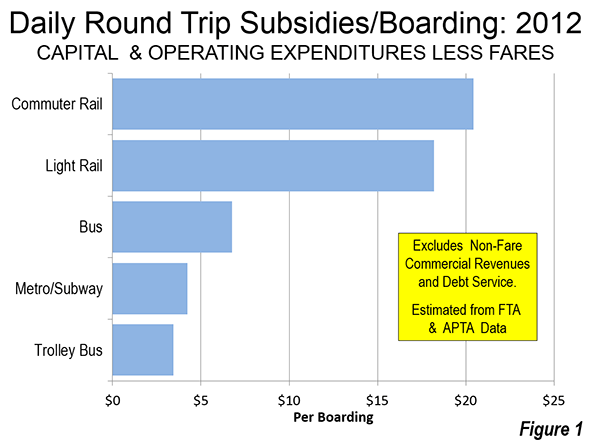
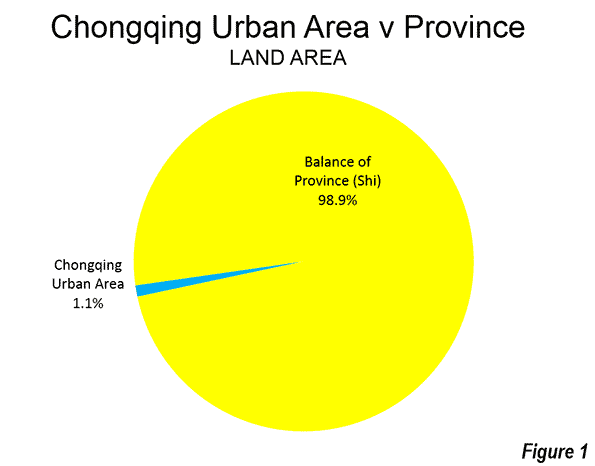
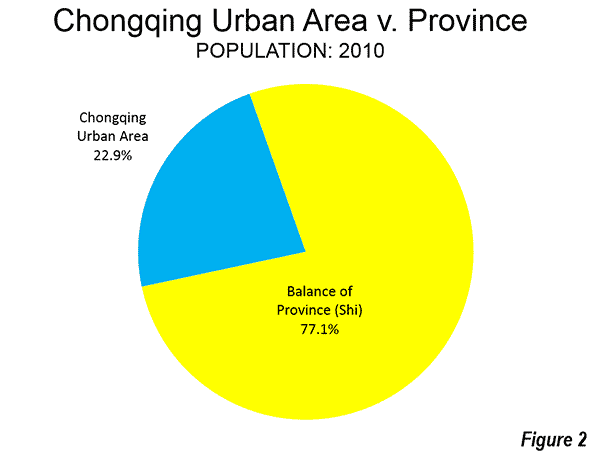
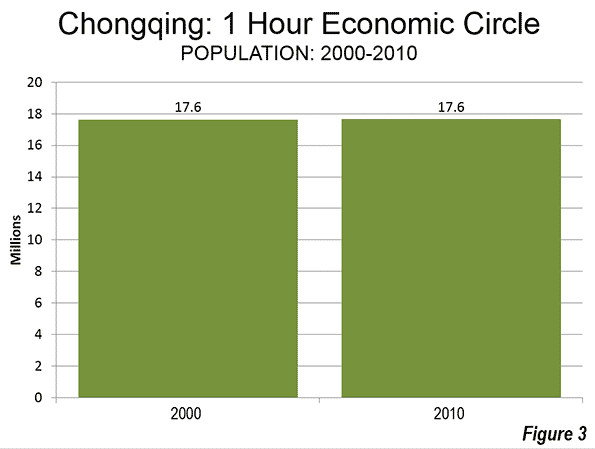
The New York Times ran an op-ed piece that helpfully demonstrated the pitfalls of lifestyle arguments in favor of urbanism, namely that they are annoying to everyone but the people making the argument.
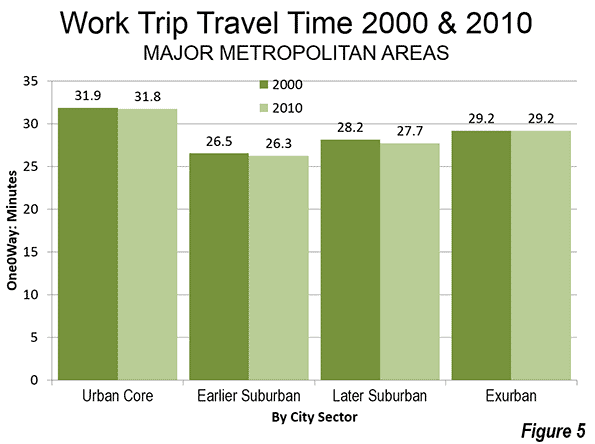
The boys, like their father, are lean, strong and healthy. Their parents chose to live in New York, where their legs and public transit enable them to go from place to place efficiently, at low cost and with little stress (usually). They own a car but use it almost exclusively for vacations.
