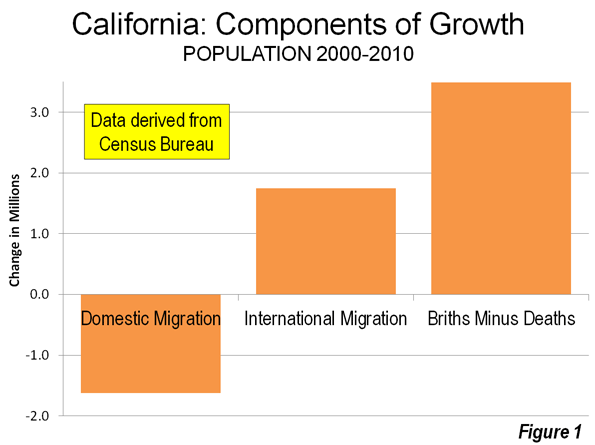
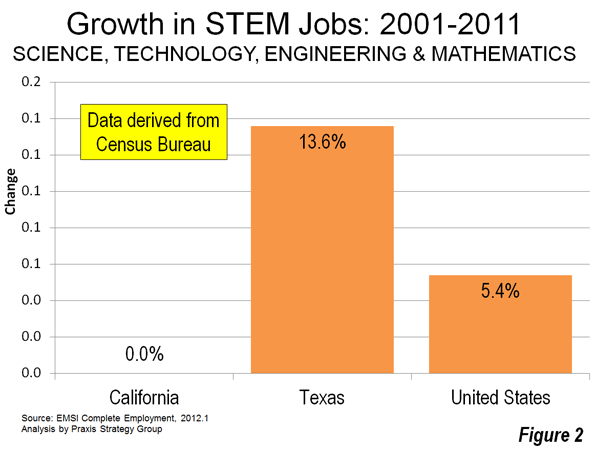
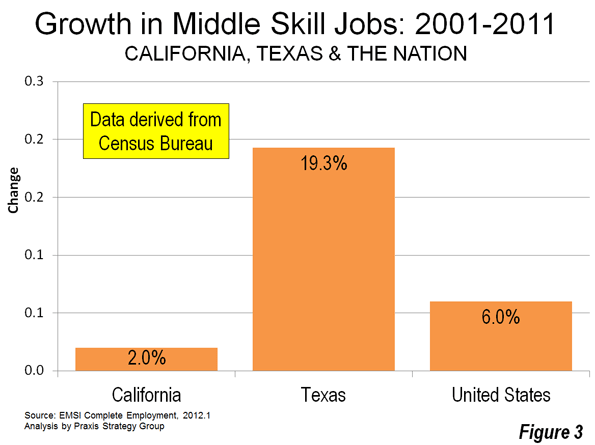
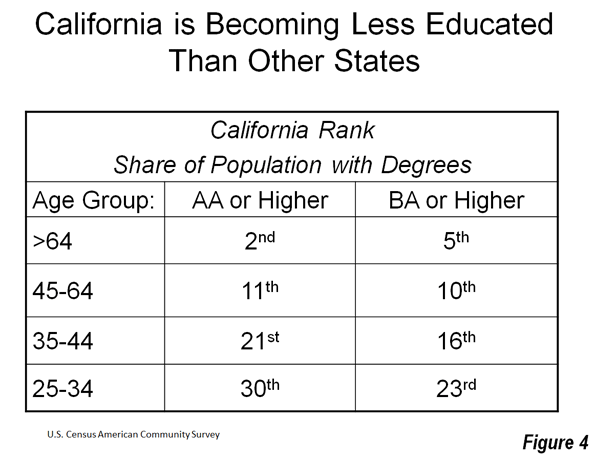
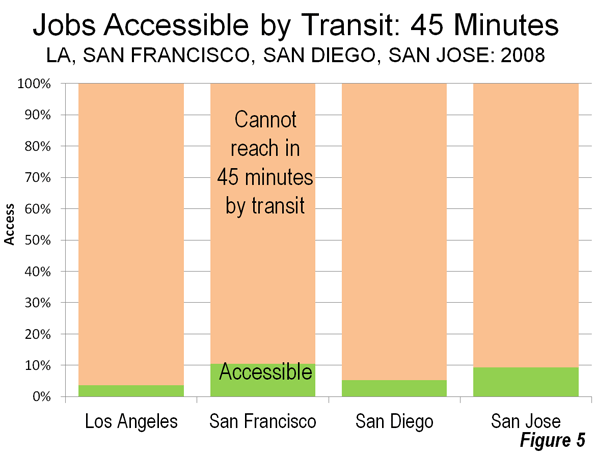
Most Californians live within miles of its majestic coastline – for good reason. The California coastline is blessed with arguably the most desirable climate on Earth, magnificent beaches, a backdrop of snow-capped mountains, and natural harbors in San Diego and San Francisco. The Golden State was aptly named. Its Gold Rush of 1849 was followed a century later by massive post-war growth.
