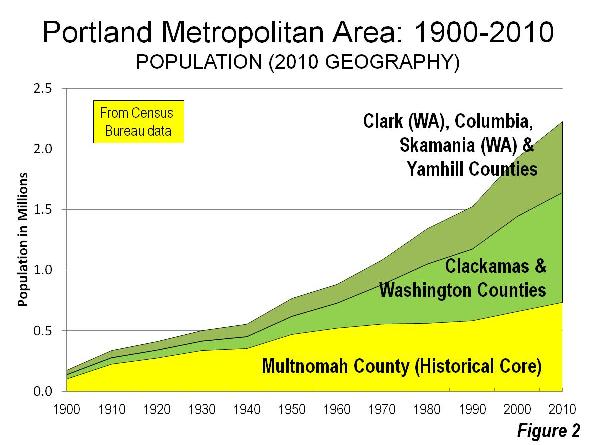
Like virtually all major metropolitan areas in the world, Portland has experienced substantial dispersion. The core county of Multnomah peaked at more than two thirds of the metropolitan area population in 1930, as defined in 2000 (Note 2). By 2010, Multnomah County had dropped to one third of the metropolitan area population (Figure 2).
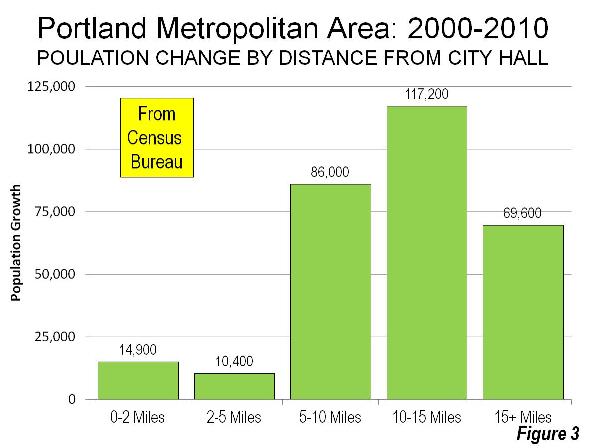
The dispersion has continued in recent years, though there has been core growth (as has been the case in many metropolitan areas). Between 2000 and 2010, the area within two miles (three kilometers) of Portland City Hall grew more than 20 percent. However, this was only five percent of the metropolitan area’s growth. In the inner ring extending to five miles (eight kilometers) from City Hall, the growth was only three percent, well below the metropolitan area’s overall 15 percent growth rate. More than 90 percent of the metropolitan area’s population growth was outside a five mile radius (Figure 3).
Portland: A Low Density Urban Area
Despite its international reputation as an exemplar of compactness , Portland is a low density urban area. Among the 875 urban areas in the world with more than 500,000 population, 797 are denser than Portland.
In the low density United States, Portland ranked 12th among major urban areas (over 1 million population), at approximately 3,500 residents per square mile (1,350 per square kilometer) in 2010. This is approximately 10% higher than the major urban area average density but barely half that of the densest, Los Angeles, with its undeserved reputation for low-density, “sprawling” development (Figures 4 and 5).

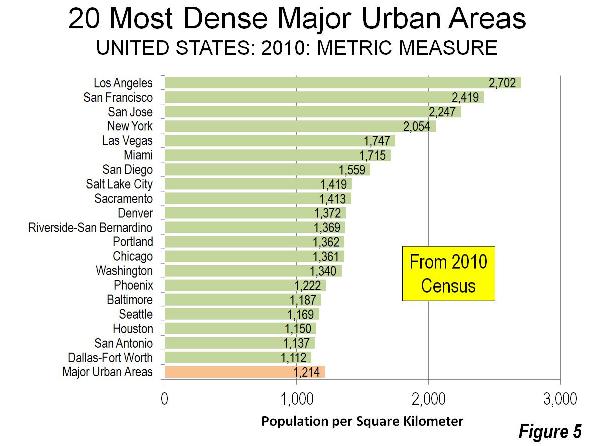
Portland is less dense than all major urban areas in the 13 western states, with the exception of Seattle. Notably, Riverside San Bernardino is denser, despite consisting almost exclusively of post-World War II automobile-oriented development. Even much smaller California urban areas, such as Stockton, Bakersfield, Lodi and Delano are denser than Portland.
