Not every local official is smitten with the romance of high-speed rail. Graphic evidence of this was provided by Springfield, Illinois mayor Tim Davlin, who expressed his concern that the proposed rail overpasses would slice the city in half. Davlin told the State Journal Register that the “Whole city would look like crap.” This is a problem faced not only by historic Springfield, the state’s capital and location of many Abraham Lincoln sites. Citizens and cities on the San Francisco peninsula are concerned that a proposed “Berlin Wall” will divide their communities if construction of an elevated high speed rail wall proceeds through their communities.
Tag: Transportation
-
Losing Touch With the Changing Definition of “Community”
Mathew Taunton opens his review of “The Future of Community – Reports of a Death Greatly Exaggerated” (Note 1) with the observation that:
“Community is one of the most powerful words in the language, and perhaps because of this it is frequently misused. A profoundly emotive word, it is also a coercive one, and a key political buzzword in modern times. That community is being eroded in modern Britain is a matter of cross-party consensus, and it is also widely agreed that one of the state’s roles is to devise means of counteracting the decline of communities.”
It is refreshing to see a writer prepared to use ‘community’ and ‘coercive’ in the same sentence. Taunton reminds us that practically all urban architecture now attempts to force social solidarity into existence, and, by definition, condemns those who do not conform for daring to exercise their choice.
Unfortunately many of these attempts to coerce community into existence tend to repress or subvert the informal processes through which people interact of their own free will.
So why do so many influential people in the UK, the United States, and other countries of the New World, hold this ‘consensus’ that communities, like morality, are in decline, requiring government interventions to restore them to good health, within some reborn urban village?
In the past, communities were primarily place-based, if only because people could not travel very far or communicate over any great distance. But as civilizations have developed, this interaction between transport and communication has reshaped the prevailing structure and meaning of communities, as each reacts with each other. The printing presses of Renaissance Europe enabled the development of scientific and religious communities, as well as a host of “communities of ideas” both conservative and revolutionary.
Last century the establishment of national broadcast networks and television helped constitute national communities of listeners or viewers, which in turn reinforced the communities of “us” and “them” through the great global conflicts of that century.
The Internet has now created a whole new class of virtual communities or tribes. Many wage their tribal wars with considerable venom.
However, these internet tribes, too, simply build on the superior transportation technologies that have enabled us to physically flee to find more friendly groupings of associates, or to avoid the ‘neighbours from hell’. Of course, place remains important to communities based on activity – people continue to visit their golf course, football field, church, beach, or shopping mall. Modern transport has gifted us with ready access to them all.
Similarly, communications technology plays an important role in communities of shared interests or ideas – the blog site, the book club, talk-back radio, and the specialist channels on cable TV or YouTube.
However, rigidly place-based communities can also be coercive traps.
In the late sixties I wrote a paper at U.C Berkeley drawing on surveys that showed that “neighboring” was more intensive in mobile-home parks than in most suburbs or inner city areas, precisely because the residents felt that if they fell out with their neighbors they could always move on. Neighboring is not without risk.
Similarly, people in camping grounds felt free to share coffee, drinks and dinners around the barbecue, precisely because they know they need not meet again.
Many retirees have discovered the pleasures of the summer nomadic lifestyle spent driving from location to location in a well-appointed motor-home.
One retired couple (my American god-parents) were keen “rock-hounds” during the seventies and spent their summers driving their motor-home from one rock-rich territory to another, attending gatherings of rock-hounds along the way. They combined technological mobility, with place-based communities, and communities of common interests within the one retirement experience.
However, these contemporary communities, no matter how plentiful and rewarding, fail to meet the expectations of urban planners trapped within their general theory of architectural or spatial determinism. They remain convinced that urban form and places determine our behaviour. Yet in reality, our behaviour and preferences actually determine how and where we chose to live, work and play.
They may also be responding, in their reflexive way, to a genuine loss of sense of political community, a loss that may be more deeply felt that we think.
For the last forty or fifty years, through most of the New World jurisdictions, ‘reform’ of Local Government has meant ‘amalgamation’ on the presumption that ‘bigger is better’, probably because this coincided with the management theories of the sixties, which presumed conglomerates were the way of the future, and that all corporate mergers would benefit the shareholders and customers alike.
The track record of such local government ‘reform’ has given scant support to the theory. Forced amalgamations in particular have proved to be disastrous. And many of the voluntary ones – i.e. those driven from the bottom up – have fared little better.
These reform programs have generally been prepared to dilute or even ignore the traditional emphasis on ‘community of interest’ in favor of ‘economies of scale’ or the benefits of ‘regional integrated planning.’ In the end citizens have generally, and genuinely, lost contact with their Mayors and Councilors. They used to meet the Mayor in the street and have a chat about their concerns. Now they have to phone, leave voice messages and wait for the return call that never comes.
Political authority, now often housed in some distant place, is more remote than ever. You can’t meet it, let alone beat it.
Citizens may know their ward councilor but their ward councilors explain they are always outvoted by a majority who has no interest in any ward but their own. This is why large councils are actually less effective at delivering satisfaction than small ones. A small council is likely to be serving a single community of interest. But if one neighborhood wants to build a municipal swimming pool, all those who live more than an hour’s drive away understandably wonder why they should pay for a pool they will never use.
This bias towards larger and larger local bodies – enhanced by the rapid population growth in many peripheral areas and regional towns – has been given a massive boost in recent times by ‘Smart Growth’ planning theory. This approach necessitates large areas of regional governance so that people cannot escape from the planned densification that most independent areas would likely reject.
The Metro planners also often seek to extend their boundaries into the rural areas so as to prevent people and businesses locating where they prefer. Instead it is all determined by where the planners say people and business should go – for their own good, of course.
It may well be that when the central planners try to create “place-based communities” they are responding to a genuine problem, but have chosen the wrong tool-box to fix it. Community can not be imposed from above and large government is clearly the wrong way to nurture it.
A better approach may be to create a new system of local governance controlled by smaller, truly local councils, based on identifiable communities of interest, which are able to freely associate with other organizations if they believe it will provide services and infrastructure beyond their financial means.
We should learn to define the services we need, and then match them to the appropriate organization, rather than trying to find the one or two magic sizes that can cope with all our needs.
We no longer need to accept being re-organized from above; the internet allows even smaller units access to sophisticated information. We have a wonderful opportunity to take control of our destiny through a new world of local government in which the people themselves decide on their common communities of interest and set up novel and innovative joint-management entities where economic efficiency and common sense demand such arrangements.
Note 1: The Times Literary Supplement, July 31, Mathew Taunton’s review of a collection of essays “The Future of Community – Reports of a Death Greatly Exaggerated”, by Clements, Donald, Earnshaw and Williams, Editors.
Owen McShane is Director of the Centre for Resource Management Studies, New Zealand.
-
Traffic Congestion, Time, Money & Productivity
It is an old saying, but true as ever: “Time is money.” A company that can produce quality products in less time than its competitors is likely to be more profitable and productive. An urban area where employees travel less time to get to work is likely to be more productive than one where travel times are longer, all things being equal. Productivity is a principal aim of economic policy. Productivity means greater economic growth, greater job creation and less poverty.
Congestion Costs: This is why such serious attention is paid to the Texas Transportation Institute’s (TTI) Annual Mobility Report, which estimates the costs of traffic congestion, principally the value of lost time as well as excess fuel costs. The fundamental premise, long a principle of transportation planning and policy, holds that more time spent traveling costs money, to employers, employees and shippers.
Mobility & Productivity: Groundbreaking Research: Yet, until fairly recently, very little research was available to document the connection between travel times and the productivity of urban areas. The pioneering work has now been done by Remy Prud’homme and Chang-Woon Lee at the University of Paris. From reviewing French and Korean urban areas, they showed that productivity improves as the number of jobs that can be reached by employees in a particular period of time (such as 30 minutes) increases.
Focused US Research: US reports on mobility’s role in reducing poverty came to similar conclusions. A middle 1990s report for the Federal Transit Administration found that low income households in inner city Boston were at a particular disadvantage in obtaining jobs in the fast growing suburbs because transit service was either spotty or non-existent. Margy Waller and Mark Allen Hughes noted in a report for the Progressive Policy Institute that “In most cases, the shortest distance between a poor person and a job is along a line driven in a car”. Steven Raphael and Michael Stoll at the University of California found that access to an automobile nearly halved the difference between African American unemployment and that of non-Hispanic Whites.
