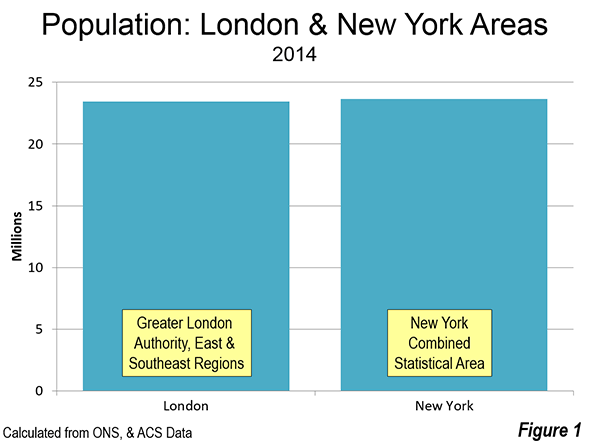
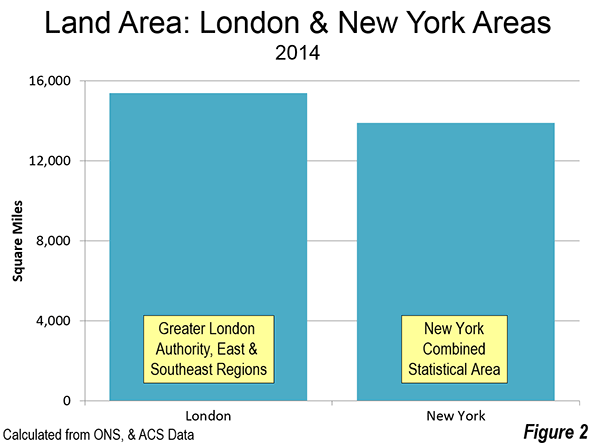
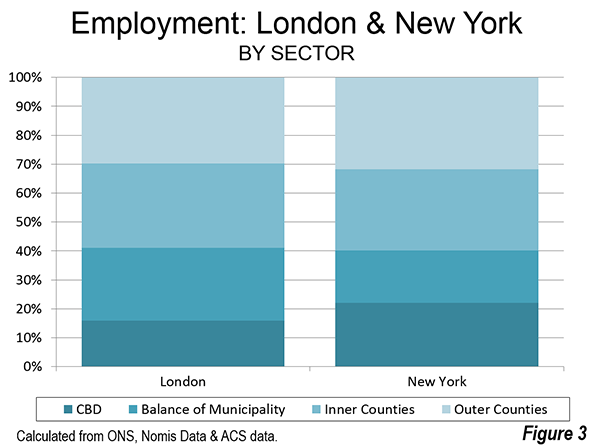
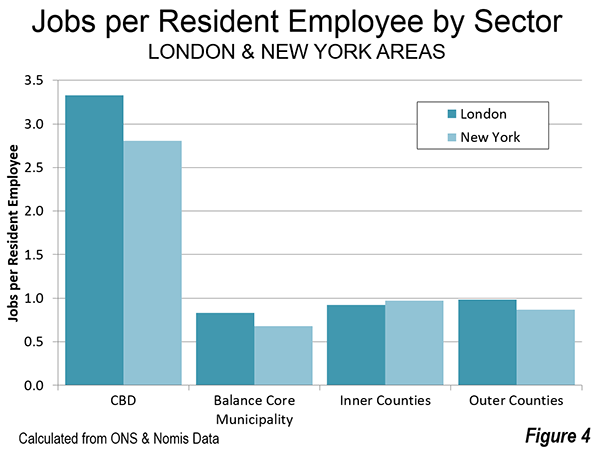
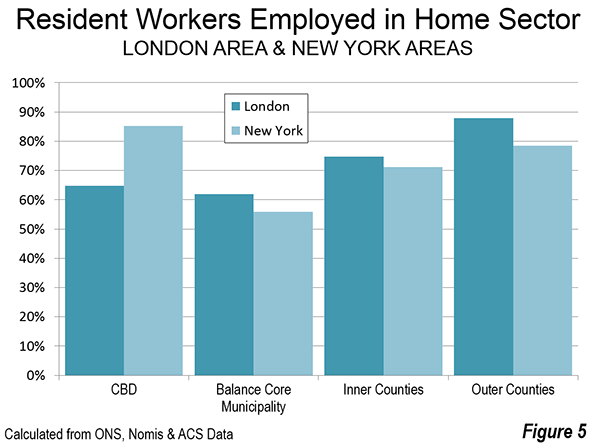
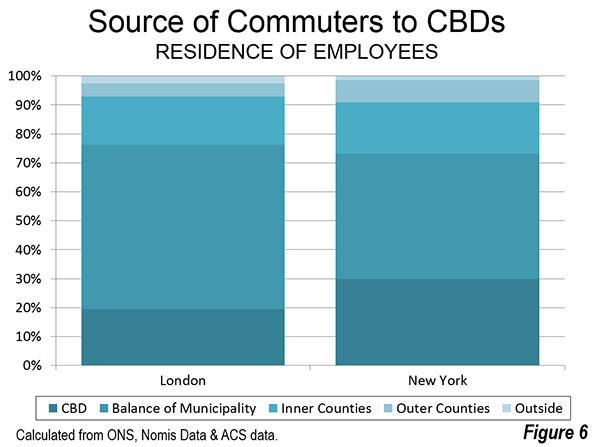
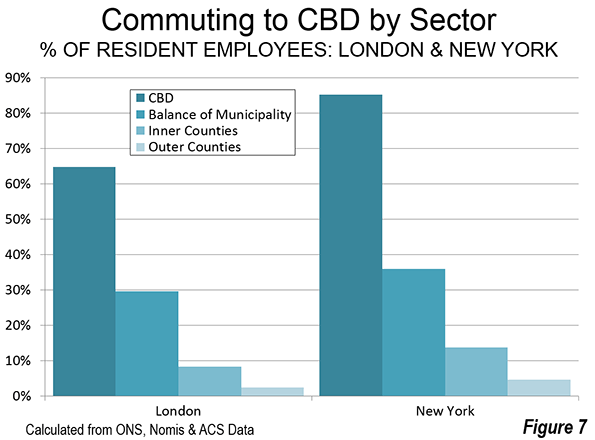
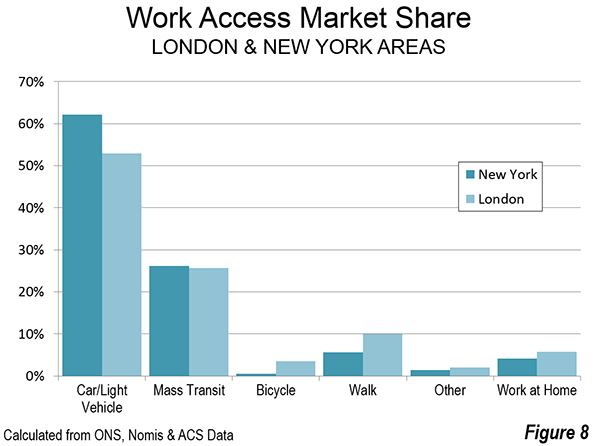
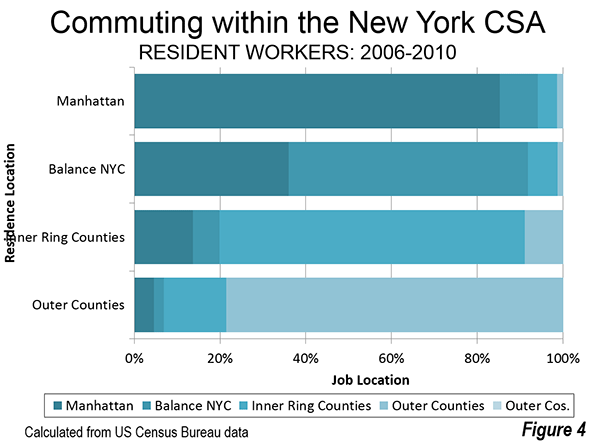
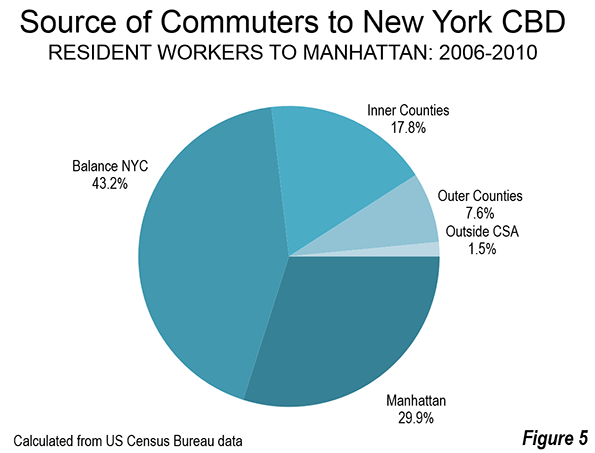
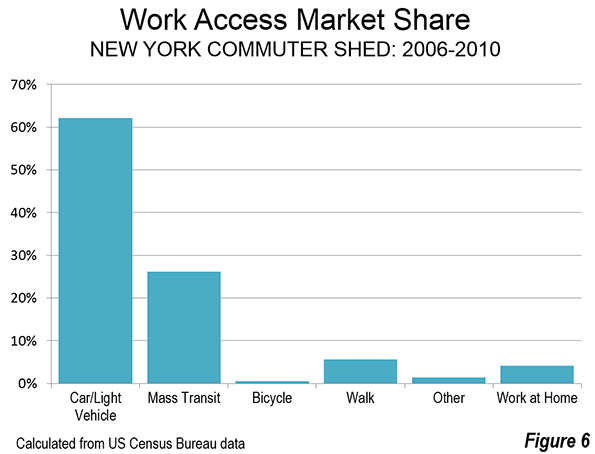
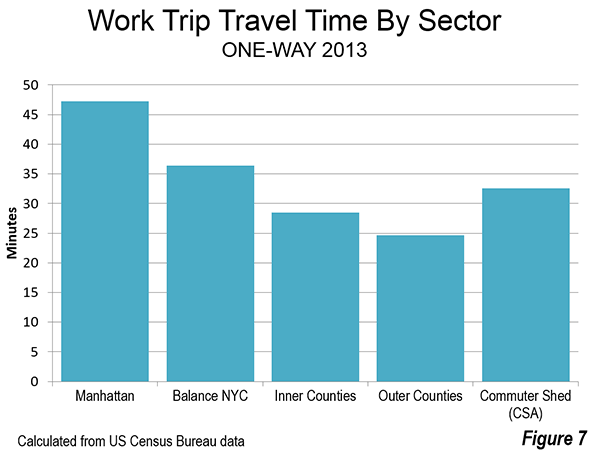
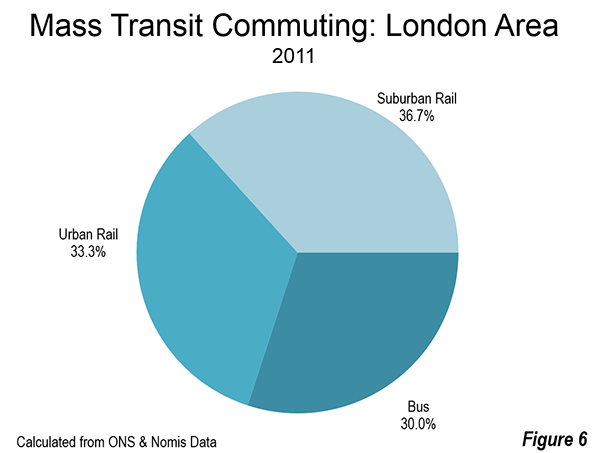St. Petersburg and Moscow are typical destinations in Russia, but if you’re looking for other places to visit, where do you go? I can’t claim to answer that question as I have not fully surveyed the realm, but I did visit the city of Kazan for a day, so want to share a few observations and photos.
Kazan is a city of a bit over a million people about 450 miles east of Moscow (a flight of around 1:20). It’s the capital of the Tatar Republic of the Russian Federation. The Tatars were a nomads of Turkish ethnicity who established an independent kingdom in the region before being conquered by Ivan the Terrible. They are very proud of their unique ethnicity and history, and have obtained a great deal of autonomy (at least as much as exists in Russia). Originally the province was called Tatariya, but they renamed it Tataristan. To locals, the “-stan” suffix suggests strength and independence on par with other fully independent republics in the region. While they can certainly choose whatever name makes them feel most proud, names ending in “-stan” certainly don’t inspire confidence in America. I don’t think they fully understand the negative brand equity in that term, but don’t let the name scare you off. It’s a modern and as far as I can tell perfectly safe city.