Portland and Houston: Density Cousins
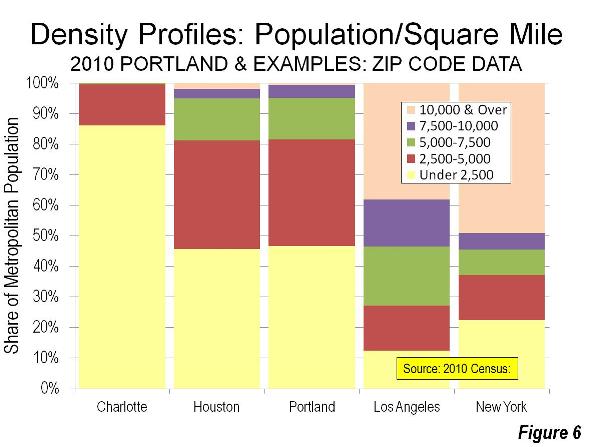
The Portland metropolitan area’s density profile nearly duplicates that of Houston, which is just as famous for its liberal land use and transportation policies nearly the opposite of Portland’s (Note 3). Both metropolitan areas have nearly the same percentage of their populations living at densities below 7,500 per square mile (2,865 per square kilometer). A 40 percent larger share lives at densities of from 7,500 to 10,000 per square mile (3,860 per square kilometer) in Portland, while Houston’s share of its population living at densities above 10,000 per square mile is three times that of Portland (Figure 6).
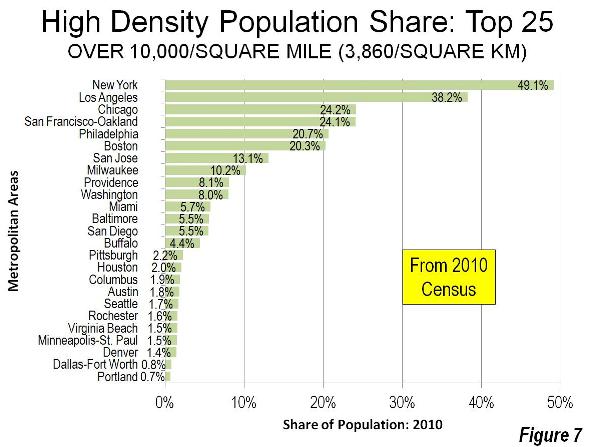
Among the nation’s 51 major metropolitan areas, Portland ranks 25th in the share of population living in zip codes with more than 10,000 people per square mile in 2010 (Figure 7).
Portland’s Job Dispersion
As in other metropolitan areas, jobs have dispersed substantially around Portland. Today, fewer than 10% of the jobs are located in downtown Portland (the central business district). The city of Portland itself has approximately 1.41 jobs per resident worker. Suburban Hillsboro, with the third largest employment base in the metropolitan area, has slightly more jobs per resident workers (a higher “jobs-housing balance”) according to American Community Survey data.
Transit in Portland
Portland has developed an extensive rail system, intended to attract drivers from their cars. Today, six light rail lines (five light rail) radiate toward the urban periphery, focusing on downtown (the central business district, or CBD).