New, Comprehensive US Research: But it was only last month that the Prud’homme-Chang research was broadly replicated in the United States. The Reason Foundation published “Gridlock and Growth: The Effect of Traffic Congestion on Regional Economic Performance” by David Hartgen and M. Gregory Fields, which looked at job accessibility in 8 US urban areas (Atlanta, Charlotte, Dallas, Denver, Detroit, Salt Lake City, San Francisco and Seattle, ). Hartgen and Fields chose a 25 minute commute period (the approximate national average one-way work trip) to evaluate accessibility and found, generally, that each 10 percent increase in the number of jobs accessible in that period resulted in a 1 percent increase in productivity, as measured by the Gross Domestic Product of the urban area. They also found that if free-flow traffic conditions could be established, considerable improvements in urban productivity would be achieved, because employees could get to more jobs in less time. At the same time, they show that traffic congestion will worsen considerably by 2030 under present plans as adopted by metropolitan planning organizations.
Hartgen and Lee looked at five sample work destinations in each urban area, the central business district, the airport, a university, a mall and a major suburb. The results by sub region were surprising:
“Contrary to conventional planning wisdom, the research suggests that regional economies might be more dependent on access to major suburbs, malls and universities than on access to downtowns or airports. Not only are models of productivity somewhat stronger for these sites than for CBD accessibility, but access to them has a stronger effect on regional productivity.”
The research indicates that achieving free flow traffic conditions to major suburbs, universities and malls would increase gross domestic products by from 6 to 30 percent. The gain in central business districts would be between 4 and 10 percent, while airports showed the least potential for adding to urban productivity, at 2 to 8 percent. These productivity gains are far from unachievable. Hartgen and Fields find that there is more than enough transportation funding in each of the urban areas to remove severe traffic congestion by 2030. These conclusions find fault with the growing emphasis by many in Washington to force people out of cars and into transit. Transit is simply not viable for the non-downtown markets, which have the greatest potential for improving job creation and economic growth.
Hartgen and Fields also show that achieving free flow operations in the studied urban areas would generally produce more in increased tax revenues by 2030 than the costs associated with reducing it.
American Urban Areas: Superior Productivity and Mobility: American urban areas are among the most mobile in the world. When compared to international urban areas of similar size, work trip travel times in the United States tend to be less. That is one of the reasons that US metropolitan areas are the most productive in the world.
For example, the Japanese megacity of Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto has somewhat fewer people than the New York consolidated (metropolitan) area and slightly more than the Los Angeles-Riverside consolidated area. Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto has perhaps the world’s second most heavily patronized transit system (after Tokyo), which carries at least 50% as many riders on its rail lines alone as all of the transit systems in the United States. Yet, in Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto, workers spend 20 percent more time traveling between work and home each year as New Yorkers. They spend 40 percent more time commuting than workers in Los Angeles, despite its having the worst traffic congestion in the nation. The difference between Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto and New York and Los Angeles lies in the fact that in the two American metropolitan areas, most workers travel to work by car, to destinations throughout the areas (Note 1).
Naïve Proponents of Poverty: However, not everyone understands that time is money. Some members of the US Senate and House of Representatives and Washington special interests would seek to restrict highway funding, making traffic congestion even worse. They would seek to reduce the number of miles that Americans travel by car in an attempt to achieve marginal greenhouse gas emission reductions (that is before the higher greenhouse gas emissions that occur in slower, more congested traffic is factored in). Secretary of Transportation Ray LaHood has indicated a desire to coerce people out of their cars.
Transit: Inherently Less Productive and Expensive: One common claim is that transit will provide alternative mobility. However, transit trips tend to be twice as long as car trips and no transit vision has ever been put forward that would replicate the efficiency of the automobile. There is good reason for this, since such a transit system would cost on the order of a metropolitan area’s entire income, each year, to operate and amortize. And, transit is expensive. The recent compact cities policy lobbying paper, Moving Cooler, shows that transit is far from a cost effective means for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, costing 20 times the maximum $50 per ton guideline as established by the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
None of this is to deny the inestimable value of transit in serving the nation’s largest downtown areas (such as Manhattan, Brooklyn, Boston, Philadelphia, Chicago and San Francisco). However these locations are commercial hyper-density aberrations in much larger low-density seas and are exceptional among America’s more diffuse metropolitan areas. Rather, the problem is overselling transit in markets that it cannot competitively serve. Disinvesting in highways (forcing people into transit) makes no more sense than to require the injection of blood clots into the bloodstreams of patients under the guise of improving the health and livability of patients.
It’s the Economy, Stupid: The United States has had enough recent experience with rising unemployment and falling economic performance. It hardly needs public policies that would increase travel time, reduce productivity and increase poverty, no matter how fervently and sincerely held are the misconceptions of the proponents. Hartgen and Fields have provided an invaluable work that could not have come at a better time.
Note 1: Calculated from United States Bureau of the Census American Community Survey and Japan Statistics Bureau data.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris. He was born in Los Angeles and was appointed to three terms on the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission by Mayor Tom Bradley. He is the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life.
”
-
Smart Growth Must Not Ignore Drivers
For the time being, battles over health care and energy seem likely to occupy the attention of both the Obama administration and its critics. Yet although now barely on the radar, there may be another, equally critical conflict developing over how Americans live and travel.
Right now this potential flash point has been relegated to the back burner, as Congress is likely to put any major transportation spending initiative on hold for at least a year, and perhaps longer. This also may be a symptom of mounting concerns over the deficit. Financing major changes in transportation, for example, would probably require higher federal fuel taxes, which would not fly amid a weak economy.
These delays could prove a blessing to the administration, providing a pause from indulging in yet another policy lurch that might thrill the “progressive” urban left but infuriate much of the country. Initial House proposals on transportation have sought to cut dramatically the share of federal gas taxes — paid by drivers — going to roads while sending more to already heavily subsidized transit. Another large chunk of transport spending would go to a very expensive, and geographically limited, high-speed-rail network.This kind of radical shift reflects the preferences of ideologues within the administration. President Barack Obama has clustered an impressive array of “smart growth” devotees around him, including Housing and Urban Development Undersecretary Ron Sims, an early climate change “evangelist,” Transportation Undersecretary for Policy Roy Kienitz and the Environmental Protection Agency’s John Frece. Their priority is not better roads for suburbanites but, as Transportation Secretary Ray LaHood put it, to “coerce” Americans out of their cars and into a denser, more transit-dominated future.
This approach can expect strong support from the influential “green team” in the administration, including climate czar Carol Browner and science adviser John Holdren. Browner’s hand was shown during the Clinton years when as head of the Environmental Protection Agency she threatened to cut transportation funds for the Atlanta region unless it adopted a smart-growth policy. The threats became moot after the change of administration in 2001.
It is not difficult to imagine such bureaucrats intruding on how communities and families function on the most basic levels. Traditions governing local land use that have existed since the beginning of the republic would be overturned. The preferred lifestyles of most Americans would come under siege.
This agenda has been widely promoted for decades, first by the Carter administration and, more recently, by both environmentalists and new urbanists. The recent concerns over global warming have provided an additional raison d’être for a policy promoting both higher transit use and denser housing patterns. The president himself has embraced this agenda, declaring in February that “the days of building sprawl” were, in his words, “over.”
The administration can expect strong support for such policies in the mainstream media concentrated in New York and Washington. These areas boast both the highest proportion of transit riders and the largest percentages working in the central core. Many among the young, single and childless couples working in media in these communities see no reason why other Americans should not live similarly.
Politically, such a remaking of America may prove difficult to pull off. Overall less than 6 percent of Americans ride public transit, a percentage that has barely changed for decades. In many states, the transit share is only 1 percent. It’s difficult to imagine a policy that disses roads, small towns and suburbs could pass Congress, 80 percent or so of whose constituents don’t live in the favored dense urban environments. And what about the 95 percent or so of Americans who get around by car? More likely, any spate of new transit and land-use regulations will be enforced through the apparat. In one scenario, administrators at the EPA could simply oppose any transport project — for example, new roads — on the basis of carbon emissions and potential pollution. States and cities with projects not deemed “smart” enough by administrators at the Department of Transportation or HUD might be threatened with loss of funding.
Yet even this approach risks engendering a backlash. Once again, the administration could be seen as imposing a true-blue policy on a largely red, or at least purple, nation. To be successful, the administration needs to address the needs of suburban, small-city and rural residents as well as those of big-city denizens.
This is not to say the administration should not address pollution and congestion concerns head-on. But this needs to be done in ways that make both political and practical sense. Mileage requirements on cars are an excellent first step that follows this playbook, getting results without trying to remake a car-driving electorate.
In addition, the government could develop incentives for increased telecommuting and more flexible work schedules in order to reduce unnecessary driving to work. There is also room for expanded, more economical bus and jitney services that could work in some suburban and small-town locations. Instead of building light rail systems that will never get large ridership, mass transit funding should flow to successful existing systems or to a handful of dense corridors emerging in places like Houston.