There is no mystery why California’s population and economy boomed after the Second World War. Education in California became the envy of the world. California’s public school system led the nation in innovation with brand new schools and classrooms. The Community College system that fed its universities was free for its students. A college education at the UC and Cal State systems was inexpensive. UC-Berkeley, with its graduate schools, was arguably the greatest in the world while Stanford developed into the Harvard of the West. An efficient highway system moved California’s automobile driven commerce while fertile soil of the Central Valley became the fruit and vegetable basket of the world.
The next wave hit in the 80s as former orchards south of San Francisco morphed into the Silicon Valley. Intel and other chip manufacturers led the computer and software revolution bringing high tech jobs and immense new wealth to the Golden State. The dot-com revolution of the 90s brought more gold to California. Innovators like Google and Apple cashed in by nurturing the Internet era. The next decade heralded the greatest housing and mortgage boom in the nation’s history. Developers from Orange County, south of Los Angeles, invented creative financing vehicles that drove home sales, and profits, to record heights by 2006.
This success has created a problem: Californians, due to their golden history, live unreflective lives. The Tea Party movement generated a political tsunami that swept more than 60 incumbents from political office in 2010, but the wave petered out at California’s state line as Democrats take every elected office in the state.
The state budget, mandated to balance by law, has been billions in the red for ten straight years. Yet Californians re-elect the same politicians, year after year, who produce budgets with multi-billion dollar deficits. California voters rejected Meg Whitman, the billionaire founder of Ebay, in favor of Jerry Brown. California now has a $16 billion deficit which “assumes” that California voters will pass massive tax increases on themselves. If they do not, the 2013 deficit becomes a mind numbing $20 billion. Yet despite the red ink, Governor Brown signed into law a “high speed rail” bill that will spend $6 billion on a train between Fresno and Bakersfield – not LA and San Francisco as promised. Polls turned against the choo-choo, but there remain no outcry from California voters.

California voters rejected Carly Fiorina, who ran Hewlett Packard, for Barbara Boxer in the 2010 Senate race. To protect the endangered Delta Smelt, a fish known better as bait, water has been diverted from Central Valley farms to the Pacific Ocean. Orchards in the Central Valley were allowed to wither and die resulting in unemployment in the Central Valley as high as 40%. Imagine Californians on food stamps, living in what was the fruit basket of American.
California’s business climate now ranks dead last according to 650 CEOs measured by Chief Executive Magazine. Apple will take 3,600 jobs to its new $280,000,000 facility in Austin Texas – jobs that California would have had in the past. Texas ranked first in the same survey. California’s unemployment rate is consistently higher than 10% of its work force, and there are few jobs for college students who graduate with as much as $100,000 in student loans. Despite overwhelming evidence that bad public policy is chasing away jobs, the same state politicians are sent back to Sacramento every two years.
California’s public education system, once the envy of the world, now ranks 46th in the nation in per pupil spending and faces a $1.4 billion cut in the fall. In the last month, three California cities declared bankruptcy. More will follow. Take Poway for example. Its school board borrowed $100,000,000 (for 33,000 students) through a Capital Appreciation Bond. The politicians told the voters there would be no payments for 20 years. What they did not explain was the residents must pay back $1 billion dollars on their $100 million loan. Beginning in 2021, tiny Poway will be forced to pay $50 million per year in bond payments. Huge property tax assessments will be required if homes do not appreciate 400% by then, which is unlikely under foreseeable circumstances.
Rather than stare at themselves in the mirror, Californians should take a look at Michigan. In the 50s greater Detroit was the fourth-largest city in America with 2 million inhabitants and the world’s most dominant industry: the automobile.
Most people had a good paying job. Its burgeoning middle class was the model of the world with excellent public schools and universities. Detroit in 2012 is a shadow of that once great metropolis. Its population has shrunk to 714,000. The average price of a home has fallen to $5,700. Unemployment stands at 28.9%. It has a $300,000,000 deficit. There are 200,000 abandoned buildings in the derelict city. Its public education system, in receivership, is a disgrace producing more inmates than graduates. In 2006, the teacher’s union forced the politicians to reject a $200,000,000 offer from a Detroit philanthropist to build 15 new charter schools. Jobs long ago abandoned Detroit for places like South Carolina and Alabama, with their “right to work” laws and low taxes.
Now Detroit’s Mayor has proposed razing 40 square miles of the 138 square miles of this once great American city returning 70,000 abandoned homes to farmland. Even such a draconian plan may not be enough to save the city. If a hurricane had hit Detroit, more of us would know of this tragedy in our midst, but this fate was man-made and not wrought by nature. Detroit has had one party rule for more than fifty years. Louis C. Miriani served from September 12, 1957 to January 2, 1962 as Detroit’s last Republican mayor. Since that time the Democrats have ruled the Motor City. John Dingell has served region since 1956. His father was the Congressman from 1930 to 1956. Despite the disastrous decline of their city, Detroit voters send him back to Congress twenty-two times.
