During tough economic times, technology is often seen as the one bright spot. In the U.S. this past year technology jobs outpaced the overall rate of new employment nearly four times. But if you’re looking for a tech job, you may want to consider searching outside of Silicon Valley. Though the Valley may still be the big enchilada in terms of venture capital and innovation, it hasn’t consistently generated new tech employment.
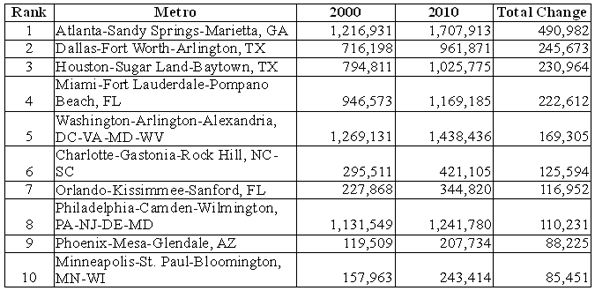
Take, for example, Seattle. Out of the 51 largest metro areas in the U.S., the Valley’s longtime tech rival has emerged as our No. 1 region for high-tech growth, based on long- and short-term job numbers. Built on a base of such tech powerhouses as Microsoft, Amazon and Boeing, Seattle has enjoyed the steadiest and most sustained tech growth over the past decade. It is followed by Baltimore (No. 2), Columbus, Ohio (No. 3), Raleigh, N.C. (No. 4) and Salt Lake City, Utah (No. 5).
To determine the best cities for high-tech jobs, we looked at the latest high-tech employment data collected by EMSI, an economic modeling firm. The Praxis Strategy Group‘s Mark Schill charted those areas that have gained the most high-tech manufacturing, software and services jobs over the past 10 years, equally weighting the last five years and the last two. We also included measures of concentration of tech employment in order to make sure we were not giving too much credence to relatively insignificant tech regions. Our definition of high tech industries is based on the one used by TechAmerica, the industry’s largest trade association.
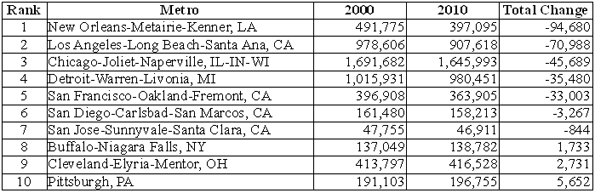
Despite the Valley’s remarkable concentration of tech jobs — roughly six times the national average — it ranked a modest No. 17 in our survey. This relatively low ranking reflects the little known fact that, even with the recent last dot-com craze sparking over 5% growth over the past two years, the Valley remains the “biggest loser” among the nation’s tech regions, surrendering roughly one quarter of its high -tech jobs — about 80,000 — in the past decade. Only New York City (No. 44) lost more tech jobs during that time.
In contrast to this pattern of volatility, our top performers have managed to gain jobs steadily in the past decade — and have continued to add new ones in the last two years. In addition to our top five, the only other regions to claim overall tech gains in the last 10 years are Jacksonville, Fla. (No. 6), Washington, D.C. (No. 7), San Bernardino-Riverside, Calif. (No. 9), San Diego, Calif. (No. 9), Indianapolis (No. 11) and Orlando, Fla. (No. 24).
So what accounts for high-tech success, and where will jobs most likely grow in the next decade? Certainly being home to a major research university makes a big difference. Seattle, Columbus, Raleigh and Salt Lake City all boast major educational and research assets.
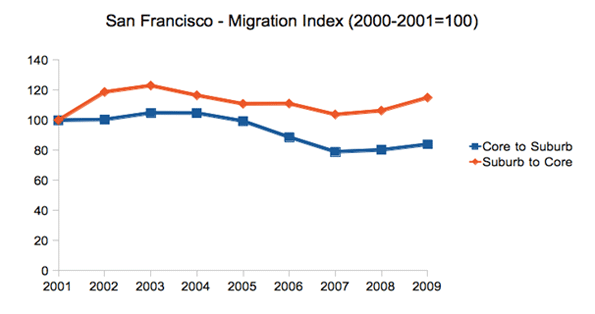
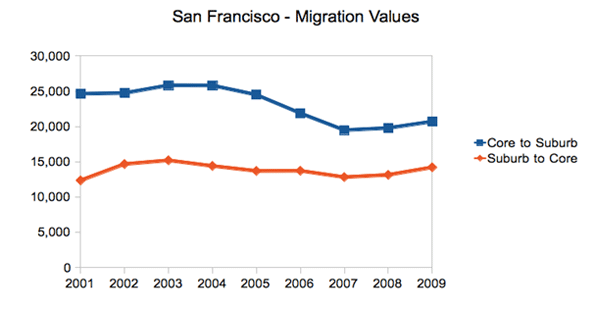
But it’s one thing to produce scientists and engineers; it’s another to generate employment for them over the long term. Clearly for the San Jose metropolitan region (which is home to Stanford) and the much-hyped No. 29 San Francisco area (home to the University of California Medical Center) academic excellence has not translated into steady growth in tech jobs. Over the past decade the Bay Area has given up 40,000 jobs, or 19% of its tech workforce, including a loss of nearly 6,000 in software publishing.