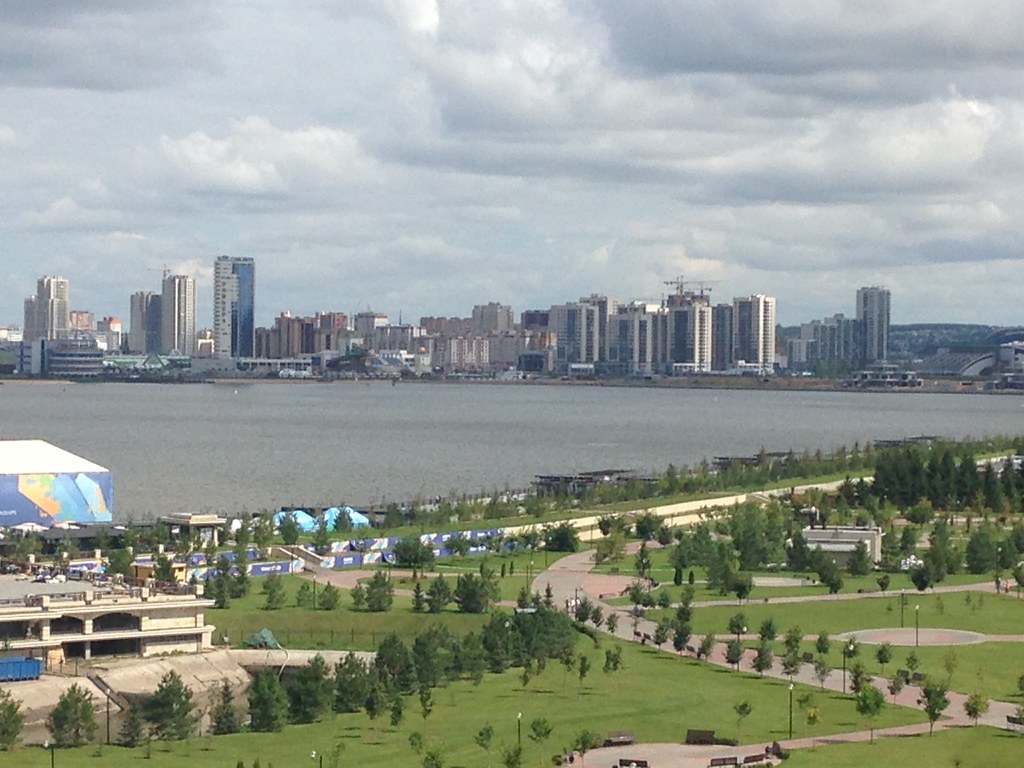
In fact, it’s extraordinarily modern and new. There’s been a vast amount of infrastructure investment, much of it done in conjunction with international sporting events. They hosted the 2013 Summer Universiade (an Olympics for students, I gather), and the 2015 World Aquatics Championship was underway while I visited. They’ve got a brand new airport, brand new freeway network, numerous new buildings, etc.
Looking at Kazan in fact, you might get the impression it’s a boomtown. But it’s not a boom of the type you’d find in the US based on private sector growth. Though the region boasts oil and gas reserves and several manufacturing operations, most revenues go to the federal treasury in Moscow, so it would appear that Putin has showered the region was cash and that is the reason for the construction boom. The difference vs. St. Petersburg, which appeared to be starved for money, was evident. Everything in Russia is more or less state directed, and this is no exception.
Having said that, the state could have invested in purely megalomaniacal projects as has happened in some other regional -stans. Instead a lot has gone into core infrastructure. Yes, some of it is tourist oriented, but the neighborhoods infrastructure I saw was in pretty good shape, and my cab driver said that the city had done a ton of upgrades to neighborhoods streets and such too. They also built a short metro system, though apparently it is under-patronized.
Putin has been favoring the region with money in part to highlight and reward what Russians described to me as “good Muslims.” The Tatar region is about 55% Muslim and 45% Russian Orthodox. The split is basically along ethnic lines (though there’s a segment of Tatars that converted to Christianity). The Muslims in the area have long been known for their moderate brand of Sunni practice, and religious relations have been good, including a high degree of intermarriage (or so I’m told). Google tells me there were some extremist attacks in 2012, so I’m not sure what the status of that is, but I personally wouldn’t let it stop me from visiting there.
The locals are really pushing the religious co-existence angle, which makes sense in a world that is looking for examples of Christianity and Islam getting along. That’s a shrewd marketing strategy.
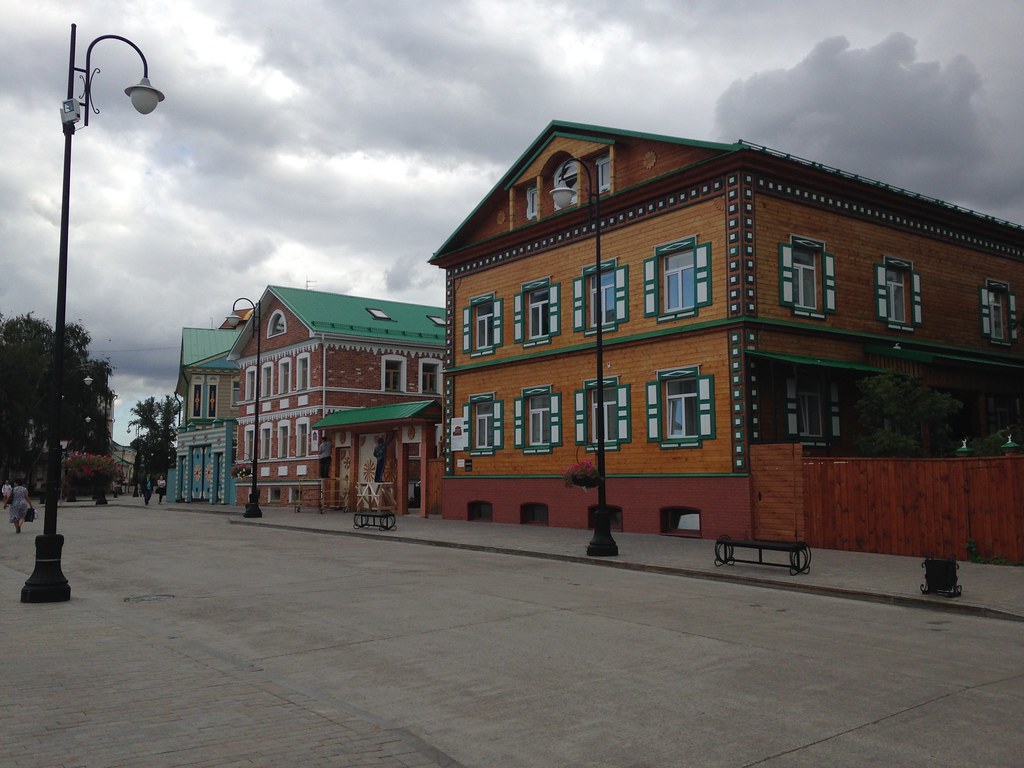
They also have gone beyond the modern and have pushed historic preservation. While no one is going to confuse Kazan for St. Petersburg, they have tried to restore what they have and have focused on obtaining UNESCO certifications. They are also pushing the Tatar cultural angle. There are plenty of elements of regional cuisine and I thought the food was excellent. Of course they would send me to their best places, but since I was only there one day, that didn’t matter. Kazan also has an important university, so has some attributes of a college town. Several famous Russians spent time living in Kazan, including Leo Tolstoy and Maxim Gorky.
