Time Magazine’s Sam Frizell imagines that the American Dream has changed, in an article entitled "The New American Dream is Living in a City, Not Owning a House in the Suburbs." Frizell further imagines that "Americans are abandoning their white-picket fences, two-car garages, and neighborhood cookouts in favor of a penthouse view downtown and shorter walk to work." The available population data shows no such trend.
Frizell’s evidence is the weak showing in single family house building permits last month and a stronger showing in multi-family construction.
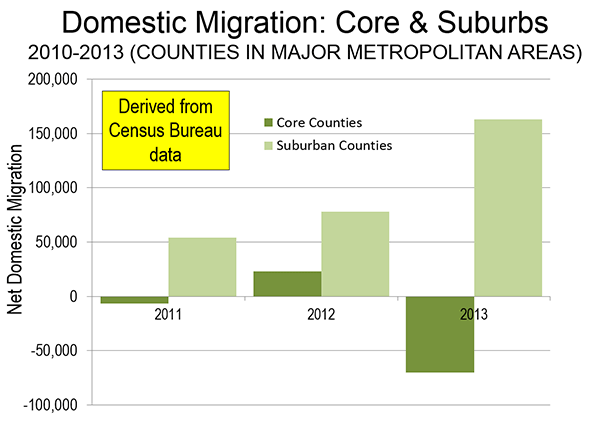
This is just the latest in the "flocking to the city" mantra that is routinely mouthed without any actual evidence (see: Flocking Elsewhere: The Downtown Growth Story). The latest Census Bureau estimates show that net domestic migration continues to be negative in the core counties (which include the core cities) of the major metropolitan areas (those with more than 1,000,000 residents). The county level is the lowest geographical level for which data is available.
At the same time, there is net domestic inward migration to the suburban counties. Moreover, much of the net domestic migration to metropolitan areas has been to the South and Mountain West, where core cities typically include considerable development that is suburban in nature (such as in Austin, Houston and Phoenix). As the tepid "recovery" has proceeded, net domestic migration to suburban counties has been strengthened (see: Special Report: 2013 Metropolitan Area Population Estimates), as is indicated in the Figure.
There is no question but that core cities are doing better than before. It helps that core city crime is down and that the South Bronx doesn’t look like Berlin in 1945 anymore. For decades, many inclined toward a more urban core lifestyle were deterred by environments that were unsafe, to say the least. A principal driving force of this has been millennials in urban core areas. Yet, even this phenomenon is subject to over-hype. Two-thirds of people between the ages of 20 and 30 live in the suburbs, not the core cities, according to American Community Survey data.
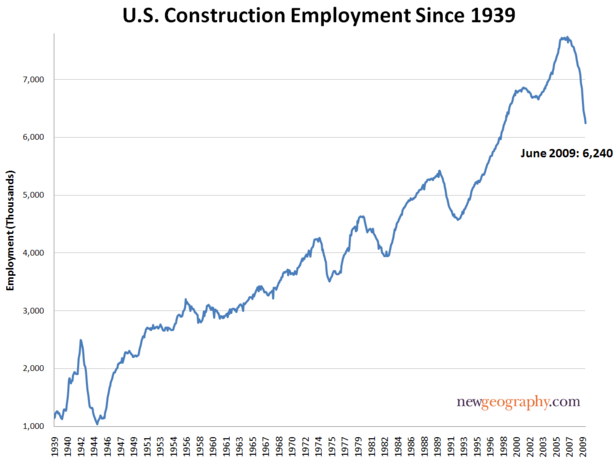
To his credit, Frizell notes that the spurt in multi-family construction is "not aspirational," citing the role of the Great Recession in making it more difficult for people to buy houses. As I pointed out in No Fundamental Shift to Transit: Not Even a Shift, 2013 is the sixth year in a row that total employment, as reported by the Bureau of Labor Statistics was below the peak year of 2007. This is an ignominious development seen only once before in the last 100 years (during the Great Depression).
In short, urban cores are in recovery. But that does not mean (or require) that suburbs are in decline.