All this speaks to a kind of pragmatism that may not please either the road-building zealots or the smart-growth aficionados. Such an approach would be far preferable — and more politically sustainable — than the current attempt to drive a 21st-century country back to a transportation model more appropriate for the 19th.
This article originally appeared at Politico.com.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University. He is author of The City: A Global History
. His next book, The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050, will be published by Penguin Press early next year.
-
Amtrak Runs Off The Rails
When the United States was in the money, the Congress grudgingly voted Amtrak a $1 billion subsidy every year, and then engaged in histrionics about how it might be cheaper to send most passengers to their destinations on private jets.
Then oil went to $140 a barrel, the United States dropped into recession, and one of the answers was to vote $12.9 billion in stimulus money, over the next five years, to Amtrak, the railroads, and state-supported transportation agencies.
Even though the American freight-train business has enjoyed a renaissance in the last twenty years — companies like the Burlington Northern Santa Fe and CSX are admirable for their competitive spirit and financial results — I am skeptical that Amtrak is the company that can lead the way to the re-birth of U.S. passenger service. Freight, let’s remember, only flourished when Conrail was privatized and the industry deregulated.
To be clear, the $8 billion appropriated for high-speed corridor service has yet to be earmarked, and is best understood as discretionary funding that can be doled out to the states, if not to loyal unions. For his part, Senate majority leader Harry Reid hopes to open a drawbridge to fund high-speed rail service between Anaheim and Las Vegas.
Somehow, it is hard to imagine that the U.S. can restore its economic prosperity by rushing heavy rollers to the blackjack tables in Vegas.
Now in its thirty-ninth year of operations, the government-controlled Amtrak provides good service between Boston, New York and Washington, and Los Angeles and San Diego. Elsewhere, it’s a land cruise company.
Beyond the corridors, Amtrak plies routes that were hastily drawn in 1971 to insure that they touch as many congressional interests as possible. That means meandering sleepers from New Orleans to Los Angeles, or Chicago to Seattle, which are a delight to vacationers (myself included), but inconsequential to the business of America, which drives or flies in order to get somewhere. Amtrak handles less than 1% of America’s intercity travel.
To defend Amtrak for a moment, it has been chronically under-funded, owns little of the track on which it operates, defers its schedule to freight interests, and is hostage to union rules, Congress and microwavable food. European trains get more subsidies in a year than Amtrak has gotten in its lifetime.
So will the $12.9 billion give the United States a passenger railroad network comparable to those that are now flourishing in Europe?
Before answering the question, let’s take a very quick rolling stock of what European railroads have on offer:
In Switzerland, where I live, the trains or a bus connect every village, town and city in the country. Geneva has more than 100 trains daily. Austin, Texas, a comparable city in terms of size, has two. But the railway is expensive for foreigners who visit the country. Round trip from Geneva to Zermatt for a family of four is about $600. Nonetheless, the rail network is a national asset.
The German passenger railway, Deutsche Bahn, is incomparable. Nothing matches its speed, comfort, and service. Its Inter-City Express trains (ICEs) are the best in the world for the cost, not to mention the beer that’s served.
The United Kingdom, which has privatized much of what was BritRail, is a mixed bag of flash roads. Private companies are now competing for passengers, which means lovely new carriages, and better pork pies on the tea trolleys. But neither the private companies nor the government is spending what is needed on Britain’s roadbed and infrastructure, which explains some of the horrible accidents in the system.
France has its Train à Grande Vitesse (TGV), which operates on segregated, elevated high-speed track, and makes the runs from Lyon and Avignon to Paris not much longer than local commuter service. I find its seats cramped in second class (too airliner-ish), and French stations are dingy, but otherwise the TGV is a model train. A comparable system in the U.S. could reduce the trip from New York to Washington or Boston to less than two hours. But it would mean building a new interstate for trains.
Italy has some excellent trains, and fast ones too. I know this, because I’ve seen them speed by as I have stood on platforms in Italy. But I never seem to catch any of them. The trains I ride have dirty seats, broken air conditioning, and inexplicable delays in places like Domodossola.
Eastern European night trains — I am partial to these, I confess — include heavy sleepers that go from Ljubljana to Belgrade, or Iasi to Bucharest, with reasonable fares, starched sheets on the berths, brandy at breakfast, and the chance to visit such exotic places as Debrecen, Lviv, and Chisinau.
The Russian Railways has, remarkably, become an excellent company, with improved passenger and freight services, including trans-Siberian container shipping that can get boxes from the Pacific to Berlin in less time than cargo ships.
How does Amtrak compare, and how is it likely to improve with stimulus funds?
Amtrak already looks good on one account: Europe’s international reservation system is medieval. Amtrak is miles ahead of Europe here. This summer I tried, in person and on the web, to book a sleeper from Geneva to Sevastopol, and failed.
In Europe, international travel usually requires a trip to the ticket window at the station. Even simpler journeys, when they cross borders, are either prohibitively expensive or impossible to book. Geneva to London comes in at about $400; EasyJet does it in an hour for $50.
While I am all for spending stimulus money, or any money, on American passenger service, I have yet to see anything remotely like a good strategic plan for its restoration. The glossy maps projecting new corridor services depend on the states, not Amtrak, to realize the dreams.
Nor am I sure that throwing money at the Amtrak model will do much more than refurbish some Amfleet coaches and make congressmen look good in mid-term elections. The railroad, like many in American history, strikes me as better at delivering pork than passengers. The current chairman is a former small-town, Illinois mayor, and Joe Biden’s son was a board member until February 2009.
Perhaps equally important, where is Amtrak’s passion for railroading? Why hasn’t the route map changed in forty years? Where are the car-carrying trains, the elegant stations, the sleepers that cater to business people with showers and wi-fi, or even the special tourist trains that would take travelers across America to Civil War battlefields, major league baseball games, rock concerts, or national parks?
Why do cities like Phoenix or Louisville have no trains at all? Where are the creative railroad financiers, selling sleeping cars as timeshares or condos? If it’s truly a government-run corporation, why aren’t there more investment-grade Amtrak bonds in world markets?
Here’s another irony of the railroad stimulus package: Freight companies are prospering with deregulation and private capital, but Amtrak is running late while on the dole.
Right now we’re in a golden age of railroads, much of it funded with investor capital. The common stock of large American railroads is attracting serious money, including that of Warren Buffet.
Around the world, private luxury trains are crossing Russia, India, China, Tibet, the Silk Road, the Alps, and the Andes. In Asia, investors are plotting to complete the line from Singapore over the Burma Road to China. A company in Africa charges about $30,000 — and gets it — for a deluxe train trip from Cape Town to Cairo. But bureaucratic protectionism keeps these dynamic groups from operating in the United States.
After World War II, America traded in the greatest railroad system in the world for interstate highways, sleazy rest stops, and now-crowded airports. Today, GM is broke, gas is three dollars a gallon, and politicians have to kowtow to Saudi princes.
I would love to think that for $8 billion, corridor service would flourish and that German-style trains would pop up around the country. Heck, I would love to ride a Romanian sleeper between New York and Bangor, Maine.
Despite my hopes, my fear is that the transportation stimulus money is probably going to end up on a roulette wheel in Vegas.
Amtrak Empire Builder at Marias Pass, Montana. Photograph by Alex Mayes.
Matthew Stevenson was born in New York, but has lived in Switzerland since 1991. He is the author of, among other books, Letters of Transit: Essays on Travel, History, Politics, and Family Life Abroad
. His most recent book is An April Across America
. In addition to their availability on Amazon, they can be ordered at Odysseus Books, or located toll-free at 1-800-345-6665. He may be contacted at matthewstevenson@sunrise.ch.
-
Beijing is China’s Opportunity City
“What the Western fantasy of a China undergoing identity erasure reveals is a deep identity crisis within the Western world when confronted by this huge, closed, red alien rising. There is a sense that world order is sliding away from what has been, since the outset of industrialization, an essentially Anglo-Saxon hegemony, and a terrible anxiety gathers as it goes.” – Adrian Hornsby, “The Chinese Dream: A Society Under Construction”.
One year after the conclusion of what may have been the most bombastic Olympic Games ever staged, the host city of Beijing has solidified its position as a growing influential global metropolis. While the rapid pace of change and development in China is well-documented by the Western media, the foreign consensus regarding The Middle Kingdom’s ascendancy to global super power remains decidedly ambivalent. Yet a closer look at China’s second largest city may yield a different, more promising outlook for this gigantic yet mysterious country.