Is Kazan a must-see? No. But if you’re interested in checking out a Russian city other than the big two, it’s definitely worth a visit.
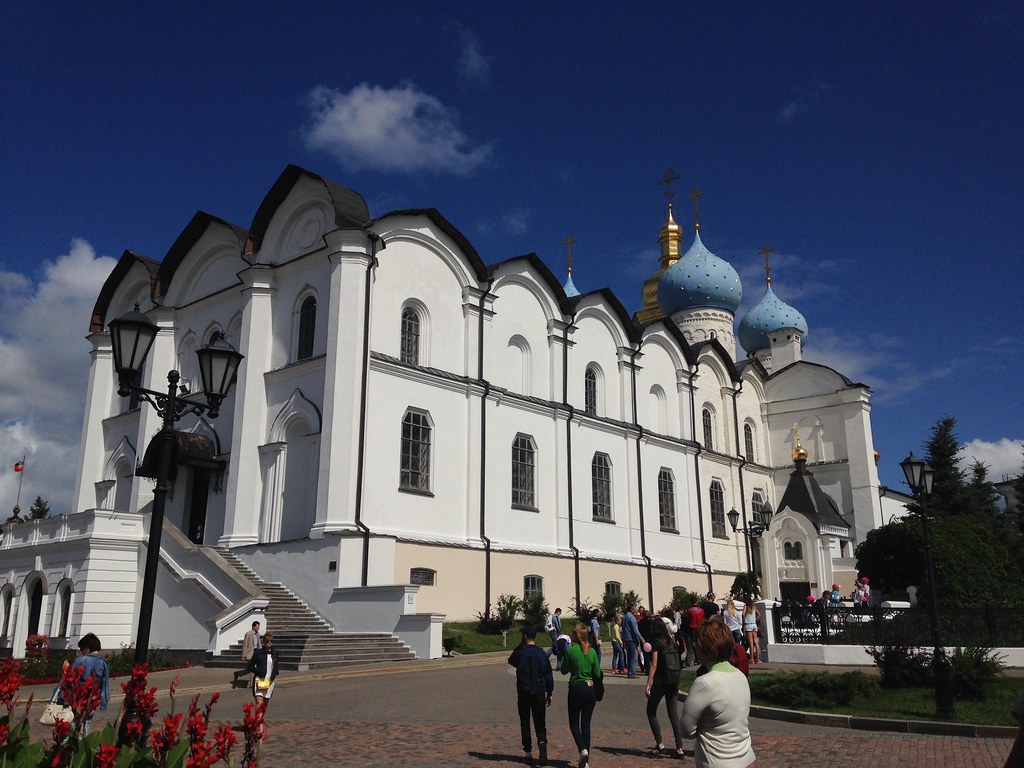
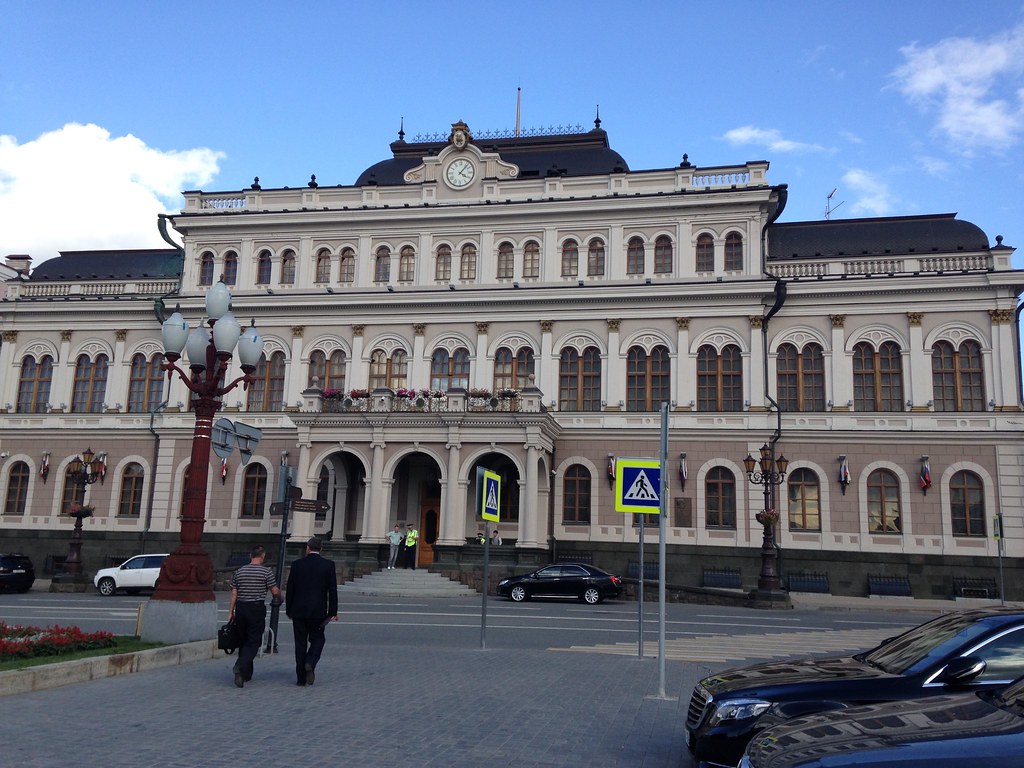
I’ll share a few photos. The one at the top is the main entrance to the Kazan Kremlin. (The term kremlin is an old word meaning “fortress”). Here’s the Russian Orthodox cathedral there:
