President Obama’s San Francisco fundraiser with the tech elites today, along with the upcoming IPO for Facebook, marks the emergence of a new, potentially dominant political force well on its way to surpassing Hollywood and even Wall Street as the business bulwark of the Obama Democratic Party.
In 2008 the industry gave Obama more than $9 million, three times what it raised for any other politician; it was the first time the digerati outspent Hollywood. The numbers will surely go up this year.
“The Facebook instant millionaires and billionaires are about all Democrats,” said Morley Winograd, a longtime California Democratic activist and chronicler of information-age politics. “There’s an enormous amount of power residing there—and it will only get greater.”
Even when they’ve competed with and acted like more established power brokers, the digital ruling class are treated with kid gloves compared to other wealthy elites, rarely suffering the disdain aimed at amoral bankers and at Hollywood’s general venality. Instead, the creators of our iPhones, social networks and Twitter accounts are held up as tool makers and business titans. That esteem is most pronounced among millenials, 75 percent of whom use social media, more than twice the percentage for boomers, according to Pew. When asked what makes their generation “unique,” the most common answer to the open-ended question is technology.
Those who will benefit most from Facebook and other IPOs resemble the “one percent” about as much as Wall Street.
In effect, it’s OK to be in the “1 percent”—or even the .0001 percent—if you develop nifty devices and invest in green companies. "We live in a bubble, and I don’t mean a tech bubble or a valuation bubble. I mean a bubble as in our own little world," Google chairman Eric Schmidt recently told the San Francisco Chronicle. "And what a world it is: companies can’t hire people fast enough. Young people can work hard and make a fortune. Homes hold their value. Occupy Wall Street isn’t really something that comes up in daily discussion, because their issues are not our daily reality."
For their part, the “Occupiers” who struggled mightily to shut down the blue-collar Port of Oakland seem to never have considered an action against the pampered techies at Facebook’s lavish campus.
The new plutocrats are unburdened by the obligations that come with existing large institutions; with no union presence, they don’t have to worry about anxious retirees or redundant older workers. Green pet causes that align with their financial interests buy more cover from the left, while conservatives, who rarely see anything wrong with extreme wealth, seem somewhat unconscious about the political orientation of the emerging new elite. Ninety-two percent of Facebook executive donations so far this year went to Democrats. This exceeds even the rock-solid support the Democrats enjoy among more established firms like Google and Apple, where support for Democrats runs to the high 80s. Although its former CEO, Meg Whitman, ran as the Republican candidate for governor in 2010, 96 percent of eBay-associated donations went to Democrats. The Seattle area’s two top digital firms, Amazon and Microsoft make two thirds or more of their donations to Democrats.
The Obama administration’s opposition to the anti-piracy bills SOPA and PIPA came despite intense lobbying for the bill by his party’s long-time allies in Hollywood. Whatever the bills’ failings, their defeat also formally introduced the new power of the digerati moguls and their millions of followers. The presence of Steve Jobs’s wife, Lauren, as Michelle Obama’s guest at the State of the Union speech further cemented the ever-closer ties between the valley’s upper echelon and the president’s party.
In California, the alliance between progressive Democrats and high tech is palpable. The digital elite has been a consistent backer of Gov. Jerry Brown’s jihad on greenhouse gases, helping finance the campaign against a 2010 measure intended to reform state’s draconian and likely job-killing energy and land-use laws. Google has emerged both as a key backer of the state’s climate-change politics and sought to profit by investing nearly a billion dollars in renewable-energy companies. These firms in turn depend on the state’s strict mandates on utilities to use “green” electricity for their revenues. It’s no coincidence that prominent valley VCs have been particularly active in alternative-energy firms such as Solyndra.
Brown and the Democratic Party increasingly have come to regard these companies as a potential source of fiscal salvation for the perennial cash-short state. As the Golden State has banked on the valley, the tech firms have become ever more indispensable and now are even dipping their toes in the grubby waters of municipal politics, helping finance the campaign of San Francisco Mayor Ed Lee—who generously concocted new tax breaks for local firms such as Twitter and Zynga.
The leftward shift by tech firms is a fairly recent development. In the 1970s and 1980s, the formative period for Silicon Valley, the area was politically contested. Valley constituencies routinely sent to Congress moderate Republicans like Pete McCloskey, Ed Zschau, and Tom Campbell. Today the GOP is virtually absent from the valley at all levels of government.