Like Detroit, California now has one party rule. The Democrats of California did not need a single Republican vote to pass their budget. Governor Brown’s plan is to address the nation’s largest deficit by raising taxes instead of cutting spending. If passed, the deficit would drop from $20 billion to a mere $16 billion. The budget does nothing to cure the systemic problems of a bloated bureaucracy. It does not eliminate one of California’s 519 state agencies.
Caltrans stopped building highways under Brown’s first term, but the people kept coming. Now 37 million Californians are locked in traffic jams each day. Brown was rewarded for such prescience with re-election as Governor. California’s egotistical politicians passed the Global Warming Solutions Act in 2006 (AB32) to “solve” climate change. Dan Sperling, an appointee to the California Air Resources Board (CARB) and a professor of engineering and environmental science at UC Davis, is the lead advocate on the board for a “low carbon fuel standard.” The powerful state agency charged with implementing AB 32 and other climate control measures, claims the low carbon fuel standard will “only” raise gasoline prices $.30 gallon in 2013. The California Political Review reported implementation of these the policies will raise prices by $1.00 per gallon.
Detroit was once the most prosperous manufacturing city in the world, a title later secured by California. Will California follow Detroit down a tragic path to ruin? In 1950, no one could imagine the Detroit of 2010. In 1970, when foreign imports started to make a foothold, the unions and their bought and paid for politicians resisted any change. In the 1990s as manufacturers fled to Alabama and South Carolina, the unions and their political minions held firm, even as good jobs slipped away. No one in Detroit envisioned their future.
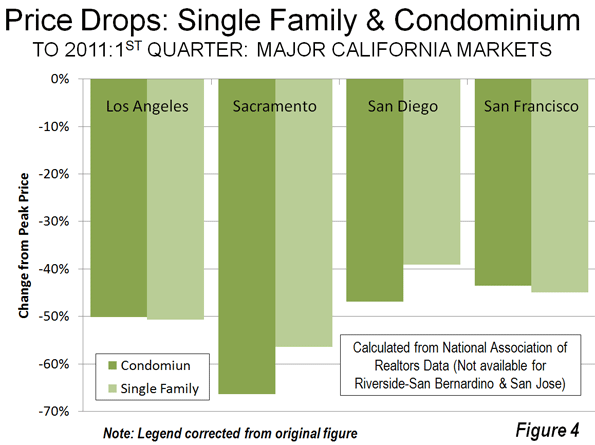
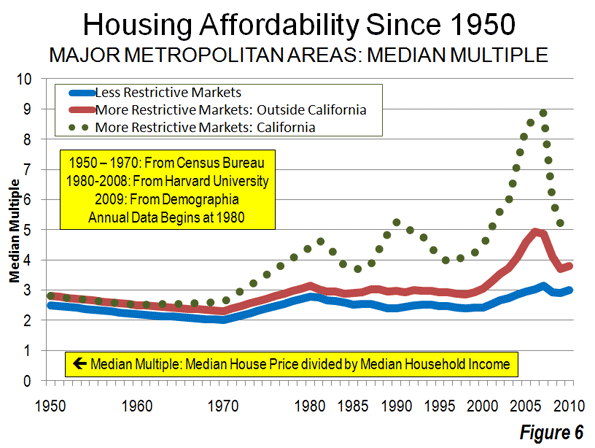
Today, California is following Michigan’s path with exploding pension obligations, a declining tax base, and disastrous leadership. Housing prices have fallen 30 to 60% across the state, evaporating trillions of dollars of equity and wealth. Unemployment remains stubbornly high and under-employment is rife. Do our politicians need any more signs?
Governor Brown’s budget will first slash money to schools and raise tuition on its students while leaving all 519 state agencies intact. He apparently will protect political patronage at all costs. Jobs, and job creators, are fleeing the state. Intel, Apple, and Google are expanding out of the state. The best and brightest minds are leaving for Texas and North Carolina. The signs are everywhere. Meanwhile, the voters send the same cast of misfits back to Sacramento each year – just as Detroit did before them.
The beaches are still beautiful. The mountains are still snow capped and the climate is still the envy of the world. Detroit never had that. But will California’s physical attributes be enough? If the people of California want to glimpse their future, they need look no farther than once proud City of Detroit and the once wealthy state of Michigan.
It can happen here.
Robert J Cristiano PhD is the Real Estate Professional in Residence at Chapman University in Orange, CA, a Senior Fellow at the Pacific Research Institute in San Francisco, CA and President of the international investment firm, L88 Companies LLC in Denver – Newport Beach – Washington DC – Prague. He has been a successful real estate developer for more than thirty years.