“Green” commuting is a priority in my family. I use a bicycle for most shopping and errands in the neighborhood, and I just bought my grandsons new bicycles for their trips to and from soccer games, accompanied by their cycling father.
These arguments – whether they’re about physical health, or “diverse” or “vibrant” or “creative” communities, or whatever else – are, at bottom, about telling people that they are lacking, and that in order to improve themselves they should become more like the author. In the 1970s, when city dwellers felt superior mainly because of their supposed cultural capital and were telling middle-class suburbanites to loosen up a little, that might have been obnoxious but harmless. In our current situation – when the city dwellers making these arguments are the economic elite (the author of this particular piece, Jane Brody, lives in gentrified brownstone Brooklyn, I believe) – it’s a lot more sinister. Brody talks about commutes as if their length and form were something that most people could freely choose, rather than something imposed upon them by their wages and the price of housing and form of development of their metropolitan area. She makes this a story about personal morality, rather than the constraints we choose to put on people through public policy.
This is related, I think, to the study about mode share in U.S. cities that got passed around the urbanist blogosphere recently. In virtually every instance, the study was presented like a sports power ranking, with the winning cities being those with the least travel by car (“city of Chicago ranks sixth among large U.S. cities for percentage of people either biking, walking, or riding transit,” is a typical formulation of the lede).
But why, exactly, do we care about mode share? The pettiest possible answer is that we doconceive of cars v. transit/biking as a sort of culture war, just like many committed drivers have alleged, and what percentage of people choose to drive or do something else is how we measure whether or not we are winning. This, clearly, is not a particularly edifying possibility. A better answer might be that we really do want everyone else to be more like us – to reap the benefits of non-car commuting, from being healthier (although, contra Brody, I spent my subway commute today scarfing down a pound of spaghetti) to polluting less – and this tells us how many people are enjoying those perks.
That’s much more reasonable, but still problematic in that, like the Times piece, it strongly implies that the issue is individual choice, rather than the circumstances that constrain that choice. The people who write for places like Streetsblog know that circumstances matter, but for the casual reader, articles about mode share makes those issues a sort of specialists’ background.
That’s too bad, because mode share does convey some important information about constraints. If we assume that, allowing for some cultural margin of error, most people will choose to get to work via whatever method they find most efficient and comfortable, then we can determine roughly what percentage of people in any given city have decent access to transit – access that’s at least in the same ballpark of convenience as driving – just by looking at what percentage of people actually use it. Obviously there are complications to this: since one major inconvenience of driving is cost, cities with high poverty rates may have mode shares that exaggerate their transit’s effectiveness, for example. And since transportation choice is basically zero-sum on an individual basis – that is, all that matters is the relative efficiency of each mode – you could get a lot of people on transit by making driving truly hellish, without providing decent service. (Although in the American context, I think there are vanishingly few places where that would be an issue.)
Moreover, if we care about mode share as a proxy for service effectiveness, then beyond a certain point – say, a quarter, a third, whatever, of commuters – you’re kind of done. It doesn’t really matter. If New York City, with one of the most comprehensive transit systems in the world, can only get 50% of its commuters on buses and trains, then surely most of the distinction between it and, say, Asian cities with much higher transit mode shares isn’t the quality of their systems (although they may be of higher quality), but the increased misery of driving in ever-denser places. The issue stops being whether we can get from 40% to 45%, but whether subregions of the metropolitan area have strongly varying mode shares, suggesting that you can only get decent access to transit if you live in the right place. And, of course, that is in fact the case.
But if what really matters is service levels and access – if what we’re trying to accomplish is giving everyone a level of service where transit is a viable option, for reasons outlined here– then why not just measure that directly? Why not have widely-disseminated statistics about the percentage of people in every metropolitan region who can walk to a transit stop? Or make a bigger deal about the number of people who can reach some given percentage of metro area jobs via transit in a reasonable time frame? I almost never see those numbers in urbanist conversations, and to the extent that I do, they’re sort of ghettoized into the “social justice” urbanist subculture.
But these seem like relevant numbers for “mainstream” urbanists, too. In fact, they seem a lot better than mode share. Generalized public arguments in favor of transit projects are more likely to benefit from language that suggests they’ll provide options, rather than language that suggests the ultimate goal of the policy is to force people out of their cars. Because, in fact, that’s what public policy should be about: making transportation easier for more people, rather than moralizing about the perfectly legitimate choices that people make, given their circumstances.
This post originally appeared in City Notes on November 11, 2013. Daniel Hertz is a masters student at the Harris School of Public Policy at the University of Chicago.
Image from BigStockPhoto.com: A metro bus in Madison, Wisconsin.