The preferred story for California’s economy runs like this:
In the beginning there was prosperity. It started with gold. Then, agriculture thrived in California’s climate. Movies and entertainment came along in the early 20th Century. In the 1930s there was migration from the Dust Bowl. California became an industrial powerhouse in World War II. Defense, aerospace, the world’s best higher education system, theme parks, entertainment, and tech combined to drive California’s post-war expansion.
Then, in the evening of November 9th, 1989, the Berlin Wall came down. On December 25, 1991, the Soviet Union was dissolved. The Cold War was over. America responded by cutting defense spending and called the savings the Peace Dividend.
California paid that peace dividend. A huge portion of California’s military industrial complex was destroyed. The aerospace industry was downsized, never to come back. Hundreds of thousands of well-paying manufacturing and engineering jobs were lost.
The ever-resilient California bounced back though. Tech, driven by an entrepreneurial culture and fed by California’s great universities drove California’s economy to new heights.
Then, there was the dot.com bust. A mild national recession was much more painful for a California dependent on its tech sector. Eventually California recovered. California’s tech sector and climate, aided by a housing boom, restored California’s prosperity.
The housing boom was followed by a housing bust. Again, California paid a high price, and unemployment skyrocketed to 30 percent above the national average.
Today, California is recovering. Its tech sector is once again bringing prosperity to the state. Furthermore, California’s green legislation is providing the motivation for a brave new future of economic growth and environmental virtue.
The story is true through the Peace Dividend. California did pay a high price for the collapse of the Soviet Union. California’s defense sector did begin a decline, and it never recovered. But, defense recovered in other places, as the country expanded defense spending by 21 percent in the 2000s. The United States has constantly been engaged in wars and conflicts for over a decade. On a real-per-person basis, the United States is spending as much on defense as it has at any time since 1960.
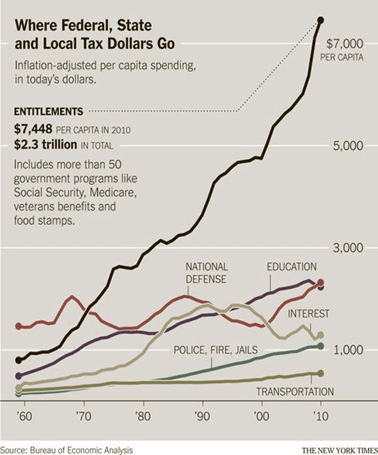
But when it comes to the present, the narrative falls down. Defense has rebounded, but not in California. California’s defense sector is small and declining, not because of a permanently smaller U.S. defense sector, but because of something about California.
California’s tech sector did boom after the collapse of California’s defense sector, but that doesn’t mean that California recovered. In fact, much of California never recovered. It’s the aggregation problem.
The 1990s’ recovery was largely a Bay Area recovery. Los Angeles hardly saw any uptick in employment. Here is a chart comparing Los Angeles County’s jobs growth rate with the San Jose Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA):
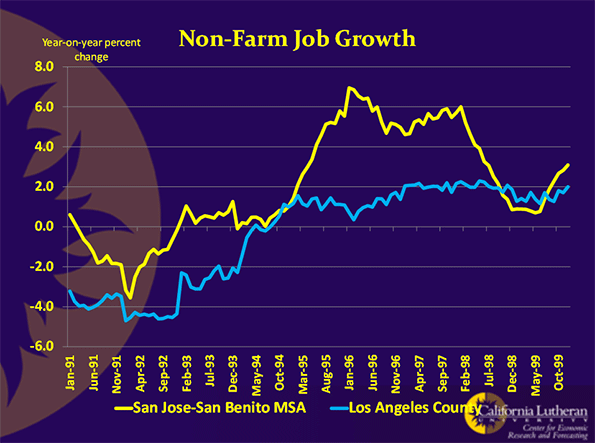
San Jose probably had California’s fastest growing job market in the 1990s. Los Angeles was not the states slowest. Still, the differences are striking.
A few years ago, a couple of my graduate students looked at California data from 1990 through 1999. They divided California into two regions, the Bay Area and everywhere else. The Bay Area was defined as Sonoma, Marin, Napa, Solano, Contra Costa, Alameda, Santa Clara, Santa Cruz, San Mateo, and San Francisco counties. Using seven indicators of economic growth, they performed relatively simple statistical tests to see if the two geographies experienced similar economies. The indicators were employment, wages, home prices, bank deposits, population growth, construction permits, and household income.
By every measure except population growth, the Bay Area outperformed the rest of the state. The exception was probably due to commuters to the Bay Area, given that region’s exceptionally high housing prices.