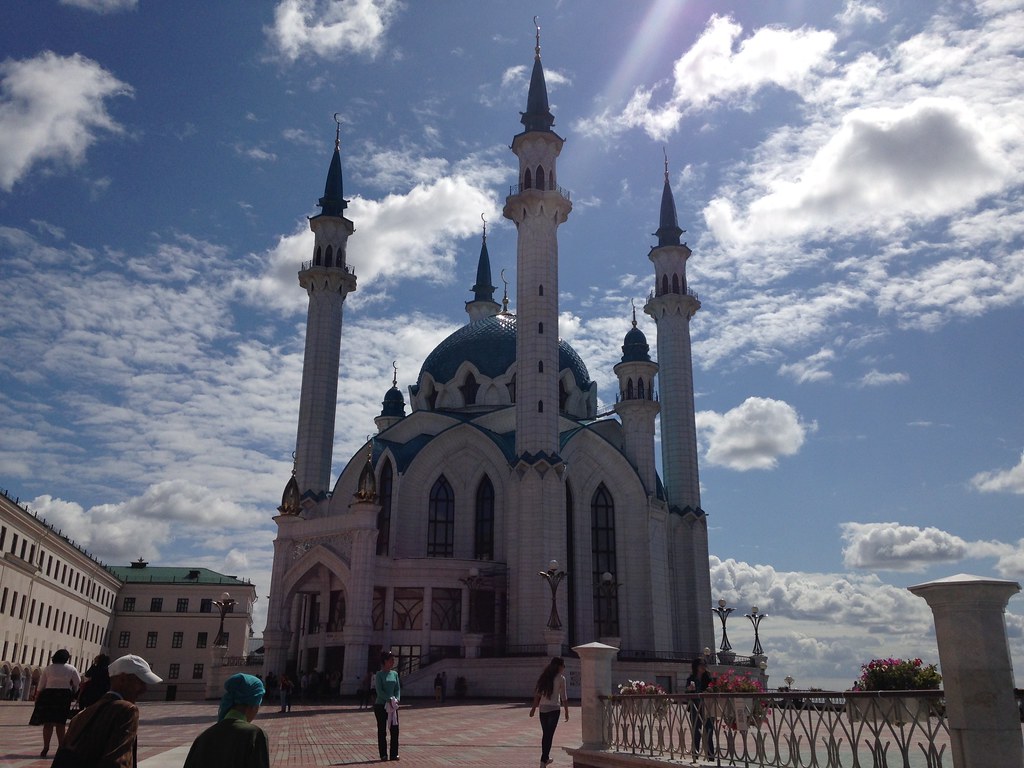
There was originally a mosque in the kremlin that was destroyed when Russians conquered the area. Recently, a new mosque was built on the site to maintain the symbolic religious balance in the area. I think it’s a very nice building.
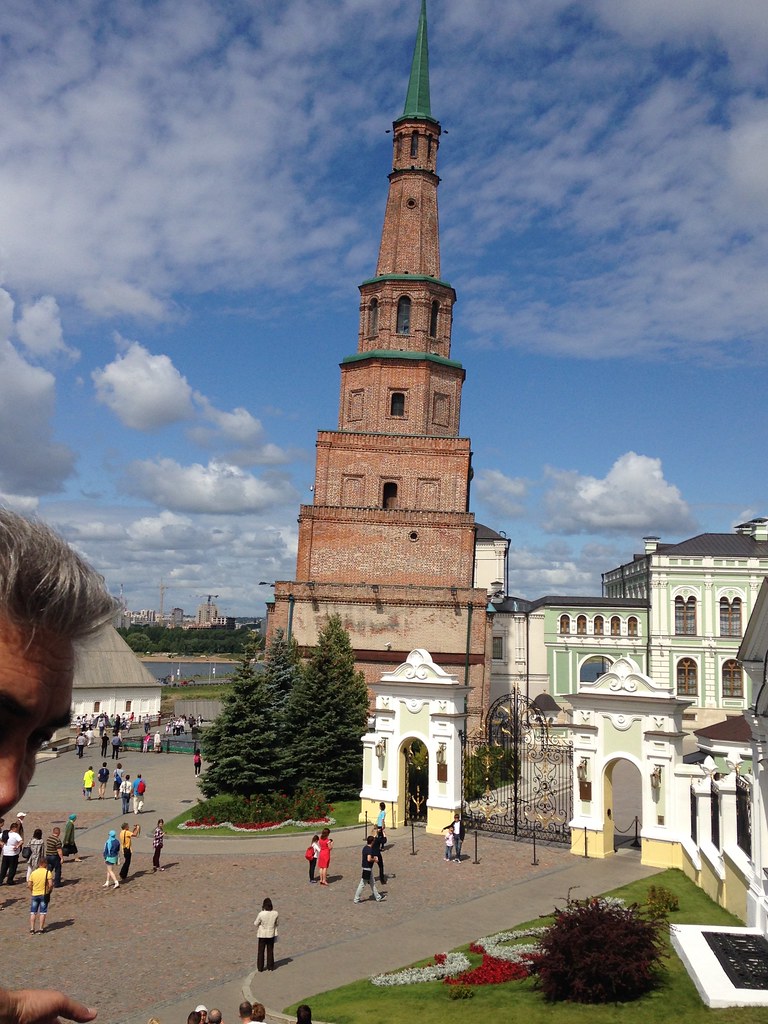
They have their own leaning tower.