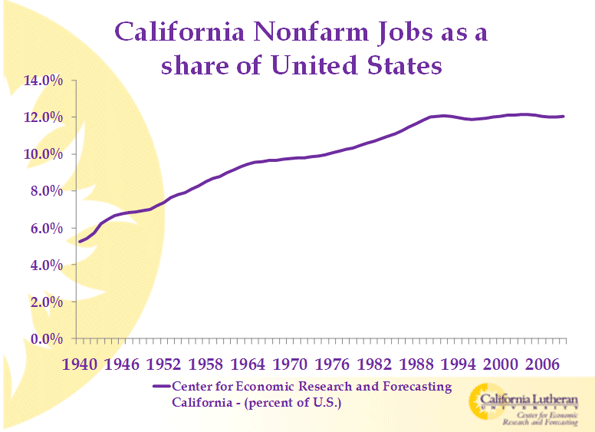
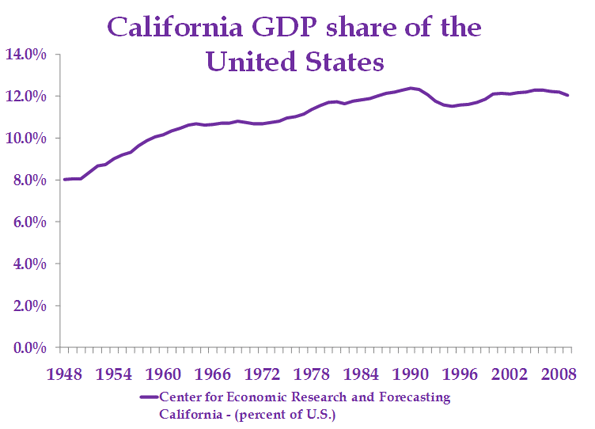
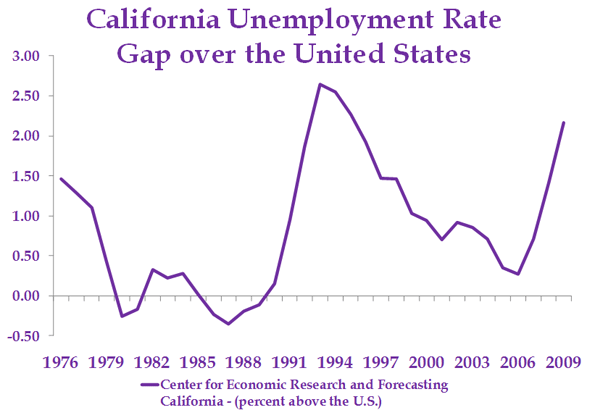
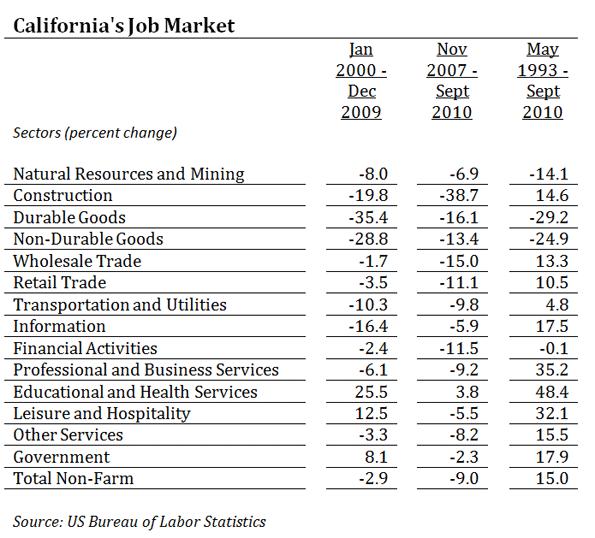
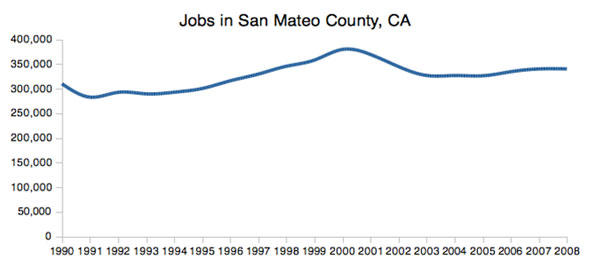
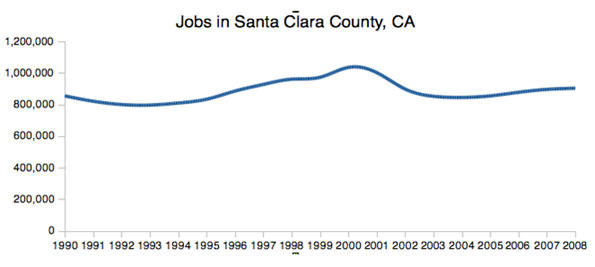
Some old-line companies, like Hewlett-Packard and Intel, still tend to be fairly evenhanded in their political donations, but they are increasingly rare. Long-time valley maven Leslie Parks explains that the shift came as the Valley’s economy changed. In the 1980s and 1990s—the area’s greatest period of growth—its roots stood solidly in high-tech manufacturing. Now it focuses almost exclusively on product design and information: software, search, and social media. Over the past decade the San Jose area lost one third of its industrial workforce while the neighboring San Francisco region lost some 40 percent—the largest consistent loser among the nation’s 51 metropolitan areas.