Much like London was to England in the 19th Century and Los Angeles was to the U.S. in the 20th Century, Beijing is today ground zero for opportunity in China. Shanghai holds on to its reputation as the country’s most cosmopolitan city and banking center, but Beijing continues to strengthen its role as political and cultural hub of China.
To call Beijing an ‘opportunity city’ is counterintuitive based on its monumental physical characteristics and history as imperialistic capital. Home to the massive Forbidden City and the adjacent Tiananmen Square, the city is defined by a tradition of architectural pomposity. Continued today in buildings like the Olympic Bird’s Nest Stadium and the ominous CCTV Building, subtlety and grace are not Beijing’s strongest suits. Yet underlying these iconic structures is a restless population of 17 million, including many newcomers eager about the prospect of upward mobility.
As construction of new buildings came to a screeching halt in the U.S. late last year, I also heeded the call of opportunity and headed to Beijing myself. My story is not unique in this regard as the phenomenon of recent American graduates moving to China for jobs was documented earlier this month in an article from the New York Times. Now working with a young, up-and-coming Chinese architecture firm, I am bearing first-hand witness to phenomenal changes.
Problems exist of course, but criticizing Beijing or the rest of China from afar for its poor air quality or the rampant destruction of its old neighborhoods is too easy. The reality underlying these problems is much more complex, much of it depending on varying perspectives of how Westerners as opposed to Chinese view the country’s direction.
For instance, Western planners and architects lament the razing of the charming alley and courtyard Hutong neighborhoods as significant losses of urban history. Yet most Chinese people view the process of destruction and rebuilding as a necessary piece of the modernization of their country. As 21-year-old film student and native Beijinger Ashley Zhang observes, “Although the loss of the Hutongs is sad, the reality is that most people would prefer to live in modern buildings where they do not have to go outside and use a shared bathroom or live in an old structure where they are going to be cold during the winter.”
Other Beijingers have noted how owners of homes in Hutongs are more than willing to trade in their digs for large paydays. Ms. Zhang went on to explain to me that a “change in accommodations will not necessarily alter the spirit or the culture of the Chinese people”. This presents a markedly different perspective from the Western view on the relative importance of permanence in the built environment.
It could be argued that a true sense of Chinese-ness exists more in the tradition of language and cuisine than in the built form. As such, the new and prolific building and infrastructure projects of China represent more a desire to join the modern world rather than to celebrate its architectural history.
Yet to say that there is no urban planning in Chinese cities would be off the mark. As put forth by the Beijing Municipal Commission of Urban Planning in 2004, the ‘Beijing 2020 Masterplan’ calls for high intensity development eastwards towards Tianjin and low intensity development westward towards the mountains. The ‘Two Axes, Two Corridors – Multicenters’ Plan’ aims at relieving congestion towards the historic center of Beijing by strengthening outlying polycenters.
Lisa Friedman of the New York Times recently lambasted the city’s development pattern as Beijing locking itself into a pattern of Los Angeles-type sprawl. In fact, Beijing’s polycentric development can be attributed to the fact that the historic core of the city is already well defined and remains off-limits to new development.
Also, contrary to most American cities, the designated ‘Central Business District’ lies east of the center of the city. Concentrations of jobs form other business ‘nodes’ in all directions around Beijing. This is not due to any desire to copy Los Angeles per se but rather because the city is gaining tremendously in population and must ‘sprawl’ in order to accommodate these newcomers. In addition, businesses prefer to set up shop in places where land is cheaper.
Detractors of rapid urban development like to note how sprawl creates unbearable automobile traffic. Yet they forget that the first great exemplars of “sprawl” – London and Los Angeles – did so with massive commuter rail systems long before the rise of LA’s freeway system or London’s ring roads.
In fact what you have in Beijing is sprawl abetted by a Metro system that would be the envy of American public transportation enthusiasts. There are currently six subway lines operating in the city and in addition, 10 new lines which are under construction are all slated to be completed by 2015. In the end, Beijing’s rail network will constitute 350 miles of track. Compare that to Los Angeles, which destroyed its own huge rail system in favor of buses, where a planned ‘subway to the sea’ consisting of a mere 14 miles of rail is estimated to not be completed until the year 2036.
Beijing is well on its way to ‘megacity’ status. Along with the city of Tianjin, about 70 miles southeast of Beijing, the Beijing-Tianjin mega-region will be one of the largest in the world. Tianjin, as the fifth-largest city in China and boasting a population of about 11.5 million residents, is going through a building boom of its own. Acting as Beijing’s main port, the two cities together form an economic powerhouse. The marriage between the two cities was consummated a year ago with the opening of the 350 km/h (217 mph) Beijing-Tianjin Intercity Rail – reducing travel time to a mere 30 minutes. I rode this train myself recently and had to cover my eyes from the constant flashbulbs going off recording the speedometer on the monitor in the front of our car.
China has come a long way since the days of Chairman Mao’s ‘Great Leap Forward’. Although still ‘Communist’ in terms of a political system of one-party rule, traversing the streets of Beijing gives the impression that China may in fact be the most capitalist place on earth. From weather-worn women selling fruit to crafty young men hawking fake watches and pirated DVDs, no piece of the city is off-limits to commerce.
There’s a huge generation gap between the younger generations and those who were unfortunate enough to have lived through the Cultural Revolution. But I would warn Westerners to not be fooled into thinking that China will forever be just a ‘cheap place to manufacture things’. The country is still very young, and as more young people get educated and travel abroad, China will evolve into an important player in everything from architectural design to green technology and the arts. At that point in time, sadly, there will no longer be any need for ‘Western experts’ like me. But for the time being, as I wait for our economy to recover, I am enjoying the ride as I witness perhaps one of the most compelling urban development stories of the 21st Century.
Adam Nathaniel Mayer is a native of the San Francisco Bay Area. Raised in Silicon Valley, he developed a keen interest in the importance of place within the framework of a highly globalized economy. Adam attended the University of Southern California in Los Angeles where he earned a Bachelor of Architecture degree. He currently lives in Beijing, China where he works in the architecture profession.
-
Taking the Fun Out of Fighting Global Warming
It is a rare spectacle when broadly respected national organizations and analysts condemn an initiative by some of the most influential players in the Washington establishment. Yet that is exactly what has happened to the Moving Cooler report, authored by the consulting firm Cambridge Systematics, published by the Urban Land Institute and sponsored by the American Public Transportation Association (APTA), the Environmental Defense Fund, Natural Resources Defense Council, the Environmental Protection Agency and others.
Forcible Removal: Moving Cooler proposes a radical agenda to reduce greenhouse gas emissions pushing people out of their cars, whether forcibly or by making it so expensive they can no longer drive as much as they need to. Moving Cooler would employ such measures as charging home owners up to $400 annually to park in front of their own houses, placing tolls on now-free interstate highways (up to $0.05 per mile by next year) and pushing as much as 90 percent of future development into existing urban footprints, in the vain hope that cutting driving would reduce greenhouse gas emissions by a similar amount. In fact, as traffic congestion increases in more densified urban areas, the one-to-one relationship between reduced driving and reduced greenhouse gas emissions is materially diminished.
More Huddled Masses: If this plan, endorsed by at least some in the Administration, occurs densification policies would impose urban growth boundaries and other restrictive regulations. Planning decisions would be removed from counties, cities, towns and villages to regional planning organizations forced to implement federal mandates as a condition of receiving back federal funding, most of which had been taken from their own taxpayers.
These restrictions would force up to 125,000,000 new residents into existing neighborhoods many of whose residents probably think are already crowded enough. Think of it as adding as many people as live and Mexico and Guatemala, without allowing urban areas to expand. All of this would worsen traffic congestion, lengthen travel times for those who can still afford to drive and severely intensify the unhealthful local air pollution that the nation has fought so successfully to reduce over the past four decades.
Ignoring Productivity: Alan Pisarski, author of the acclaimed “Commuting in America” series and one of the most respected names in transportation policy issued a cutting indictment on these pages. For example, Pisarski notes that Moving Cooler does not count travel times, “so shifting from a 15 minute car trip to an hour on transit or walking has no penalty.” In a world where time and productivity are inextricably associated, lost time is lost time, whether in a car, in transit or walking. In the broader economy, lost time is lost jobs, lost income and lost economic productivity.
Misleading Policymakers? C. Kenneth Orski, whose career has included assignments at the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development in Paris and as Associate Administrator at the Urban Mass Transportation Administration (now the Federal Transit Administration) reported in Innovation Briefs that the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO), an original member of the Moving Cooler coalition, walked away from the study, saying that Moving Cooler overstates the greenhouse gas emissions that can be realistically expected from its strategies, underestimates the potential of more fuel efficient cars and telecommuting and minimizes the returns from improved transportation operations and car pooling, which are already yielding “remarkable” results. AASHTO further charged that the Moving Cooler report “did not produce results upon which decision-makers can rely.” In the polite world (really) of Washington transportation policy, these are damning words indeed.