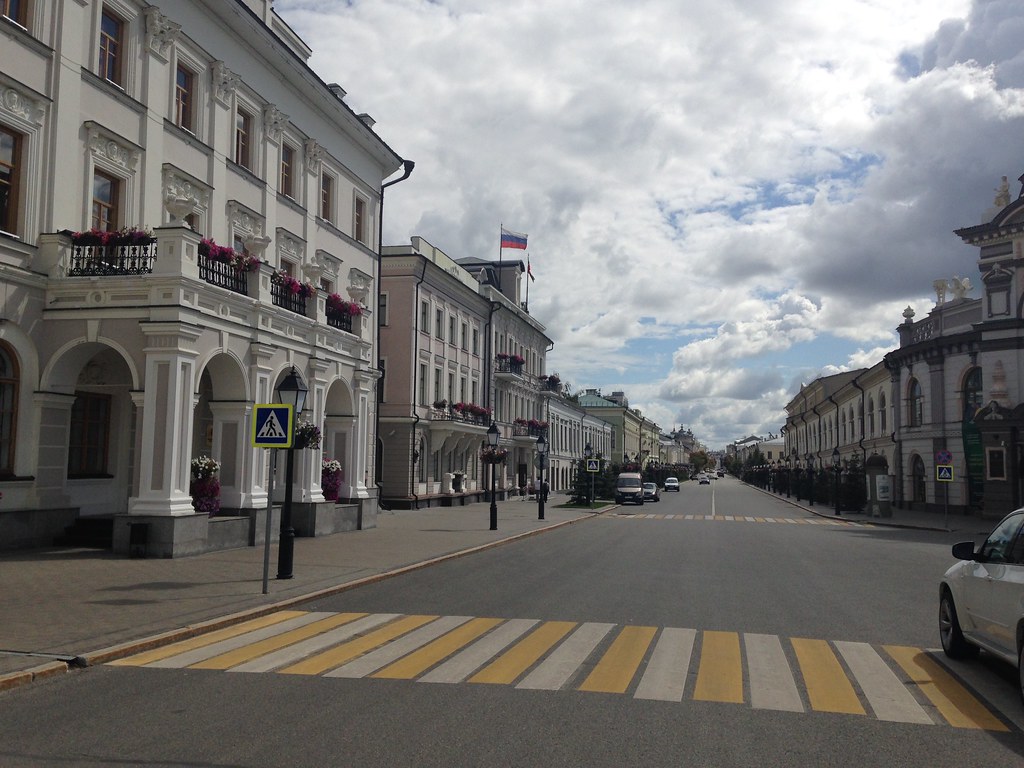
The main street leading to the kremlin.
The kremlin has nice views. There are several rivers and lakes in the area, including the Volga, and plenty of nice vistas.
Take a nice stroll along the lake.
Renovated buildings in the old Tatar Quarter
There’s a bit too much hardscape on that redone street for my taste. But it’s interesting because they took out a streetcar and pedestrianized the street. Apparently the vibrations were causing problems with the old buildings in the area, so they wanted to eliminate all vehicles.
Not sure what this is, but it’s in my Kazan file.
Dittos.
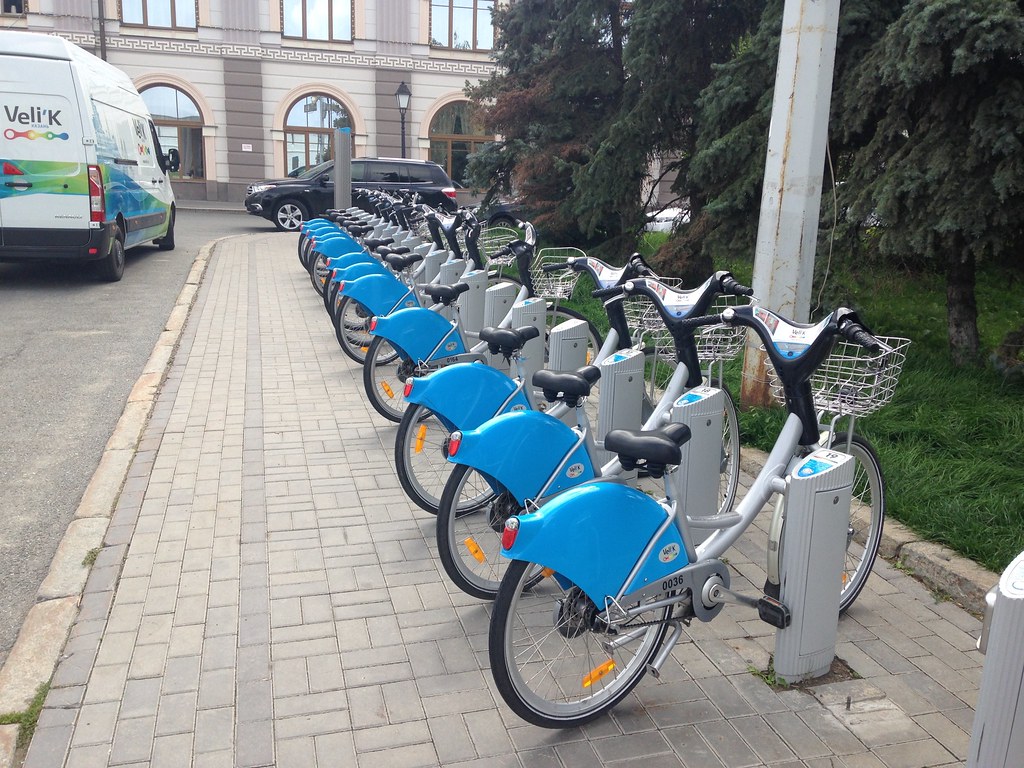
I’ll wrap up with a bit of transport geekery. Yes, they have a bike share system.
