Sydney’s Daily Telegraph announced on April 20 that Sydney is more dense than Mexico City, London, Los Angeles and Paris. Of course, anyone who has been to Mexico City or London knows that this is untrue and it may surprise some that Sydney is not even as dense as Los Angeles.
The article never indicates, quite for sure, what it means by Sydney, the Sydney city council area (the urban area’s core local government authority, or LGA) or the Sydney urban area. Nor does the article provide an overall density, instead only indicating that there are 8,800 persons per square kilometer in "Sydney’s east" and 7,900 per square kilometer in "Sydney City’s west."
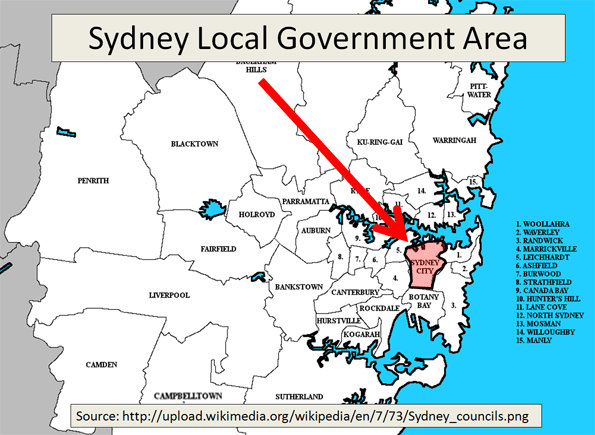
In fact, the figures are from the latest statistical local area estimates of the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) for 2010, and dated March 31, 2011. A "statistical local area" is a part of an LGA (See map: Sydney Local Government Area). The statistical local areas cited by The Daily Telegraph are Sydney-East and Sydney-West, which have a combined density of 8,300 per square kilometer. The small size of the Sydney-East and Sydney-West statistical local areas is illustrated by the fact that each is about the same size as the Sydney Olympic Park.
Comparing Urban Area Densities: The Daily Telegraph’s contention results from a profound misunderstanding of urban geography. The result was a comparison of urban geographies that are not comparable.
The Daily Telegraph compares the density of these two small areas of the Sydney LGA, with the urban area densities of Mexico City (which the Daily Telegraph places at 8,400), London (5,100), Los Angeles (2,750) and Paris (3,250). These figures were taken from an earlier edition of Demographia World Urban Area. (Our latest Demographia World Urban Area data, including estimated population densities for all urban areas in the world of more than 500,000 population is here). Urban areas are areas of continuous urban development.
The appropriate Sydney geography for comparison to the urban area populations of Mexico City, London, Los Angeles and Paris is the urban area (the international term), which is called the urban centre by ABS (See map: Sydney Urban Area).
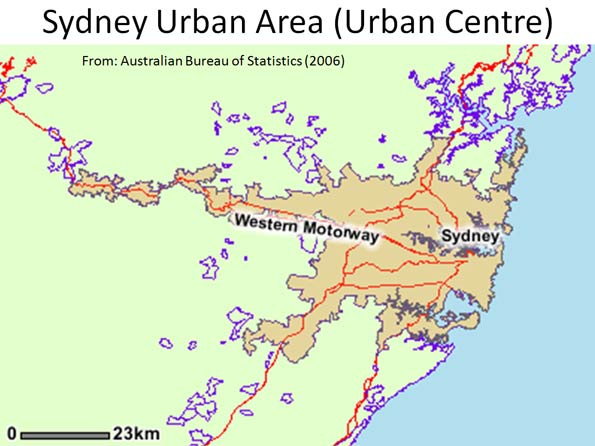
The Sydney urban centre covers an area extending south to Campbelltown, north to Palm Beach and well into the Blue Mountains on the Great Western Highway. According to the ABS, the Sydney urban area (urban centre) had a population of 3.641 million in 2006 (latest available data), and covered a land area of 1,788 square kilometers. This means that the population density of the Sydney urban area was 2,037 in 2006. Thus, the Sydney urban area has a lower density than all four international urban areas used in The Daily Telegraph comparison (Figure 1).