According to Orski, researchers provided AASTHO with a litany of criticisms including findings that Moving Cooler relied on “assumptions that are not plausible,” analysis that was “flawed and incomplete” and an “invalid” peer review process. Costs were characterized as “incomplete and misleading,” greenhouse gas emission results were “not comparable or plausible” and “many assumptions are extreme, unrealistic and in some cases, downright impossible.” Moving Cooler was dismissed because of its “Heroic assumptions about land use and travel behavior and extraordinary pricing do not come close to the GHG reductions needed by 2050.”
Orski himself characterized the report as containing “flawed analysis and unrealistic assumptions that could mislead policymakers and the public and raise unreasonable expectations about how much progress can be achieved using these strategies.”
There is plenty of reason to be concerned. Already Senators Jay Rockefeller (D-WV) and Frank Lautenberg (D-NJ) had introduced legislation that would require annual reductions in how much Americans drive. The senators have confused reducing driving with reducing greenhouse gases. They are not the same thing. After all the federal government is dedicating literally billions of dollars to improving vehicle fuel efficiency. The President himself has promised 150 mile per gallon automobiles. There is significant potential for improving the carbon footprint of cars without forcing people to reduce their driving.
Land Use & Transit: Meager Returns: Orski strikes a nerve, especially with respect to the Moving Cooler coalition’s favored policies of densification and transit expansion. Moving Cooler itself produces embarrassingly modest (and probably exaggerated) estimates of the potential for densification and transit to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. According to Moving Cooler, these combined strategies would reduce greenhouse gas emissions no more than 7 percent from a 2050 base, and woefully short of any meaningful contribution. Not surprisingly, Moving Cooler ignores the fact that banning development on most suitable land around urban areas would raise land prices and thus home prices, a relationship noted by economists from the left, center and right of the spectrum and grudgingly admitted even in smart growth’s most influential advocacy document, The Costs of Sprawl — 2000.
As the Tomas Rivera Institute said in a report decrying the barriers to home ownership that California’s similarly restrictive land use policies impose on Hispanic and Latino households: “While there is little agreement on the magnitude of the effect of growth controls on home prices, an increase is always the result.” (Note 1).
Transit and High Speed Rail? Cross Them Off the List: Moving Cooler endorses significant expansion of transit service and establishment of high speed rail systems, but its own data speaks to the contrary. The maximum necessary cost for removing a ton of greenhouse gas emissions is $50, according to the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Moving Cooler’s data puts transit expansion at more up to 20 times the $50 standard ($900) and high speed rail at 14 times the standard (more than $700). To put the matter in context, if the nation were to spend as much per ton to reach the Waxman-Markey “Cap and Trade” legislation’s greenhouse gas reduction target, the annual bill would be more than $5 trillion, more than one-third of the gross domestic product of the United States. With all of the talk in Washington about cost control and reducing the budget deficit, such extravagantly expensive strategies like transit expansion and high speed rail should be crossed off the public policy list.
And, indicative of the implausible greenhouse gas results noted by the AASHTO researchers, Moving Cooler excludes the greenhouse gases emitted in construction. This leads one to wonder if there are “good” greenhouse gas emissions (like from building high speed rail) and bad greenhouse gas emissions (like from driving). Construction emissions can be very substantial. For example, it has been reported that construction emissions from proposed high speed rail lines in the United Kingdom would offset any reductions achieved in daily operations compared to airplanes.
Incompatible Bedfellows: Pitifully, Moving Cooler attempts to associate itself with a highly respected study by McKinsey & Company and The Conference Board that concludes significant greenhouse gas reductions can be achieved by 2030 at less than $50 per ton. Moving Cooler cites itself as “companion piece” Yet, the McKinsey/Conference Board study specifically rejects the high-handed social engineering proposed by Moving Cooler, indicating that its strategies would involve “maintaining comparable levels of consumer utility,” which they defined as: “no change in thermostat settings or appliance use, no downsizing of vehicles, home or commercial space and traveling the same mileage annually relative to levels assumed in the government reference case” (Note 2).
The Mantra: Moving Cooler chants a mantra about how automobile fuel efficiency will improve, but that continued growth in driving will largely cancel out those gains. However, to do so Moving Cooler lumps automobile and other light-duty vehicle data in with railroads, trucks and buses.
In fact, the Energy Information Administration of the US Department of Energy projects a 13 percent reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from cars and other light-duty vehicles by 2030, and that is before accounting for the more stringent fuel economy standards adopted by the Obama Administration a few months ago. Further, Moving Cooler buries its laughingly ineffective and expensive policy favorites, smart growth, transit expansion and high speed rail, among a panoply of other strategies that would account for the “lion’s share” of the emission reductions it anticipates.
The Real Agenda? As Pisarski indicated: Maybe the saddest part of it all, the authors appear not to take global warming or energy security very seriously at all. Rather these public concerns are just a convenient hook, the cause du jour, on which to hang their favorite solutions. Given this apparent reality, it is probably not surprising that two of the three Moving Cooler cover pictures are from Europe, which the smart growth movement has worshipped for years.
The Moving Cooler strategies would not only force people to live in ways they would not voluntarily choose, and for scant gain and no reason. Moving Cooler’s radical measures need to be rejected forcefully. There are better, more effective and far less intrusive ways to reduce greenhouse gases.
That would, however, probably take the fun out of fighting global warming for those whose real intent is telling others how to live.
Note 1: “Growth controls” is a synonym for smart growth strategies, such as urban growth boundaries and development impact fees.
Note 2: The 2007 government reference case used by McKinsey and The Conference Board assumed that per capita driving would increase more than 50 percent between 2005 and 2030. Later estimates have reduced that figure.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris. He was born in Los Angeles and was appointed to three terms on the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission by Mayor Tom Bradley. He is the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life.
”
-
Playing with the Big Boys: The Costs of Fruitless Passenger Rail Tours
In these hard times the New Zealand public is somewhat excited about the travel costs incurred by our Government Ministers and MPs. Overseas travel attracts particular rage and fury.
A particularly galling example is a proposal by Christchurch City Mayor Bob Parker, his CEO Tony Marryat, and an urban planner, to visit the US to investigate the performance of light rail in Los Angeles, San Francisco Bay Area, Seattle and Vancouver.
These cities seem unlikely to provide any relevant information, if only because their populations are many times those of Christchurch, a metropolis of roughly 370,000 and a downtown population of a mere 8000. In comparison:
- Los Angeles – 13.8 million
- San Francisco/San Jose – 5.3 million
- Seattle – 3.3 million
- Vancouver – 2.1 million
The reason the Christchurch team cannot investigate a rail system in the US serving a metropolitan area of only some 350,000 people, and with a CBD of only 8,000 people, may be that because so far, at least, even the most enthusiastic Smart Growth planners in the US are not that silly.
Randal O’Toole, who has made many studies of urban rail systems, points out in “Unlivable Strategies” that spending money on expensive forms of rail transit is fundamentally inefficient because other transportation systems cost far less to build.
Light rail, he argues, has become popular in the United States precisely because it is expensive. Congress gives transit grants to cities on a first-come, first-served basis. So the cities that build the most expensive transit systems get the largest share of federal transit funding.
Naturally, dozens of cities are in line to get their share of the pork.
But that does not prove that light rail is worthwhile. Too many cities have built expensive rail lines and then found that, due to overruns, high operations and maintenance costs, or heavy mortgages, they have to cut back bus service. The result is that rail construction has actually led to reduced transit ridership in many, if not most, cases.
The Grand Tour: My Version
Los Angeles and San Francisco Bay
Here is what the Christchurch Mayor and his team should learn from their visits to the Los Angeles and San Francisco Bay.
- Los Angeles reinforces the Portland experience (a much smaller city) where cost overruns forced Portland to raise bus fares and cut bus service during construction of its first light-rail line in the 1980s. As a result, a smaller proportion of Portlanders ride transit to work and other places today than did so in 1980. A similar situation in Los Angeles led to a 17 percent decline in transit ridership between 1985 and 1995. The NAACP sued the transit agency for cutting bus service in low-income neighborhoods while building rail to middle-class neighborhoods. The suit forced the agency to scale back its rail plans and restore bus service, which led to a recovery of ridership.
- In the San Francisco Bay Area, due to heavy rail debt, San Jose was forced to drastically cut bus and rail service in 2001 and lost 35 percent of its riders. The transit system had to make further cuts in 2007.