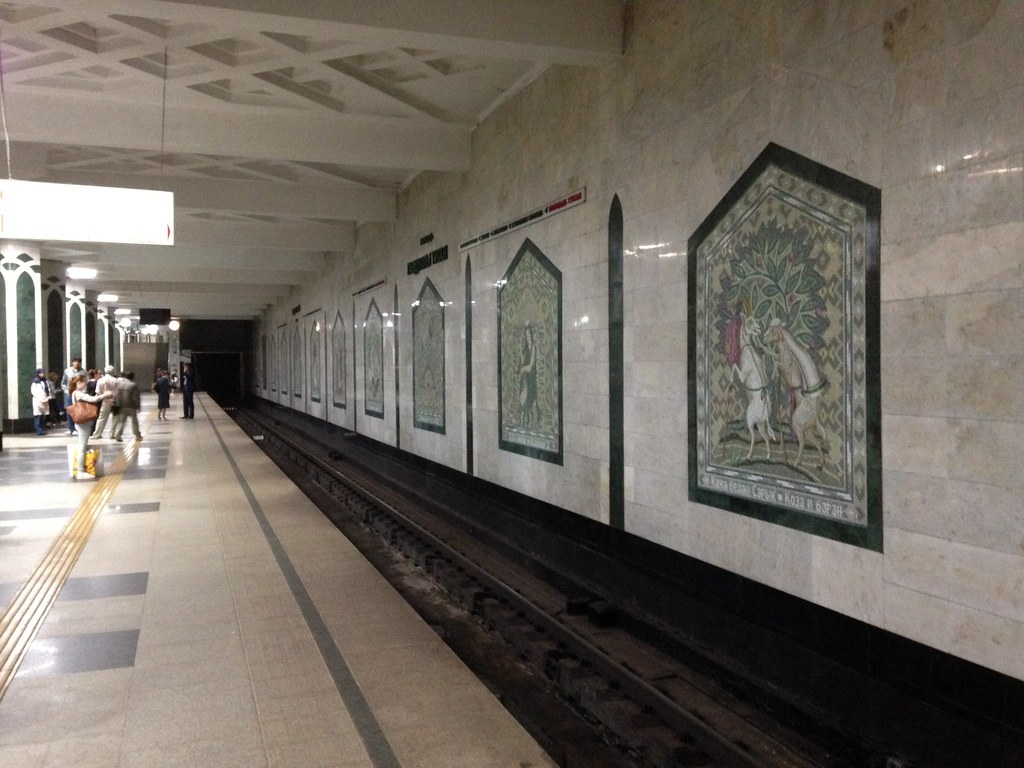
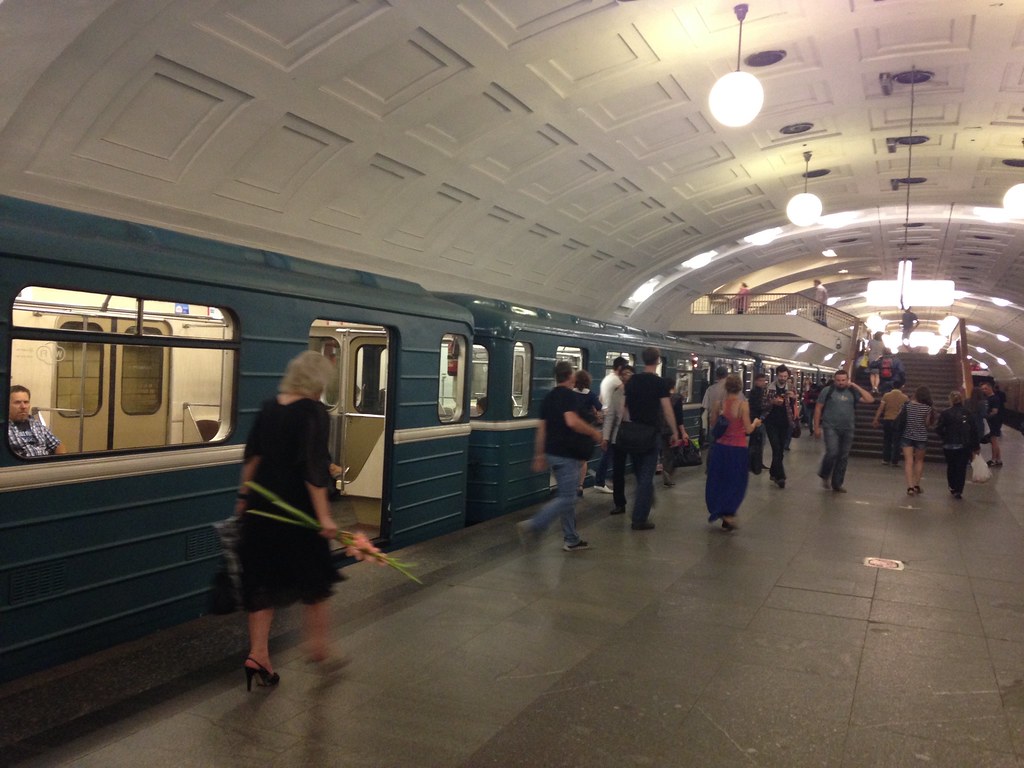
Their new metro system is in the Russian style with lots of marble, etc. The system “M” logo is similar to Moscow but in green (the traditional color of Islam). Instead of Moscow style tap cards they are using plastic tokens.
A metro station.
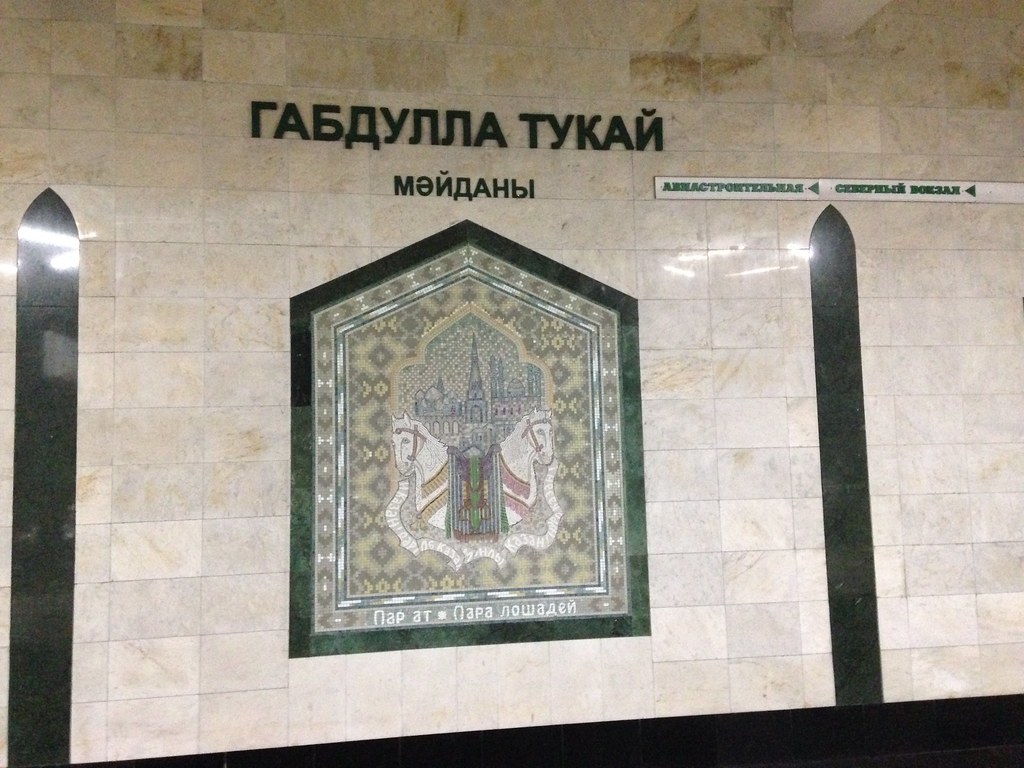
Station name signage. I believe the top is Russian and the bottom is the Tatar language, which is also written using the Cyrillic script. Interestingly, for at least while into the Soviet period, Tatar was written using the Latin alphabet, but they were apparently forced to change.