High-tech firms once concerned themselves with many of the same things as other manufacturing companies. They worried about electricity rates, obtrusive environmental legislation, high housing prices, and dysfunctional public education. Many naturally supported Republicans, or business-oriented Democrats.
But as tech separated from industry, the valley moved leftward.
Today’s digital aristocrats manufacture virtually nothing here; anything made in volume is produced outside California and usually out of the country. Software-based firms don’t worry about energy costs, since they can simply place their heavy user server farms in places like the Pacific Northwest with low electricity rates. They do not use much in the way of toxic chemicals or groundwater, making it easier to avoid scrutiny and harassment from California’s hyper-aggressive environmental regulators. Because they rely on an increasingly narrow band of highly educated employees from elite schools, the secular decline of the state’s higher education system hardly impacts them. And as many of their employees are young and tend to buy houses after collecting the spoils of an IPO, even high housing costs and poor public K-12 education don’t matter much.
The growing diversity of the valley has also helped the Democrats. Although relatively few Latinos or African-Americans work in the new companies, new immigrants from Asia and the Middle East and their offspring abound. “You had a big change in diversity, and let’s face it the Republicans do not do well with diversity,” said Parks, who is Japanese-American. “The Democrats, particularly Obama, recognized appealing to these people was a necessity.”
Many who celebrate this emerging power elite are still slow to recognize that they are in these company’s sights. As we become more dependent on internet based news and entertainment, cultural power is migrating away from New York publishers and Los Angeles studios towards Palo Alto and Menlo Park. Old-line media firms such as newspapers, book companies and the major networks may find themselves overmatched.
This growing power may do more to concentrate economic power than any development since the Second World War. With their stockpile of personal data on their hundreds of millions of users, firms like Google and Facebook could prove the biggest threat to privacy since Big Brother. As Jason Lanier, a scholar-at-large at Microsoft Research, noted in a recent New York Times op-ed piece, the same companies that led the fight to keep the Internet “free” want to sell hundreds of billions of dollars in advertising built from that free, user-provided information.
While the old valley empowered people by supplying technology, says Chicago law professor Lori Andrews, social-media firms instead leverage our personal information into fodder for not just advertisers but people reviewing job applications, medical records, and more.
What’s more, the dominant firms are rapidly becoming oligopolies. In the old days, valley companies battled over everything from semiconductor chips and disk drives to servers and operating systems. In contrast, today’s digital industry tends to gravitate to the best-financed (usually by venture capital) and most well-connected companies. Microsoft, for example, still controls 90 percent of the operating-system-software industry; Facebook is likely to continue with a 60 percent to 70 percent share of the social-media marketplace. Google enjoys a higher than 80 percent share in search.
This is a degree of control that exists in few older industries. Like the railroads of the old robber barons, those few firms who control the limited number of digital platforms can limit the profitability of smaller would-be competitors—and could end up slowing the rate of innovation in order to maintain their own positions. They may wear T-shirts to work, but the tycoons of Silicon Valley are, in some respects, J.P. Morgan’s true heirs.
Populism may now be de rigeur inside of the Democratic Party, but the world being created by the new digital haute bourgeoise is anything but social democratic. Parks notes that the lower end of the valley economy, like janitors or food-service workers, generally labor for flinty-eyed outside contractors so they share as little as possible of the wealth collected by higher-skilled employees.
Even Silicon Valley’s geography is increasingly unfriendly to the mass middle class, much less the aspiring working class. Due largely to strict land-use regulations, median housing costs, even adjusted for income, are among the highest in the nation, more than twice as high as those in places like Raleigh, Salt Lake City, Houston. or Dallas. With a 2,300-square-foot home in Palo Alto going for nearly $1.8 million, the digital heartland is largely off limits for most of us.
Those who will benefit most from Facebook and other IPOs resemble the “1 percent” about as much as Wall Street. They may see themselves as “progressive,” but they create few broad-based opportunities for members of the middle and working class. A bit of their wealth may trickle down to Democratic politicians, but the rest of us, as dependent as we have become on their technology, have reaped little financial benefit from them. Whatever the value of their creative efforts, the new digital aristocracy’s political ascendency threatens both the populist roots of the Democratic Party and perhaps the delicate social balance of our Republic as well.
This piece originally appeared in TheDailyBeast.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University, and contributing editor to the City Journal in New York. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050, released in February, 2010.
Official White House Photo by Pete Souza.