Furthermore, despite (or because of) several extensions of the BART line, transit ridership in the San Francisco Bay Area has fallen by more than 10 percent since 1982. Several transit advocacy groups, including the Sierra Club (Piper, 2004), the Bay Area Transportation and Land Use Coalition (BATLUC, 2003), and the Bay Rail Alliance (Carpenter, 2007), actively oppose a proposed extension of BART to San Jose because they know investments in other forms of transit are much more cost effective.
Overall, US urban areas with rail transit have not fared as well as areas with bus transit. Between 1990 and 2000, the number of people in regions with rail transit who commute to work by transit actually declined, while the number in regions with bus-only transit systems increased.
The saddest part of these stories is that the people who lose tend to be those most dependent on transit due to low incomes or an inability to drive, while the people who end up riding rail lines tend to have higher incomes and plenty of auto-mobility. (Winston and Shirley, 1998, p. 9).
Rail transit actually represents a transfer of resource from the poor to the well-off – Robin Hood at work in reverse gear.
Seattle
After getting voter approval for rail transit in 1996, Sound Transit began operating 31 miles of commuter rail service between Tacoma and Seattle in 1999. It also built a 1.6-mile streetcar line in downtown Tacoma at a cost of $50 million a mile, a third more than planned. As of December, 2003, Sound Transit also operates a 35-mile commuter rail line from Everett to Seattle.
Sound Transit’s Seattle-Tacoma commuter-rail line is one of the least productive in the nation, carrying less than one seventh as many passenger miles per route mile as the average commuter-rail line. As a result it has one of the highest operating costs per trip or per passenger mile of any commuter rail line. Despite starting out with free service, the Everett line has been running more than 70 percent empty.
Transit’s growth in travel and market share is almost entirely due to bus transit, not rail transit. But the growth in the region’s congestion is due to decisions made early in the decade to concentrate on rail transit rather than highway construction. Those decisions have harmed Seattle area residents in many ways, including cost overruns, congestion, transit’s cost ineffectiveness, and housing prices.
Future plans: The Sound Transit agency originally projected that the cost of building a 24-mile light-rail line from the Seattle-Tacoma airport to the University of Washington and Northgate would be $2.4 billion. Shortly after receiving voter approval, the agency increased this estimate to $3.6 billion.
After many stops and starts, last year voters endorsed an $18 billion Sound Transit plan for a 53 mile network which they hope will attract 25,000 daily riders by 2030.
Our Christchurch team should learn from the Seattle story that, once embarked upon, these rail plans tend to eat ever increasing amounts of money.
Vancouver
We can only wish them luck on getting useful information out of Vancouver. There seem to be no collections of the statistics on the performance of the transit systems as are available to US researchers here and here (Excel files).
However, we do note that in 2008 the operating cost of the Translink Sky Trains was C$773,737,000 and this was ‘covered’ by C$359,911,000 of fares and advertising, $262,298,000 motor fuel taxes,$255,741,000 property tax, parking site taxes $8,758,000 and others of $33,313,000.
So the transfers from motorists and property owners are greater than the fare revenues.
In 2008 the Long-term debt was C$1,822.7 million.
Grand Plans
Christchurch Mayor and his team are presumably looking at these rail systems as a means of supporting their Smart Growth plans for the Greater Christchurch area.
If the Mayor and his team ask the right questions, and collect the right data, it will be evident to Blind Freddy’s dog that if these boondoggle systems have failed in these major cities, with their major concentrations of employment, then there is no way that light rail can provide a cost effective and efficient service to Christchurch and its environs.Sorry about that. Enjoy the trip.
Owen McShane is Director of the Centre for Resource Management Studies, New Zealand.
-
Vetting the Volt: Toward Meaningful Electric Car Fuel Consumption Ratings
The 230 Miles per Gallon Claim: The General Motors (GM) announcement last week that the Chevrolet Volt would achieve 230 miles per gallon in city driving and a rating of more than 100 miles per gallon with combined city and highway driving sadly contains more hype than reality. The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid vehicle that GM intends to begin marketing in 2010. GM has indicated that the car will be able without gasoline for 40 miles, on its rechargeable battery. After the battery is depleted, the car would begin to use gasoline. The 230 mile per gallon figure, according to GM, was calculated using a proposed but yet not revealed Environmental Protection Agency fuel economy testing procedure. Similarly, the details of the GM calculation were not revealed.
Criticisms: Rather than the expected praise, the GM claim was met by a barrage of questions and criticism. Consumer Reports said that the 230 miles per gallon claim might be the exaggeration of the century. Automaker Nissan, facetiously responded with a claim that its forthcoming all electric (not hybrid) “Leaf,” would achieve 367 miles per gallon in a Twitter post. Nissan, unlike GM can be excused for not providing the details of its calculation, since it was “making fun.” EPA distanced itself from the GM announcement, indicating that it had not yet tested the Volt.
The criticisms and questions revolved around a single issue: How had General Motors calculated the 230 miles per gallon figure. Regrettably, General Motors has yet to provide a complete answer.
From the sketchy details released, it appears that the 230 mile per gallon rating was based upon the assumption that a driver would travel less than 40 miles each day and recharge the battery at night. Using this methodology, there would never be a reason for the car to use gasoline, so long as the daily mileage is less than the battery capacity.
A New EPA Rating System: Reportedly, the EPA’s fuel economy testing procedure for plug-in electric vehicles (whether hybrid or not) will report kilowatt hours (KWH) of electricity consumed per 100 miles. Presumably, this rating will be placed on the fuel economy window sticker on new cars, perhaps alongside some miles per gallon conversion. GM indicates that the Volt will consume 25 kilowatt hours per 100 miles in city driving.
Policy Imperative for Improving Fuel Efficiency: The impetus for improving automobile fuel economy is being driven by public policy objectives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, especially carbon dioxide (Note 1), and away from the consumption of petroleum .
Even though the Volt will produce no greenhouse gas emissions from its tailpipe when operating in the electric mode, the electricity that drives its battery would come from power plants, many of them relying on fuels like coal, which produce high amounts of greenhouse gas emissions. In fact, coal accounts for roughly 30 percent of all electricity production in the country; other fossil fuels another 35 percent.
A Flawed EPA Fuel Economy Rating System? Neither the GM calculation nor apparently the proposed EPA rating system include greenhouse gas emissions from electricity generation. A greenhouse gas gram emitted from an electric power plant smokestack has the same impact as one from an auto tailpipe. Any EPA fuel efficiency rating system that does not take into consideration power generation emissions would be shockingly incomplete and misleading. Consumers would not be given reliable information on the greenhouse gas emissions from cars they might purchase. One would expect that a government committed to greenhouse gas emission reduction would task its implementing agency with ensuring the availability of relevant and reliable information.
Power Generation and Plug-In Cars: On average in the United States, the generation of each KWH produces 610 grams of carbon dioxide (1.35 pounds). By comparison, combustion of a gallon of gasoline emits nearly 8,900 grams of carbon dioxide. Thus, nearly one gallon of gasoline is the equivalent of approximately 15 KWH of electric power in its greenhouse gas emissions (Note 2).
Thus, if the Volt uses 25 KWH to travel 100 miles in an urban area, then the greenhouse gas emissions from generating its power will be somewhat over 15,000 grams (Note 2), or the same as 1.7 gallons of gasoline (Note 3). Under these average operating conditions, the Volt would achieve approximately 60 miles per gallon (Note 4).
Exaggeration Doesn’t Help: Now there is nothing to be ashamed about 60 miles per gallon, unless, that is, you have claimed 230 miles per gallon. Regrettably, General Motors, which could have claimed a great environmental advance, has diminished it by failing to “level” with the public. This kind of public relations will not help a company whose performance has cost it market share for well over a generation. .
The Volt (and the Leaf) Will Get Better: Of course the equivalent miles per gallon would be much higher if US power generation were more efficient. And, it will be. For example, it has been proposed that electric power generation needs to become at least 80 percent less greenhouse gas intensive by 2050. If this is accomplished, the Chevrolet Volt could indeed achieve 230 equivalent miles per gallon and perhaps the Leaf 367. But neither car will reach these plateaus in the short term.
A Better Fuel Economy Rating System: Since the EPA fuel economy rating system has not been finalized, its potential defects can be corrected. Any EPA fuel economy rating system should include a greenhouse gas emissions indicator. This should be provided for city driving, for highway driving and a combined overall figure. Moreover, such a rating must include the very real emissions that occur at the power plant. It would be appropriate for EPA to continue reporting miles per gallon and adding KWH per 100 miles, so that the cost impacts are clear to purchasers.
