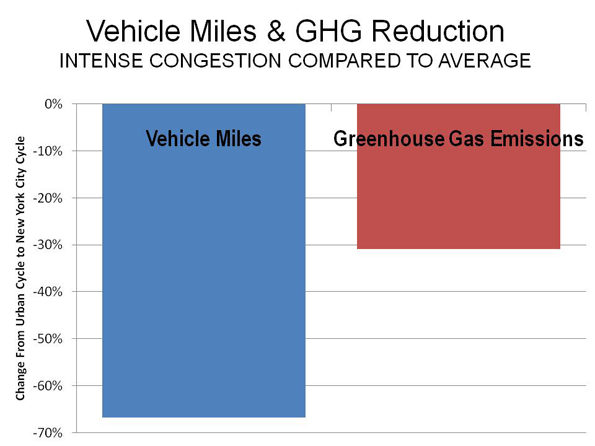
The “cash for clunkers” (or CARS) program that was widely predicted to be extended by the Congress has been, if nothing else, a clear public relations win for the Obama Administration. It may also be, at least for the short-term, a shot in the arm for the beleaguered American auto industry (including domestic dealerships of foreign car companies, like Honda and Toyota). But the program’s extension may also be bad news for anyone who was hoping that candidate Obama’s campaign promises to fix our domestic energy policy would translate into something resembling a robust make-over.
Don’t get me wrong; I am a huge fan of President Obama. And I am generally very supportive about what the Administration is trying to do. The President’s agenda is nothing if not ambitious, or may be better described as audacious. In no particular order, President Obama is seeking to fix the environment, reform the healthcare system, overhaul banking and financial services regulations, reverse a downwardly spiraling national and global economy, repair race relations in America, and get drivers to cease texting and talking on their cell phones while driving.
And yet, one of President Obama’s greatest strengths may also be his greatest weakness: The willingness and ability to compromise, as it is the fundamental nature of compromise that the outcome will inevitably be less than ideal. This consequence of compromise can be seen clearly in the President’s efforts to secure Congressional approval of an additional $2 billion in funding for the CARS program.
The initial concept behind CARS was elegant in its simplicity: give owners of “gas-guzzlers” (i.e. automobiles with highly inefficient internal combustion engines) a monetary incentive to trade their fuel inefficient vehicles for highly fuel-efficient replacements. The auto industry – albeit more centered in Tokyo than Detroit on this point – clearly is producing numerous passenger vehicles capable of achieving a combined city/highway rating of 30 miles-per-gallon (mpg) or more. Yet there remain a number of registered motor vehicles in the U.S. with substantially less than 18 mpg ratings under the program (any vehicle with a mpg rating above that is not worthy of the “clunker” moniker).
If this was the Administration’s original goal for the CARS program, the $1 billion authorization could have had a considerable impact on fuel consumption. Assuming the maximum rebate of $4,500 on every trade-in, almost a quarter of a million (222,222 to be exact) fuel-inefficient vehicles would have been voluntarily taken off America’s roads. Great idea! Triple that program funding amount to $3 billion, coupled with the same lofty goal, and two-thirds of a million fuel inefficient cars would have been swapped out for highly fuel efficient cars. If the average driver puts 12,000 miles per year on a car, and the average improvement in fuel efficiency is 12 mpg (i.e. from 18 mpg to 30 mpg) the program would save 1,000 gallons of gas per car, per year, or 666,666,000 gallons of gas annually.
If only this purpose – to incentivize drivers to purchase only the most fuel efficient vehicles – had remained the thrust of the CARS program. However, it seems that the elegant simplicity behind the CARS concept became intertwined in the “since the government now owns GM and Chrysler don’t you think we should do something to spur domestic car sales” debate. All of a sudden, light trucks (the product type on which the Big Three hung their hats and, subsequently, on which they were hung by their collective petard) became eligible provided they are more fuel-efficient than the millions of light trucks already registered and on domestic highways. So, instead of a rising fleet of truly efficient cars we now see sales of new SUVs of all sizes and dimensions, and not just the recently introduced hybrid versions, being allowed a “cash-for-clunkers” rebate. All that is necessary is for the trade-in vehicle to qualify under CARS and the newly purchased SUV achieve a paltry 18 combined mpg.