Some economists will tell you that California saw faster-than-national job growth from the mid 1990s until the great recession. This is another aggregation problem. The claim is technically true, but only in the sense that California had a higher proportion of the nation’s jobs in 2007 than it did in 1995. If you look at annual data, you will see that California’s share of the nation’s jobs only grew from 1995 through 2002. Since then, California’s share of United States jobs resumed its decline:
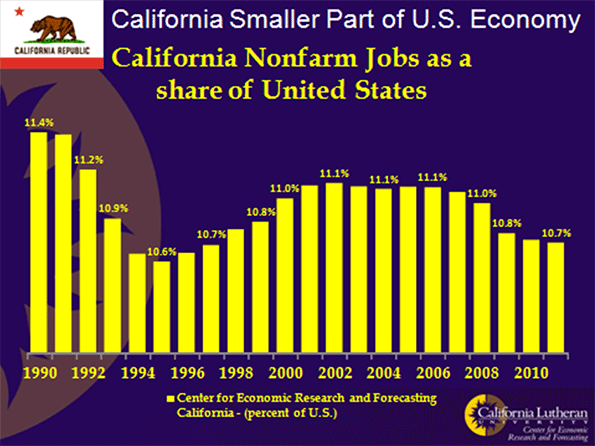
In reality, California never recovered from the dot.com bust. California, perhaps the best place on the planet to live, couldn’t keep up in a housing boom. Something was wrong.
California had lost its mojo.
Opportunity is now greater outside California than inside California. For almost 150 years, California was as widely known for its opportunity as it was for its sunshine. The combination was like a drug. George Stoneman, an army officer destined to become California’s 15th governor, spoke for millions when he said "I will embrace the first opportunity to get to California and it is altogether probable that when once there I shall never again leave it."
They did come to California, and they made an amazing place. Opportunity-driven migrants are different than other people. They take big risks to leave everything they know for an uncertain future in a new place. They are confident, bold, and brash. California became just as confident, bold, and brash. The Anglo-American novelist Taylor Caldwell spoke the truth when she said "If they can’t do it in California, it can’t be done anywhere."
That was then. Today, California can’t even rebuild an old Hotel.
The Miramar Hotel is a partially-demolished eyesore beside the 101 Freeway in Montecito, just south of Santa Barbara. The Hotel’s initial structure was built in 1889. Over the years, it was expanded to a 29 structure luxury hotel and resort. In September 2000 it was closed for renovations which were expected to take 18 months. That was when the fighting started. Community groups, neighbors, and governments all had their own idea of what the Miramar should be. Two owners later, and after millions of dollars, the future to the Miramar is still uncertain.
The Miramar Hotel is a case study of what is wrong with post-industrial California, precisely because it should have been easy, and because it is not unique. Everything is hard to do in California. The state that once moved rivers of water hundreds of miles across deserts and over or through mountain ranges can’t rebuild a hotel.
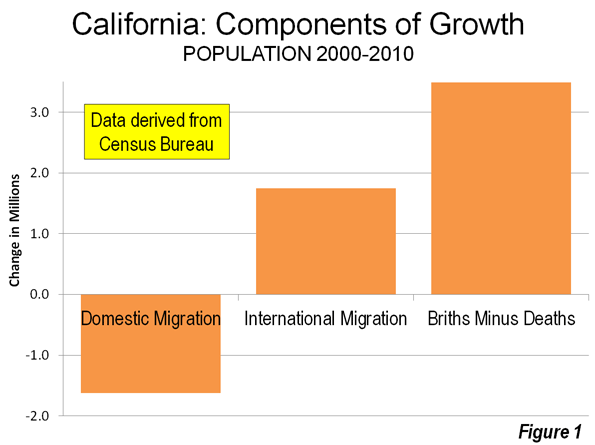
The situation will get worse. California has become the place people are leaving. The following chart shows that for 20 years more people have left California for other states than came to California from other states:
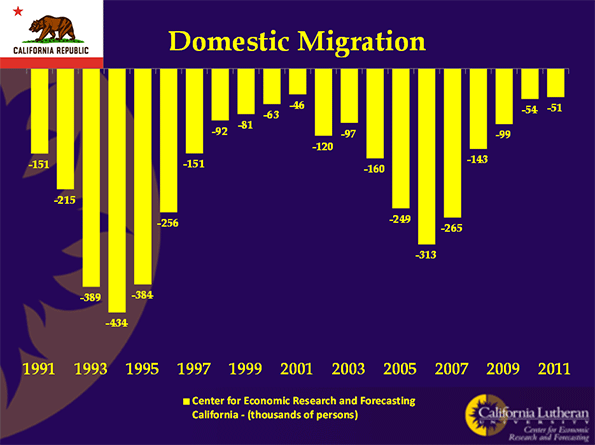
California’s population is still increasing because of births and international immigration.