Regional Variations: There is another complicating factor – regions. For example, in North Dakota fuel economy would be approximately 35 miles per gallon equivalent with full electric operation, well below the average 60 equivalent miles per gallon. On the other hand, in the state of Washington, the Volt would achieve its 230 miles per gallon equivalent, nearly 7 times the North Dakota fuel efficiency. This is not because people in Washington are more environmentally sensitive than North Dakotans. The difference is in type of power generation. Nearly 80 percent of Washington’s power is generated by hydro-electric and nuclear plants, which produce virtually no carbon dioxide emissions. On the other hand, nearly 80 percent of North Dakota’s electric power is produced with fossil fuels. These differences will be moderated as electric power production becomes less greenhouse gas intensive.
The Bottom Line: Despite the exaggeration and misleading information, this story is far more positive than negative. Congratulations to General Motors (and Nissan) on the strong advances they have apparently made in vehicle technology. This is just further evidence of the potential of human ingenuity. From the 150 mile per gallon cars to which President Obama is committed to the zero emission petroleum car system demonstrated by a Georgia Tech team, the good news is that people can continue to live as they like, while admirably reducing their greenhouse gas emissions to meet whatever objectives are ultimately adopted.
Notes
1: Carbon dioxide accounts for the overwhelming share of greenhouse gas emissions from motor vehicles.
2: Calculation: 8,900 (divided by) 610
3: Calculation: 25 KWH (times) 610
4: Calculation: 15,000 grams (divided by) 8,900 grams
5: Calculation: 100 (divided by) 1.7
6: A grams per mile rating system should include “upstream” activities, such as the greenhouse gas emissions required to produce and distribute petroleum, which by various estimates increases the emissions by 20 to 25 percent. Similarly, upstream electric power production emissions should be included.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris. He was born in Los Angeles and was appointed to three terms on the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission by Mayor Tom Bradley. He is the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life.
”
-
Immigrants Are ‘Greening’ our Cities, How About Giving them a Break?
Debate about immigration and the more than 38 million foreign born residents who have arrived since 1980 has become something of a national pastime. Although the positive impact of this population on the economy has been questioned in many quarters, self-employment and new labor growth statistics illustrate the increasingly important role immigrants play in our national economy.
There has also been an intense debate within the environmental community about the impact of immigrants. Yet there has been relatively little research done about how immigrants get to work and where most immigrants live. As the ‘green’ movement in the U.S. has increasingly pushed for higher-density housing and transit-oriented development in order to improve public transportation (specifically rail), few have considered how immigrants use transit and what might be the best way to accommodate their needs. In fact, all too often, “green” policies advocate transit choices – favoring such things as light rail over buses – that may work against the interests of immigrant transit riders.
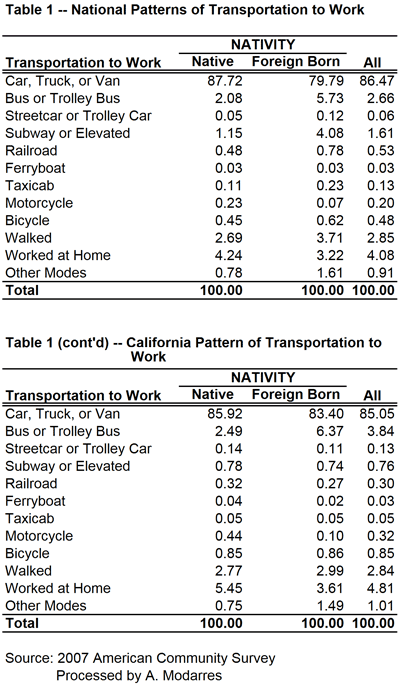 Based on the 2007 American Community Survey, 117.3 million native-born and 21.9 million foreign-born individuals commuted to work. As Table (1) illustrates, a higher percentage of immigrants rode buses (5.7% vs. 2.1%) and subways (4.1% vs. 1.2%) and many walked to work (3.7% vs. 2.7%). A much smaller percentage drove to work (79.8% vs. 87.7%). Unfortunately, despite their higher usage of alternate means of transportation to work, or perhaps because of it, the commute to work time was on average longer for the foreign-born commuters than their native-born counterparts (28.8 minutes versus 24.7).
Based on the 2007 American Community Survey, 117.3 million native-born and 21.9 million foreign-born individuals commuted to work. As Table (1) illustrates, a higher percentage of immigrants rode buses (5.7% vs. 2.1%) and subways (4.1% vs. 1.2%) and many walked to work (3.7% vs. 2.7%). A much smaller percentage drove to work (79.8% vs. 87.7%). Unfortunately, despite their higher usage of alternate means of transportation to work, or perhaps because of it, the commute to work time was on average longer for the foreign-born commuters than their native-born counterparts (28.8 minutes versus 24.7).Clearly in terms of using public transportation, immigrants are a bit greener than those born here. But why? Is this habit formed elsewhere? In that case, are recent immigrants even more likely to use public transportation than those who immigrated earlier? Or is it their income that affects their transportation choices?
Table (2) provides the answer to the first question. Recent arrivals are clearly less likely to drive to work and have a higher propensity toward using public transportation, compared to all foreign-born individuals (and significantly more than the native-born). Additionally, over 6% of the immigrants who have arrived since 2000 walk to work.
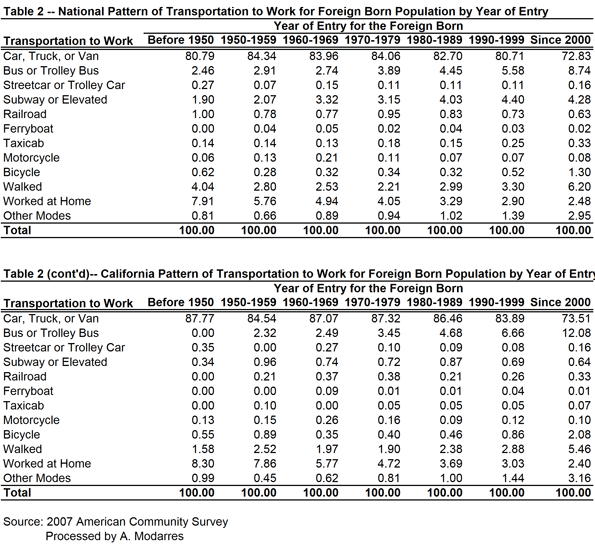
Overall, more than a quarter of the immigrants who have arrived since 2000 use an alternative mode of transportation to work. If the rest of America could do the same, we’d be a bit ‘greener’ already. However, it seems that as immigrants stay longer, they eventually tend to use cars more often because automobile usage allows for access to better jobs, better shops, and better schools. For example, immigrants who arrived in the U.S. in the 1970s (which means they have been here over three decades) drive a bit more and use public transportation less.
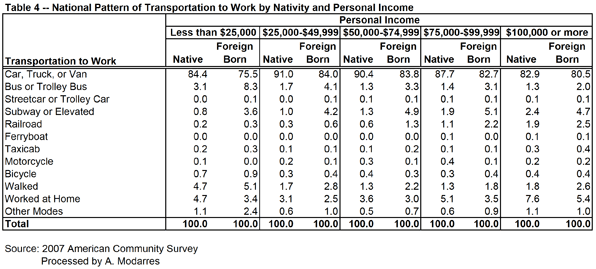
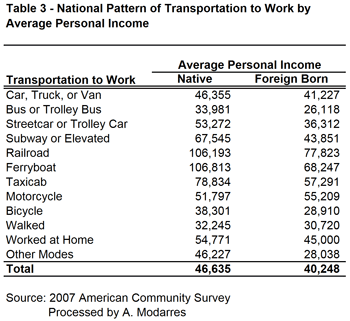 Even so, their rates are still slightly better than the native-born (compare Tables 1 and 2). This may be in part because of their lower incomes (see Table 3) yet at every level of income they are still more likely to take transit. Table (4) illustrates this point by grouping commuters into income categories and their nativity. In every income category, immigrants use their cars less and are more likely to use public transportation, even though their car ridership increases with income.
Even so, their rates are still slightly better than the native-born (compare Tables 1 and 2). This may be in part because of their lower incomes (see Table 3) yet at every level of income they are still more likely to take transit. Table (4) illustrates this point by grouping commuters into income categories and their nativity. In every income category, immigrants use their cars less and are more likely to use public transportation, even though their car ridership increases with income. The message from these statistics is loud and clear. Immigrants are more likely to ride public transportation than those born in the U.S., regardless of their income. The ones arriving more recently are even more likely to do so. Overall, this suggests that familiarity with public transportation, combined with the effects of income and place of residence, has made the immigrants’ lives in the U.S. a bit ‘greener’ than those of the native-born. In fact, one factor that may contribute to their higher usage of public transportation stems from their living in neighborhoods whose densities are, on average, 2.5 times higher than those of the native-born. Immigrants, in essence, are doing precisely what planners want the rest of us to do.