In other words, the concept behind the initial legislation appears to have quickly devolved from “let’s incentivize the best consumer behavior possible when it comes to fuel efficiency” to “let’s get people to buy passenger cars, SUVs, and light trucks.” The Hummer H3, for example, with an MSRP of less than $45,000 (the maximum MSRP allowed under CARS), and a combined city/highway mpg of 18, could qualify for the rebate program (hoping the irony is not lost on anyone that a vehicle, the Humvee, that was the exclusive product of a publicly owned entity, the Defense Department, ended up being the product of another publicly owned entity, GM).
There’s no doubt that CARS was wildly successful in its public debut, so much so that the $1 billion in federal rebate funds were projected to run out within the first 30 days of the program’s roll-out. Car dealerships and automakers were as ecstatic in their praise for the program as they were vociferous in their clamor to seek the additional $2 billion in Congressional funding. However, the pace at which the CARS rebates were utilized strongly suggests that the cash-for-clunkers program would have been equally successful even if Congress had stuck to the original premise of the program: To get car owners to trade in the worst mpg offenders for the exemplars of fuel efficiency. Instead, Congress and the Administration have botched the chance to make a real, lasting difference, while spending $3 billion in the process.
So here are the “outcomes” of CARS thus far: According to cars.com, the top ten fuel-efficient cars sold in the U.S. range from the Honda Fit (32 combined mpg) to the Toyota Prius (46 combined mpg). However, based on statistics tracked by jalopnik.com, of the top ten new vehicles purchased using CARS rebates only two, the Toyota Prius (#1 in fuel efficiency and #4 in most-purchased) and the Honda Fit (#10 in fuel efficiency and #9 in most-purchased), are on both lists (see the table below). In fact the list of the most-purchased vehicles using CARS rebates appears to be comprised of more lower-priced cars (e.g. the Chevy Cobalt and Hyundai Elantra) and cars that were already very high-volume sellers before the economic downturn (e.g. Toyota Camry and Corolla).
| Ten Most-Purchased Vehicles Using CARS Rebate* |
Ten Most Fuel-Efficient Vehicles Sold in the U.S.** |
||
|
1 |
Toyota Corolla |
1 |
Toyota Prius 48/45/46 mpg |
|
2 |
Ford Focus FWD |
2 |
Honda Civic Hybrid 40/45/42 mpg |
|
3 |
Honda Civic |
3 |
Smart Fortwo 33/42/36 mpg |
|
4 |
Toyota Prius |
4 |
Nissan Altima Hybrid 35/33/34 mpg |
|
5 |
Toyota Camry |
5 |
Toyota Camry Hybrid 33/34/34 mpg |
|
6 |
Hyundai Elantra |
6 |
Volkswagen Jetta TDI 30/41/34 mpg |
|
7 |
Ford Escape FWD |
7 |
Ford Escape Hybrid*** 34/31/32 mpg |
|
8 |
Dodge Caliber |
8 |
Toyota Yaris 29/36/32 mpg |
|
9 |
Honda Fit |
9 |
MINI Cooper/Clubman 28/37/32 mpg |
|
10 |
Chevrolet Cobalt |
10 |
Honda Fit 28/35/31 mpg |
|
*as posted on jalopnik.com Aug. 7th |
**as posted on cars.com Aug. 7th, city/hwy/combined mpg *** also includes Mercury Mariner/Mazda Tribute Hybrid |
||
Inasmuch as Congress has already approved the additional $2 billion for the CARS program – without improving the fuel efficiency goals the program incentivizes – then why don’t we at least be honest about it and just add the $3 billion CARS price tag to the federal auto industry bailout. Sadly, as it stacks up now, claiming that this program is all about fuel efficiency or domestic energy policy is a sham.
Peter Smirniotopoulos, Vice President – Development of UniDev, LLC, is based in the company’s headquarters in Bethesda, Maryland, and works throughout the U.S. He is on the faculty of the Masters in Science in Real Estate program at Johns Hopkins University. The views expressed herein are solely his own.