Or look at the Boston region (ranked No. 22), which arguably boasts the most impressive concentration of research universities in the country. The region did add jobs in research and computer programming, but these were not enough to counter huge losses in telecommunications and electronic component manufacturing. Over the past decade, greater Beantown has given up 18% of its tech jobs, or more than 45,000 positions.
One possible explanation may lie in costs, including very high housing prices, onerous taxes and a draconian regulatory environment. In tech, company headquarters may remain in the Valley, close to other headquarters and venture firms, but new jobs are often sent either out of the country or to more business friendly regions.
Just look at the flow of jobs from Bay Area-based companies to places like the Salt Lake area. In the past two years Valley companies such as Twitter, Adobe, eBay, Electronic Arts and Oracle have all expanded into Utah. This region has many appealing assets for Bay Area companies and workers. Salt Lake City is easily accessible by air from California, possesses a well- educated workforce, has reasonable housing costs and offers world-class skiing and other outdoor activities.
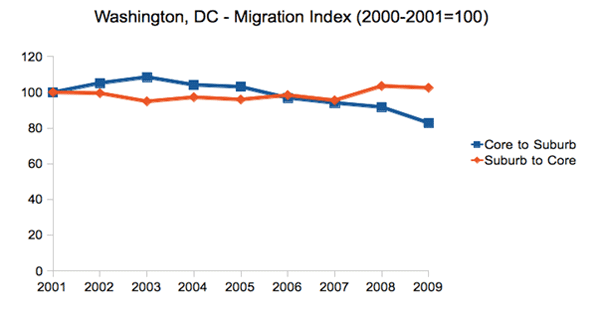
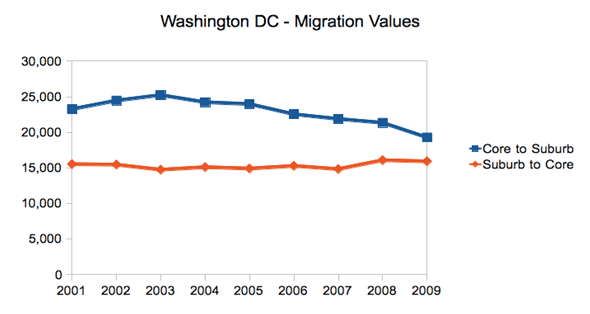
Another huge advantage appears to be closeness to the federal government, which expends hundreds of billions on tech products both hardware and software. This explains why Baltimore, primarily its suburbs, and the D.C. metro area have enjoyed steady tech growth and, under most foreseeable scenarios, likely will continue to do so in the coming years. Both regions have seen large gains in technology services industries, particularly programming, systems design, research, and engineering.
Yet even business climate, while important, may not be enough to drive tech job growth. Texas ranks highly in most business surveys, including our own, but it did not fare so well in this one. Indeed No. 32 Austin, often thought as the most likely candidate for the next Silicon Valley, lost over 19% of its high-tech jobs over the past decade, including more than 17,000 jobs in semiconductor, computer and circuit board manufacturing. No. 18 Houston did far better, although it has also lost 6% of its tech jobs over the same period due to the cutbacks in the engineering service, a big sector there. Even more shocking: No. 46 Dallas, generally a job-creating dynamo, has seen roughly a quarter of its high-tech jobs go away, due primarily to losses in telecommunications carriers and in manufacturing of communications equipment and electronics.
How about other potential up and comers for the coming decade? Two potentially big and somewhat surprising winners. The first: Detroit. Though the Motor City area lost 20% of its tech jobs in the past decade (ranking 40th on our list), it still boasts one of the nation’s largest concentrations of tech workers, nearly 50% above the national average. In the past two years, the region has experienced a solid 7.7% increase in technology jobs, the second highest rate of any metro area.
