California was once the world’s leading economy. People came here even during the depression and in the recession after World War II. In bad times, California’s economy provided a safe haven, hope, more opportunity than anywhere else. In good times, California was spectacular. Its economy was vibrant and growing. Opportunity was abundant. Housing was affordable. The state’s schools, K through Ph.D., were the envy of the world. A family could thrive for generations.
Californians did big things back then. The Golden State built the world’s most productive agricultural sector. It built unprecedented highway systems. It built universities that nurtured technologies that have changed the way people interact and created entire new industries. It built a water system on a scale never before attempted. It built magnificent cities. California had the audacity to build a subway under San Francisco Bay, one of the world’s most active earthquake zones. The Golden State was a fount of opportunities.
Things are different today.
Today, California’s economy is not vibrant and growing. Housing is not affordable. There is little opportunity. Inequality is increasing. The state’s schools, including the once-mighty University of California, are declining. The agricultural sector is threatened by water shortages and regulation. Its aging, cracking, highways are unable to handle today’s demands. California’s power system is archaic and expensive. The entire state infrastructure is out of date, in decline, and unable to meet the demands of a 21st century economy.
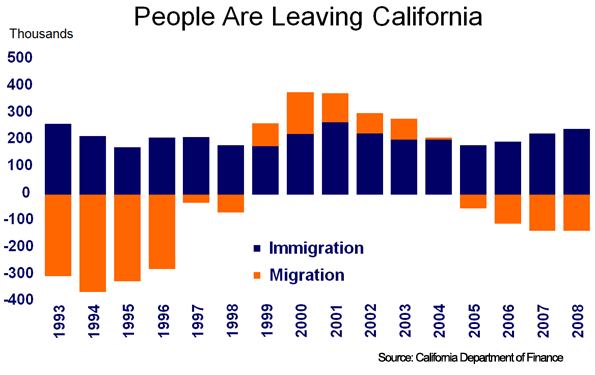
Indications of California’s decline are everywhere. California’s share of United States jobs peaked at 11.4 percent in 1990. Today, it is down to 10.9 percent. In this recession, California has been losing jobs at a faster pace than most of the United States. Domestic migration has been negative in 10 of the past 15 years. People are leaving California for places like Texas, places with opportunity and affordable family housing.
California’s economy is declining. Those of us who live here can all see it. Yet, Californians don’t have the will to make the necessary changes. Like a punch-drunk fighter, sitting helpless in the corner, California is unable to answer the bell for a new round.
Pat Brown’s California – between 1958 and 1966 – crafted the Master Plan for Higher Education, guaranteeing every Californian the right to a college education, a plan that has served the state very well. That system is threatened by today’s budget crisis and may be on the verge of a long-term secular decline. California was a state where people said yes, a state where businesses could be created, grow, and prosper. Some of these businesses were run by Democrats, others Republicans but all celebrated a culture of growth and achievement.
Today’s California is a state where building a home requires charrettes with the neighbors, years in the planning department, architects, engineers, and environmental impact studies – we built the transcontinental railroad in three years, faster than a builder can get a building permit in many California communities. People here dream of a green future but plan and build nothing. There’s big talk about the future, but California now turns more and more of our children away from college, and too many of our least advantaged children don’t even make it through high school.
Once, California was a political model of enlightened government. Now it’s a chaotic place where everyone has a veto on everything; a state where people say no; a state where business is wrapped up in bureaucracy and red tape; a state our children leave, searching for opportunity; a state with more of a past than a future.
Some things have not changed. California’s physical endowment is still wonderful. The state is blessed with broad oak-studded valleys, incredible deserts, magnificent mountains, hundreds of miles of seashore, and an optimal climate. California’s location on the Pacific Rim situates the state to profit from growing international trade with the dynamic Asian economies. California didn’t change, Californians changed. Californians have forgotten basics that Pat Brown knew instinctively.
How did California get to this point? How did it move from Pat Brown’s aspirational California to today’s sad-sack version? What did Pat Brown know in 1960 that Californians now forget?
First thing: Pat Brown knew that quality of life begins with a job, opportunity, and an affordable home. Other Californians in Pat Brown’s time knew that too. His achievements weren’t his alone. They were California’s achievements.
It seems that California has forgotten the fundamentals of quality of life. Instead, the state has embraced a cynical philosophy of consumption and denial. The state’s affluent citizens celebrate their enjoyment of California’s pleasures while denying access to those less fortunate, denying not only the ticket, but the opportunity to earn the ticket. At best California offers elaborate social services in place of opportunity.
Today, too many Californians don’t rely on the local economy for their income. For them, quality of life has nothing to do with jobs, opportunity, or affordable homes. Many see the creation of new jobs as bad, something to be avoided. They see no virtue in opportunity. They have theirs, after all. It is their attitude that if someone else needs a job, let them go to Texas; if people are leaving California, so much the better.
They see someone else’s opportunity as a threat to them. Perhaps the upstarts will want a house, which might obstruct their view. They see economic growth as a zero sum game. Someone wins. Someone loses.
This type of thinking is unsustainable. Opportunity is not a zero sum game. It may be a cliché, but it is true, that if something is not growing it is dying. Many of the things that make California the place it is are not part of our natural endowment. The Yosemite Valley is part of the state’s natural endowment, but the Ahwahnee Hotel is not. Monterey, Santa Barbara, San Francisco, the wine countries, and California’s many other destinations were made possible and built because of economic growth. Will California add to this impressive list in the 21st century?
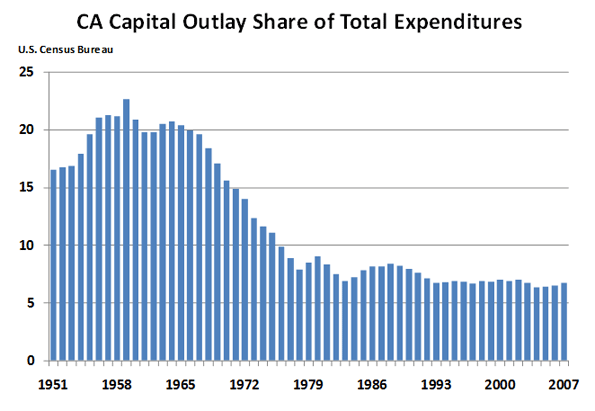
Not likely. Today, we are not even maintaining our infrastructure. Infrastructure investment’s share of California’s budget has declined for decades. In Pat Brown’s day California often spent over 20 percent of its budget on capital items. Today, that number is less than seven percent. It shows.
Pat Brown also knew that with California’s natural endowment, all he had to do was build the public infrastructure and welcome business, business will come. Too many today act as if they believe that business will come, even without the infrastructure or a welcoming business climate. Indeed, many Californians – particularly in the leadership in Sacramento – seem to think that business will come no matter how difficult or expensive the state makes doing business in California. This is just not true.
California needs to embrace opportunity and economic growth. It is necessary if California is to achieve its potential. It is necessary if California is to avoid a stagnant future characterized by a bi-modal population of consuming haves and an underclass with little hope or opportunity and few choices, except to leave.
Bill Watkins is a professor at California Lutheran University and runs the Center for Economic Research and Forecasting, which can be found at clucerf.org.