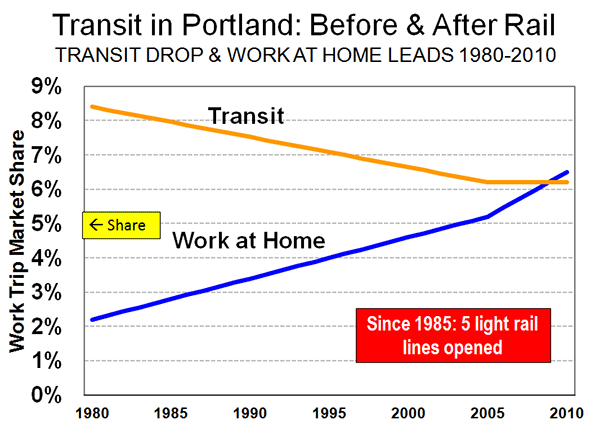
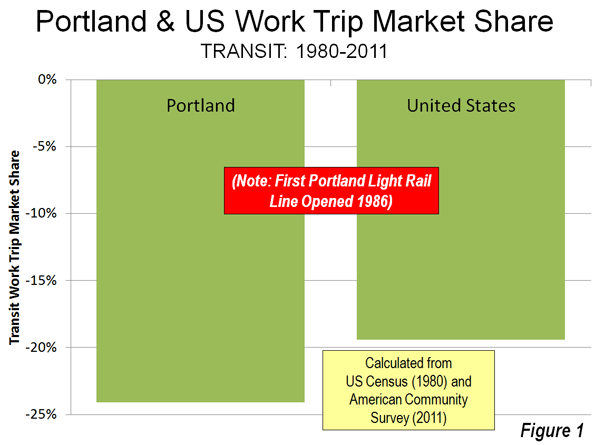
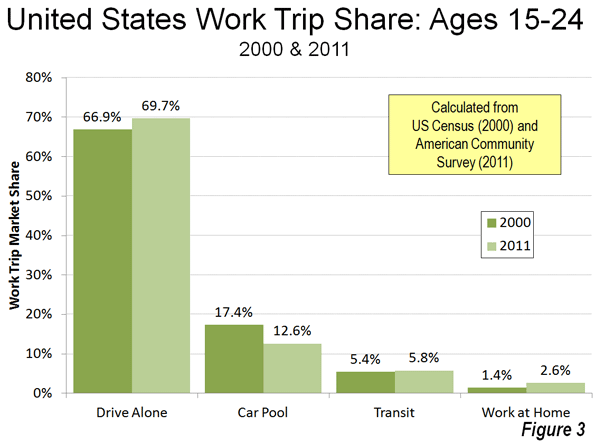
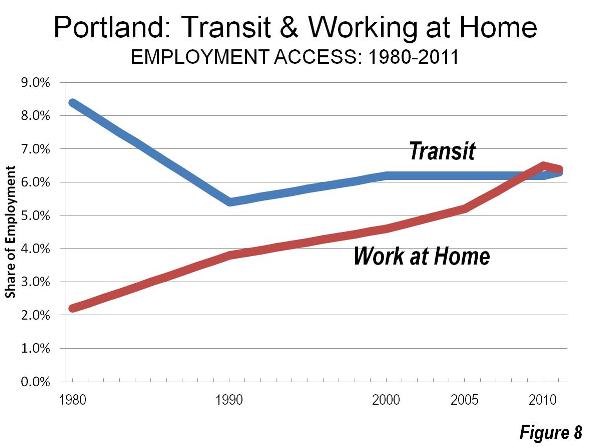
Yet the share of commuters using transit has fallen by a quarter since 1980, the last data available before the first light rail line opened. In short, rail has not changed the calculus of travel in Portland. Working at home, which is a less expensive and more environmentally friendly work access mode, has caught up with and now exceeds transit, as has occurred in most US major metropolitan areas. (Figure 8)
Worse, transit may have already experienced its “best of times.” The future could be grim. Opposition to rail expansion has grown, and longer term transit service cuts of up to 70 percent have been threatened. (See Portland’s Transit Halcyon Days?)
As elsewhere, transit in Portland is “about downtown.” The Portland Business Alliance estimates that 36% of downtown workers commute by transit. This is nearly one-half of all transit commuting in the Portland metropolitan area. Even in the job rich suburbs of Hillsboro and Beaverton, the share of people using transit for the work trip is less than the 5.0 percent national average.