The Motor City region seems to have some real high-tech mojo. According to the website Dice.com, Detroit has led the nation with the fastest growth in technology job offerings since February — at 101%. This can be traced to the rejuvenated auto industry, which is increasingly dependent on high-tech skills. Manufacturing is increasingly prodigious driver of tech jobs; games and dot-coms are not the only path to technical employment growth. This could mean good news for other Rust Belt cities, such as No. 28 Cincinatti or No. 38 Cleveland, as well as our Midwest standout, Columbus, which could benefit from growth sparked by the local natural gas boom.
Another potential standout is No. 8 New Orleans, whose tech base remains relatively small but has expanded its tech workforce nearly 10% since 2009 — the highest rate of any of the regions studied. With low costs, a friendly business climate and world-class urban amenities, the Crescent City could emerge as a real player, aided by the growing prominence of research and development around Tulane University. There has also been a recent growing presence of the video game industry in the city.
Looking forward, however, it makes sense to be cautious about where tech is heading. By its nature, this is a protean industry; the mix of jobs and favored locales tend to change. If the current boom in social media continues, for example, the Bay Area could recover more of its lost jobs and further extend its primacy. Similarly a surge in manufacturing and energy-related technology could be a boon to tech in Houston, Dallas as well as New Orleans. But based on both historic and recent trends, the surest best for future growth still stands with our top five winners, led by the rain-drenched, but prospering Seattle region.
| Best Places for High Tech Growth | ||
| Ranking of 2, 5, and 10 year growth, industry concentration, and 5 and 10 year growth momentum | ||
| Rank | Metropolitan Area | Rank Score |
| 1 | Seattle | 82.2 |
| 2 | Baltimore | 75.7 |
| 3 | Columbus | 67.9 |
| 4 | Raleigh | 63.2 |
| 5 | Salt Lake City | 60.0 |
| 6 | Jacksonville | 59.2 |
| 7 | Washington, DC | 58.9 |
| 8 | New Orleans | 58.8 |
| 9 | Riverside-San Bernardino | 58.2 |
| 10 | San Diego | 56.1 |
| 11 | Indianapolis | 55.9 |
| 12 | Buffalo | 55.8 |
| 13 | San Antonio | 54.0 |
| 14 | Charlotte | 53.5 |
| 15 | St. Louis | 51.6 |
| 16 | Pittsburgh | 50.8 |
| 17 | San Jose | 50.5 |
| 18 | Houston | 50.2 |
| 19 | Hartford | 50.0 |
| 20 | Nashville | 49.6 |
| 21 | Providence | 49.2 |
| 22 | Boston | 48.3 |
| 23 | Minneapolis-St. Paul | 48.3 |
| 24 | Orlando | 48.1 |
| 25 | Portland | 48.1 |
| 26 | Philadelphia | 47.4 |
| 27 | Louisville | 47.2 |
| 28 | Cincinnati | 46.6 |
| 29 | San Francisco | 46.6 |
| 30 | Denver | 46.4 |
| 31 | Richmond | 45.6 |
| 32 | Austin | 45.1 |
| 33 | Atlanta | 44.6 |
| 34 | Virginia Beach-Norfolk-Newport News | 42.4 |
| 35 | Memphis | 42.2 |
| 36 | Milwaukee | 41.5 |
| 37 | Rochester | 41.2 |
| 38 | Cleveland | 40.9 |
| 39 | Phoenix | 38.5 |
| 40 | Detroit | 37.7 |
| 41 | Tampa | 37.5 |
| 42 | Miami | 33.2 |
| 43 | Sacramento | 32.1 |
| 44 | New York | 31.4 |
| 45 | Las Vegas | 31.2 |
| 46 | Dallas-Fort Worth | 31.0 |
| 47 | Chicago | 30.2 |
| 48 | Los Angeles | 29.5 |
| 49 | Oklahoma City | 26.7 |
| 50 | Birmingham | 23.5 |
| 51 | Kansas City | 21.6 |
| Rankings measure employment in 45 high technology manufacturing, services, and software industry sectors. | ||
This piece first appeared at Forbes.com.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University, and an adjunct fellow of the Legatum Institute in London. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050, released in February, 2010.
Mark Schill of Praxis Strategy Group perfomed the economic analysis for this piece.