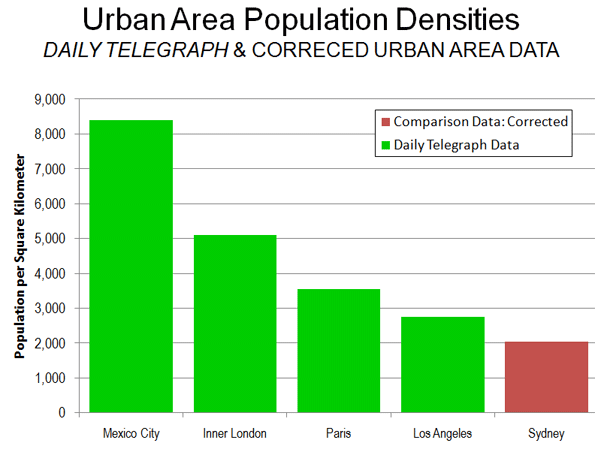
If the Sydney urban center were as dense as the Los Angeles urban area, the population would be 5 million, instead of 3.6 million. If the Sydney urban centre were as dense as the Mexico City urban area, the population would be 15 million.
Comparing Core Densities: The small area densities that The Daily Telegraph cites are also smaller than those that exist in the core areas of the cited international urban areas (Figure 2).
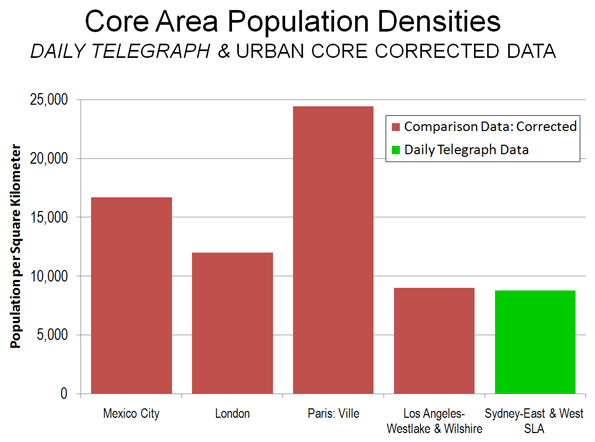
- In Mexico City, the delegation (district) of Ixtacalco has a population density double that of the Sydney-East and Sydney West statistical local areas (approximately 17,000), in an area nearly twice as large.
- The 2001 census placed the inner London borough of Kensington and Chelsea at 12,000 persons per square kilometer, in an area approximately the same size as Sydney-East and Sydney-West combined.
- The ville de Paris has a population density of more than 24,000 per square kilometer, nearly three times that of the combined Sydney-East and Sydney-West statistical local areas. The ville de Paris covers approximately eight times as much land area and smaller area densities are even higher.
- The 2000 census placed the adjacent Wilshire and Westlake Community Districts of Los Angeles at 9,000 per square kilometer. This is slightly higher than the density of the combined Sydney-East and Sydney-West statistical local areas, in an area nearly four times as large.
The Sydney urban center and statistical local area data is summarized in the table.
The Australian Population Debate: An important public policy debate is under way in Australia on the issue of population growth. As Ross Elliot indicated (Malthusian Delusions Grip Australia), some interests believe that the nation is running out of land. In fact, only 0.3 percent of Australia’s land area is urban, a figure one-tenth that of the United States. The starting point for these discussions needs to be valid data and an understanding of the terms involved.
| SYDNEY URBAN CENTER & DENSE STATISTICAL LOCAL AREAS |
| Areas Cited by The Daily Telegraph |
|
|
|
|
| |
2006 Population |
Land Area (Square Kilometers) |
Density |
2010 Density |
| Sydney-East Statistical Local Area |
46,738 |
6.0 |
7,790 |
8,799 |
| Sydney-East Statistical Local Area |
38,382 |
5.7 |
6,734 |
7,852 |
| Combined |
85,120 |
11.7 |
7,275 |
8,338 |
| Share of Sydney Urban Area (Urban Centre) |
2.3% |
0.7% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Balance of Urban Area (Urban Centre) |
3,556,301 |
1,776.4 |
2,002 |
Not Available |
|
|
|
|
|
| Total Sydney Urban Area (Urban Centre) |
3,641,421 |
1,788.1 |
2,036 |
Not Available |
|
|
|
|
|
| Notes: |
|
|
|
|
| Data from Australian Bureau of Statistics |
|
|
|
|
| Urban centre data available only for census years |
|
|
|




 The fact is that
The fact is that