Two decades of negative domestic migration has taken its toll. Millions of risk-taking, confident, bold, and brash people have left California. They took California’s mojo with them.
That seems pretty clear when you look at some statistics: California’s unemployment is way above the national average. With only about 12 percent of the nation’s population, California has over 30 percent of the nation’s welfare recipients. San Bernardino has the nation’s second highest poverty rate among cities over 200,000.
Sometimes though, aggregated data can hide California’s weakness, and some, representing the always-present constituency for the status quo, use these data to deny that California’s future is any less golden.
Most recently, those representing the constituency for the status quo have used California’s aggregated jobs data to argue that all is well in California. They argue that California’s tech sector is leading California to a new golden future.
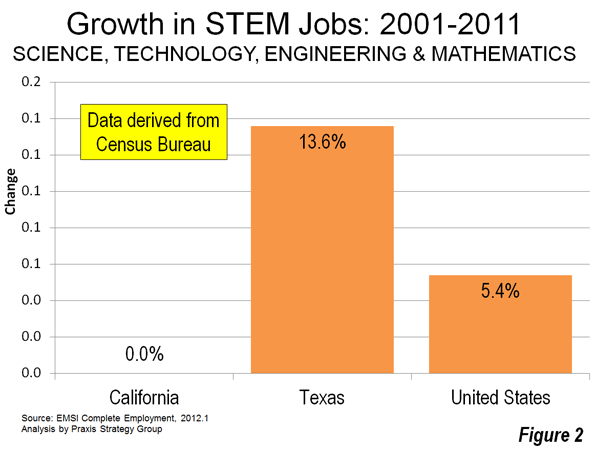
Year-over-year data confirm that, through August 2012, California gained jobs at a faster pace than the United States. Once again, though, that growth is largely confined to one industry and one geography. California’s tech sector is recovering, and amidst a generally weak recovery, it appears strong enough to generate pretty impressive aggregated results. If we disaggregate California’s data, we will find that there is not just one California. There is a rich and mostly coastal California, with a few smaller inland counties on the San Francisco-Lake Tahoe corridor. Another California is very poor and mostly inland.
Here’s a list of California’s poorest counties by poverty rate:
| County |
Poverty Rate |
Child Poverty Rate |
Rank |
|
Del Norte |
23.5 |
30.6 |
3 |
|
Fresno |
26.8 |
38.2 |
1 |
|
Imperial |
22.3 |
31.8 |
6 |
|
Kern |
21.4 |
30.3 |
10 |
|
Kings |
22.5 |
29.7 |
5 |
|
Madera |
21.7 |
31.7 |
8 |
|
Merced |
23.1 |
31.4 |
4 |
|
Modoc |
21.9 |
32.5 |
7 |
|
Siskiyou |
21.5 |
30.7 |
9 |
|
Tulare |
33.6 |
33.6 |
2 |
Here’s a list of California richest counties by poverty rate:
| County |
Poverty Rate |
Child Poverty Rate |
Rank |
|
Calaveras |
11.1 |
18.3 |
10 |
|
Contra Costa |
9.3 |
12.7 |
4 |
|
El Dorado |
9.4 |
11.6 |
5 |
|
Marin |
9.2 |
10.9 |
3 |
|
Mono |
10.8 |
15 |
8 |
|
Napa |
10.7 |
14.7 |
7 |
|
Placer |
9.1 |
10.7 |
2 |
|
San Mateo |
7 |
8.5 |
1 |
|
Santa Clara |
10.6 |
13.3 |
6 |
|
Ventura |
11 |
15.3 |
9 |
There are some big differences here. The percentage of Fresno’s children living in poverty is four and half times the percentage of San Mateo children living in poverty. In fact, the data for California’s poorest counties looks like third-world data.
When disaggregated, the job-growth data shows the same story. Through 2012’s second quarter, jobs in the San Jose MSA were up 3.6 percent on a year-over-year basis. In Los Angeles, jobs were up only 1.1 percent, while in Sacramento they were up only 0.6 percent. For comparison, U.S. jobs were up about 1.3 percent for the same time period.
You can perform this analysis for all types of data. When the data are disaggregated, the story is always the same. It’s telling us that California needs to get its mojo back, and the current tech boom is likely not to be enough for its recovery.
Bill Watkins is a professor at California Lutheran University and runs the Center for Economic Research and Forecasting, which can be found at clucerf.org.
Unemployment photo by BigStockPhoto.com.