Moving to Southern California
Southern California still stands as the icon of immigration and multiculturalism and is home to a large number of immigrants in the urban region that extends from eastern Ventura County to the southern tip of Orange County and the Inland Empire. As Figure (1) illustrates, in a number of neighborhoods in Southern California, the foreign-born population outnumbers the native-born by large margins. For example, in areas west and south of downtown Los Angeles, immigrants are more than three times as numerous as the native-born.
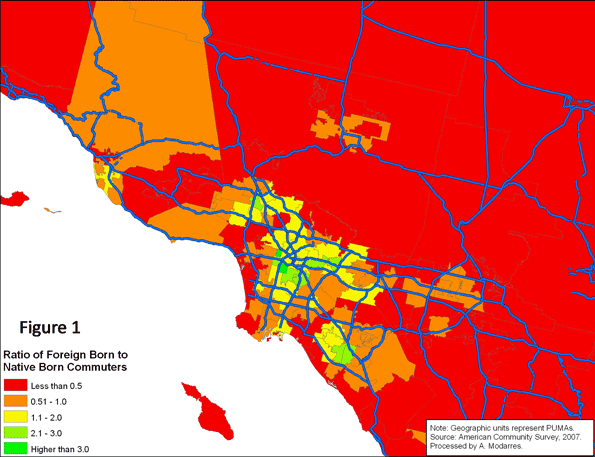
A comparison of Figures (2) and (3) suggests a wide geographic difference between the native-born and the foreign-born and how long it takes them to get to work. The foreign-born population experiences much longer commutes in highly urbanized areas around downtown Los Angeles and the San Gabriel Valley. Conversely, in the more rural areas, such as northern Ventura County, the foreign-born population experiences shorter commutes compared to their native-born counterparts.
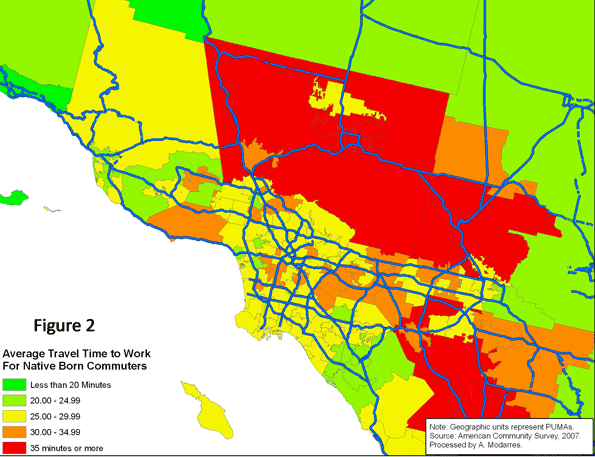
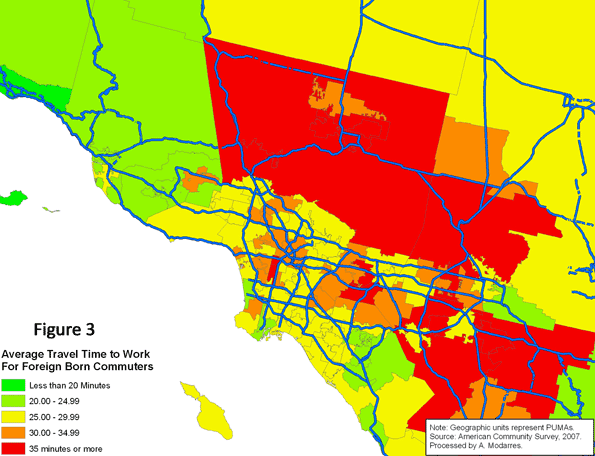
Figure (4) provides a clear comparison of average travel time to work for both populations (visually comparing Figures 2 and 3). In all areas appearing in the darkest shade of green, the foreign-born population experienced shorter commutes compared to the native-born. These shorter commutes, however rarely occur in high density areas (compare with Figure 5). Conversely, in areas such as Santa Monica, the Wilshire corridor, East Los Angeles, and southern sections of downtown Los Angeles, the foreign-born population experiences much longer commutes than the native-born.
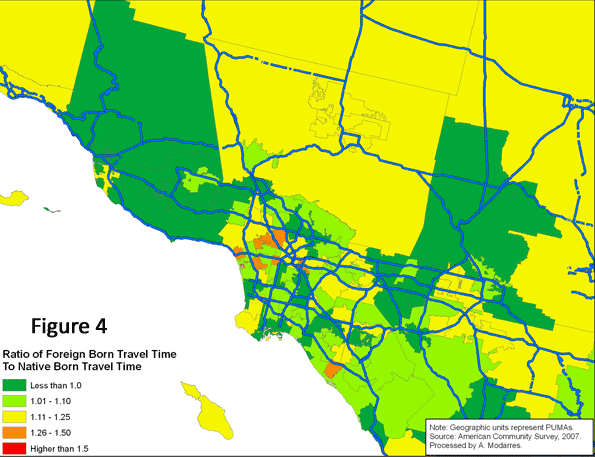
Statistically speaking, there is a positive relationship between average travel time and density – i.e., the higher the density, the higher the reported average travel time. For the foreign-born population who live in higher density areas, this means much longer commutes, a problem caused by a number of factors, including their dependency on slower public transportation systems and the long distances they have to travel to reach job centers outside the city center.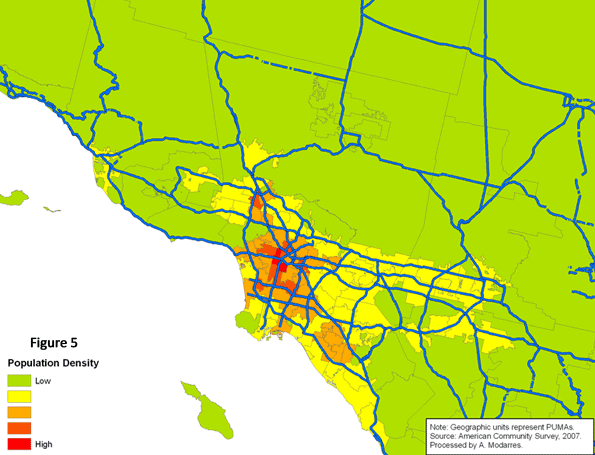
Figure (6) illustrates the geographic pattern of bus ridership among the foreign-born commuters. As with national patterns, immigrants in Southern California are more likely to settle in high density areas and use public transportation to work, but unfortunately, they also suffer much longer commutes.
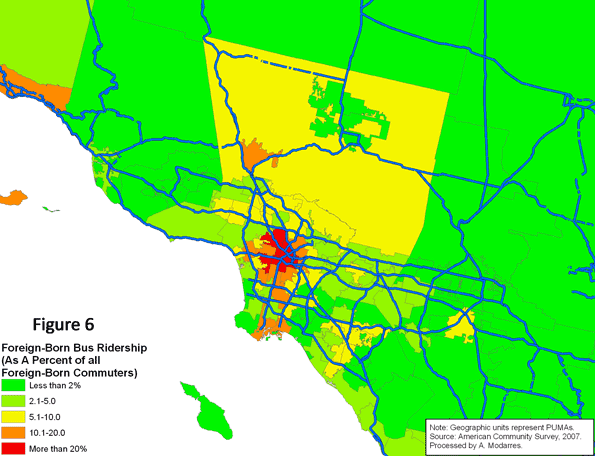
What should the policy responses be? One may be to promote increased car ownership among immigrants and low-income populations in the U.S. This may be objectionable to some environmentalists and planners, but it’s clear that those people who live by the principles of higher density and public transportation use are not rewarded and indeed suffer longer commutes.
An even more relevant question is why advocates for public transportation focus disproportionately on rail, when buses are so frequently used by low income populations, including immigrants. In California, these riders outnumber the native-born on buses. The situation is reversed on rail and subways. An intelligent policy response to public transportation planning would suggest that buses should receive much more attention. Major metropolitan areas have become polycentric in their employment patterns, and most major employment centers are located at long distances from the central city. Specially-designed buses for reverse commutes could help alleviate transportation problems while helping working immigrants reach their destinations more quickly.
This challenges the priorities of some public transport advocates, who tend to focus on very expensive rail projects designed primarily to draw more middle class, largely native-born riders who commute to places like downtown Los Angeles. Meanwhile those ‘new’ Americans who already live by a number of ‘green’ standards suffer from the misallocation of transit resources. Those who are already doing what we hope the middle class will do deserve better.
Ali Modarres is an urban geographer in Los Angeles and co-author of City and Environment.