Signs.
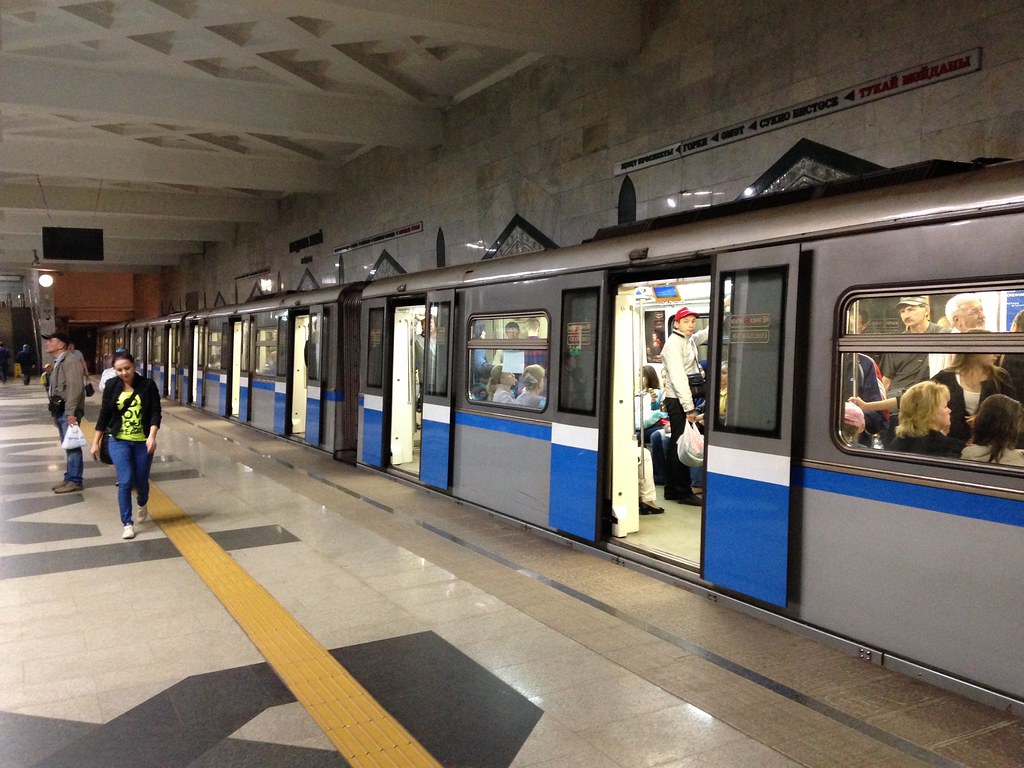
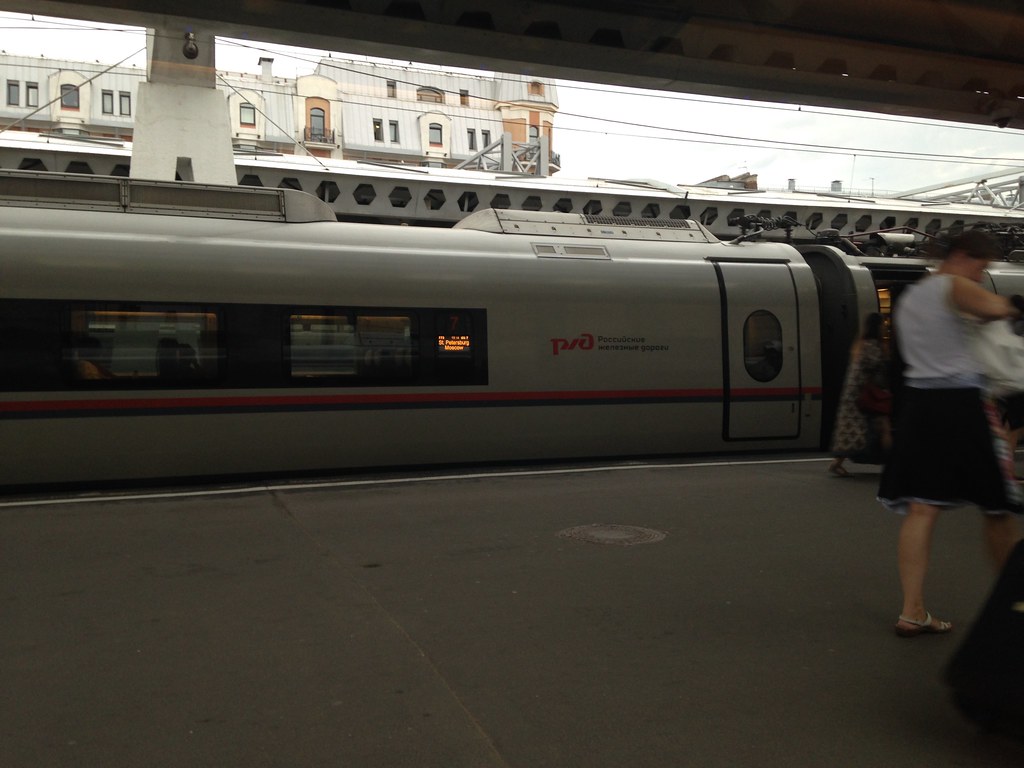
Here’s a train in the station. These are the exact same trainsets as the new Moscow ones I mentioned by didn’t have a picture of.
As I said, I was only there a day but was glad I went. It was good to get to see a city further into the Russian interior. Lots of money is being spent there, so I’d expect many further developments in the future.
Aaron M. Renn is a senior fellow at the Manhattan Institute and a Contributing Editor at City Journal. He writes at The Urbanophile, where this piece first appeared.