Portland: Intensifying Traffic Congestion
Clinging to the fantasy transit can materially reduce automobile travel, Oregon officials have blocked substantial roadway expansions. Residents have been rewarded with much intensified traffic congestion.
The Texas A&M Texas Transportation Institute Annual Mobility Report (Note 4) reveals Portland to have the 6th worst traffic congestion in the nation among major metropolitan areas. This compares to a before-rail ranking of 39th in 1982. Now Houston, Atlanta, Dallas-Fort Worth and Phoenix all have lower levels of traffic congestion than Portland (Figure 9). Without decades of urban containment and anti-mobility policies, these metropolitan areas have improved traffic congestion relative to Portland. This is despite far larger increases in travel demand. Since the early 1980s, each of these metropolitan areas has added more residents than live in the entire Portland metropolitan area. Portland also ranks among the worst (5th) in commuter stress (a measure of peak direction traffic congestion), according to the Annual Mobility Report
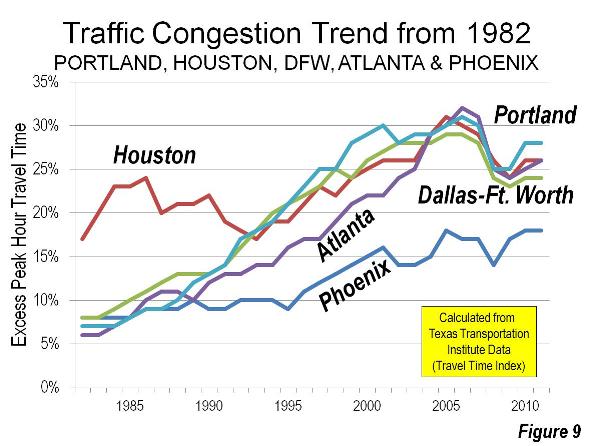
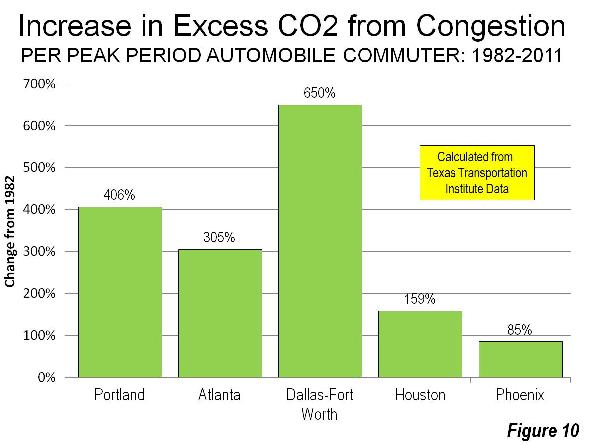
Portland: Congestion and Higher Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Reflecting the reality that greater traffic congestion increases greenhouse gas emissions, Portland’s carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions per automobile commuter have increased substantially and transit has made only the scantest difference. Between 1982 and 2011, Portland’s increase in CO2 emissions was greater than Houston, Atlanta and Phoenix, though less than Dallas- Fort Worth (Figure 10).
Deteriorating Housing Affordability in Portland
In Portland, consistent with both economic principle and considerable research, urban containment policy drives house prices up relative to incomes higher by rationing the supply of land and housing. In 2010, values of comparable land on either side of the urban growth boundary varied by more than 10 times in value per acre (a phenomenon also identified in Auckland, New Zealand by Chairman of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, Arthur Grimes).
The most recent Demographia International Housing Affordability Survey indicated that Portland’s median multiple (median house price divided by median household income) was 4.3. In normally functioning housing markets, the median multiple is typically 3.0 or less, a ratio last achieved in Portland in 1995. This higher median house price means than approximately 125,000 fewer Portland households —or 15% of households — are able to afford the median priced house. (Note 5).
Higher housing costs retard the standard of living by reducing discretionary incomes (gross income minus taxes and necessities). This, in turn, leads to less demand for other goods and services (in the “discretionary economy”), less job creation and less economic growth.
Even so, Portland’s rising house prices have been moderated by the nearby availability of less expensive houses on larger lots in the Vancouver area (Clark County, Washington). There, more liberal land use regulation permits consumer-driven housing choice, rather forcing households to choose from the limited offerings planning authorities prefer.
In part due to rising prices, Portland is becoming less diverse . Indeed, Aaron Renn has called Portland the penultimate example in his searing critique, The White City. After the results of the 2010 census were announced. The Oregonian quoted then Mayor Sam Adams’ concern about the exodus of African-Americans from the city (municipality), saying that Portlanders should care about the fact that we offer ¬such limited access to equal opportunities. Local policymakers are largely oblivious to the role that urban containment policy may have played in diminishing those opportunities.
Misplaced Priorities
Despite all of this, Portland has its advantages.
As in Houston, Seattle, Atlanta and virtually all other major metropolitan areas regardless of land use regulations, a core renaissance is underway that is making a dense urban lifestyle more practical for the relatively few who both prefer it and can afford it. The suburban lifestyle, dominant virtually everywhere in the United States, remains alive and well in Portland (Note 6). Portland’s physical location remains the envy of most metropolitan areas. There is little better scenery than the nearby Columbia Gorge or majestic Mt. Hood, which crowns the area on clear days.
However, Portland has been sidetracked by a pre-occupation with urban design, at least partially driven by concerns about reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The good news is that technological advances are poised to do far more to reduce greenhouse gas emissions than could ever be achieved by urban containment policy.
But scenery aside, cities are primarily economic organisms. Cities have grown by serving the aspirations of people for a better standard of living. The very purpose of cities is to facilitate affluence and minimize poverty among residents (see Toward More Prosperous Cities). Yet policies, such as urban containment, that inherently reduce household discretionary incomes and impose greater congestion costs reduce discretionary incomes. Despite intentions to the contrary, the results show this to be the real Portland story.
—————————————–
Note 1: Some other metropolitan areas that have embraced urban containment policy have produced even worse results. For example, traffic congestion is worse in Vancouver, Sydney, Melbourne and far smaller Auckland, according to the “Tom Tom Congestion Index,” a real-time traffic reporting competitor to INRIX. Portland has seriously unaffordable housing, though has not retarded the standard of living nearly so much as in Vancouver, Sydney, Melbourne or Auckland, where housing is severely unaffordable. Attention is drawn to Portland’s negative outcomes because of the extent to which its policies are revered in the urban planning community around the world.
Note 2: Multnomah County is used in this analysis, instead of the historical core city of Portland, which has grown in large measure by annexation. Since 1950, the city added 108 percent to its land area and little more than half (56 percent) to its population.
Note 3: Houston is sometimes referred to as having deregulated land use. This is not strictly correct, though Houston is closer to a deregulated model than any other US metropolitan area. The city of Houston does not have zoning, though some municipalities in the suburbs are zoned. Many neighborhoods in the city of Houston have private land use covenants.
Note 4: The Annual Mobility Report has been the authoritative measure of traffic congestion in US urban areas for three decades. More recently, the report’s traffic congestion measures have been significantly strengthened by the use of actual global positioning data from INRIX, which also produces its own Traffic Scorecard both for US and international urban areas, using satellite based real-time traffic data.
Note 5: Estimated from income qualifying income requirements as reported by the National Association of Realtors for the third quarter of 2012 and the metropolitan income distribution modeled based on the 2011 American Community Survey.
Note 6: In 1999, new urbanist architect Andres Duany evaluated Portland in a commentary for The Oregonian: “To my surprise, as soon as I left the prewar urbanism (to which my previous visits had been confined), I found all the new areas on the way to the urban boundary were chock full of the usual sprawl one finds in any U.S. city, no better than in Miami. The outcome wasn’t that different after all.”
————————-
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris and the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life.
Photo: Mount Hood (by author)